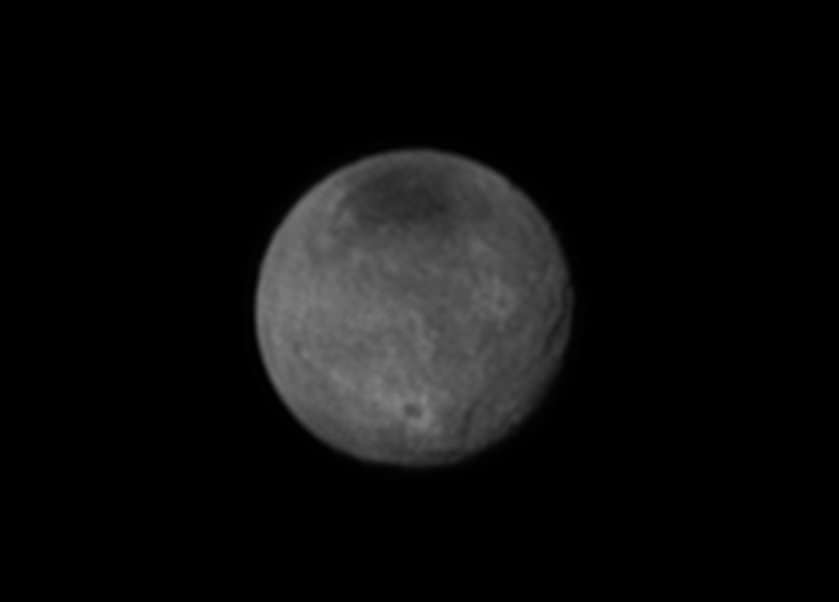
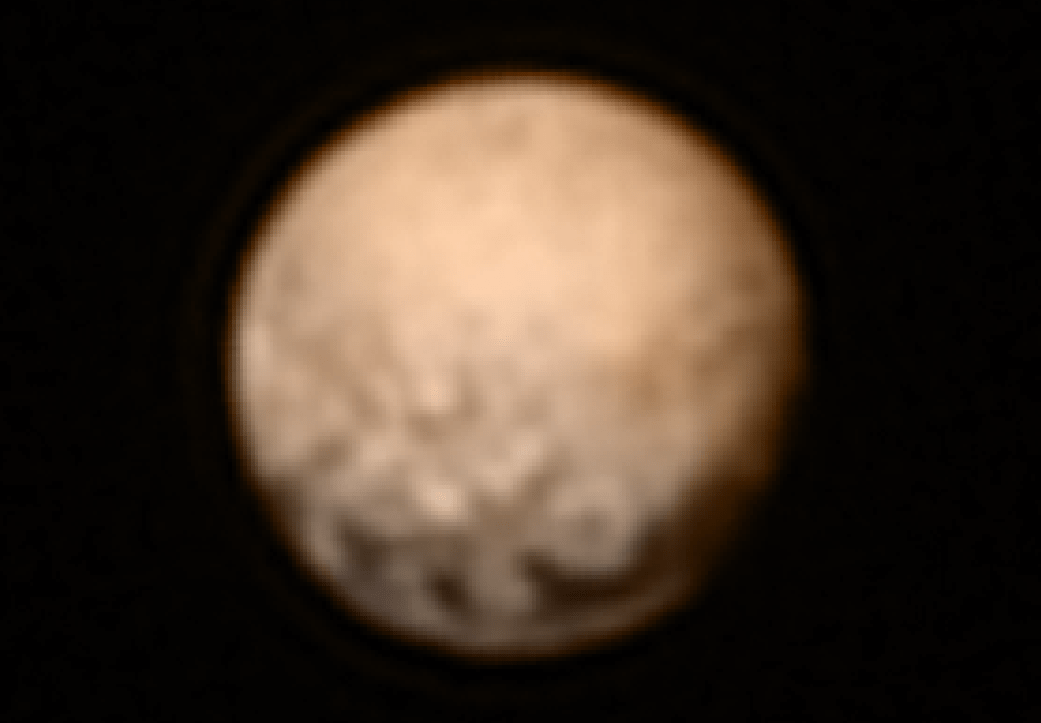
Spectacular imagery of huge regions of flowing ice, monumental mountain ranges and a breathtakingly backlit atmospheric haze showing Pluto as we’ve never seen it before, were among the newest discoveries announced today, July 24, by scientists leading NASA’s New Horizons mission which sped past the planet for humanity’s first ever up-close encounter only last week.
New Horizon’s revealed Pluto be an unexpectedly vibrant “icy world of wonders” as it barreled by the Pluto-Charon double planet system last Tuesday, July 14, at over 31,000 mph (49,600 kph).
The scientists publicly released a series of stunning new images and science discoveries at Pluto that exceeded all pre-flyby expectations.
“The images of Pluto are spectacular,” said John Grunsfeld, NASA’s associate administrator for the Science Mission Directorate, at today’s media briefing.
“We knew that a mission to Pluto would bring some surprises, and now — 10 days after closest approach — we can say that our expectation has been more than surpassed. With flowing ices, exotic surface chemistry, mountain ranges, and vast haze, Pluto is showing a diversity of planetary geology that is truly thrilling.”
Over 50 gigabits of data were collected during the encounter and flyby periods of the highest scientific activity in the most critical hours before and after the spacecrafts closest approach to Pluto, its largest moon Charon and its quartet of smaller moons.
Data from the flyby is now raining back to Earth, but slowly due to limited bandwidth of an average “downlink” of only about 2 kilobits per second via its two transmitters.
“So far we’ve seen only about 5% of the encounter data,” said Jim Green, director of Planetary Science at NASA Headquarters in Washington.
At that pace it will take about 16 months to send all the flyby science data back to Earth.
Among the top highlights is the first view ever taken from the back side of Pluto, a backlit view that humans have never seen before.
It shows a global portrait of the planets extended atmosphere and was captured when NASA’s New Horizons spacecraft was about 1.25 million miles (2 million kilometers) from Pluto. It shows structures as small as 12 miles across.
“The silhouette of Pluto taken after the flyby and show a remarkable haze of light representing the hazy worlds extended atmosphere,” Alan Stern, principal investigator for New Horizons at the Southwest Research Institute (SwRI) in Boulder, Colorado, said at the media briefing.
“The image is the equivalent of the Apollo astronauts Earth-rise images.”
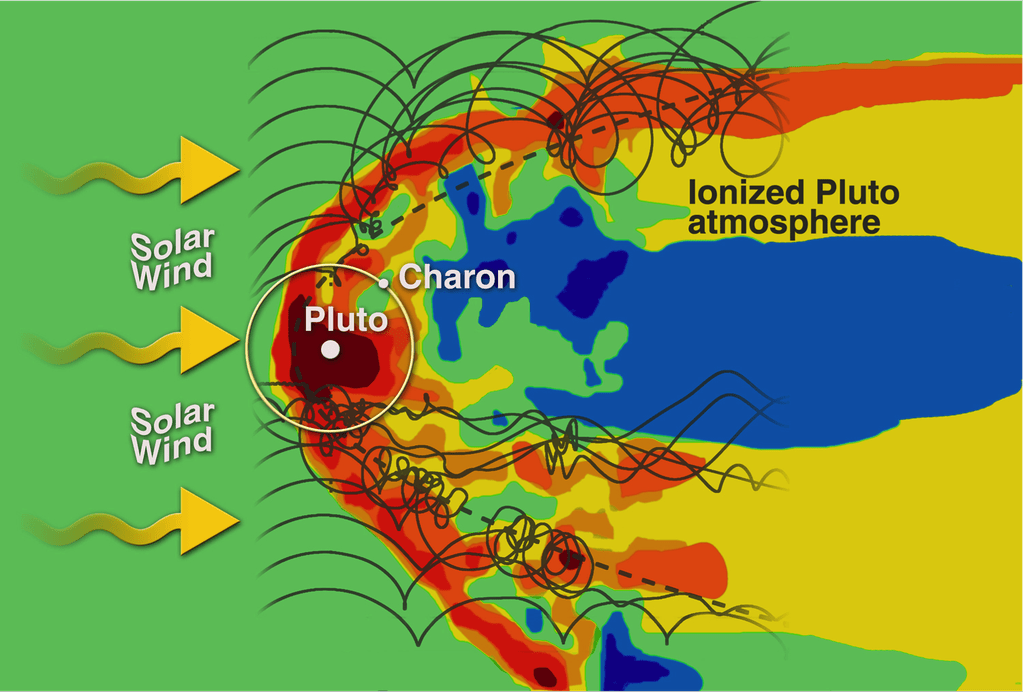
“It’s the first image of Pluto’s atmosphere!” said Michael Summers, New Horizons co-investigator at George Mason University in Fairfax, Virginia, at the briefing.
“We’ve known about the atmosphere for over 25 years,” and now we can see it. There are haze layers and it shows structure and weather. There are two distinct layers of haze. One at about 30 miles (50 kilometers) and another at about 50 miles (80 kilometers) above the surface.”
“The haze extend out about 100 miles! Which is five times more than expected.”

The image was taken by New Horizons’ high resolution Long Range Reconnaissance Imager (LORRI) while looking back at Pluto, barely seven hours after closest approach at 7:49 a.m. EDT on July 14, and gives significant clues about the atmosphere’s dynamics and interaction with the surface. It captures sunlight streaming through the atmosphere.
“The hazes detected in this image are a key element in creating the complex hydrocarbon compounds that give Pluto’s surface its reddish hue.”
Methane (CH4) in the upper atmosphere break down by interaction of UV radiation and forms ethylene and acetylene which leads to more complex hydrocarbons known as tholins – which the team says is responsible for Pluto’s remarkable reddish hue.
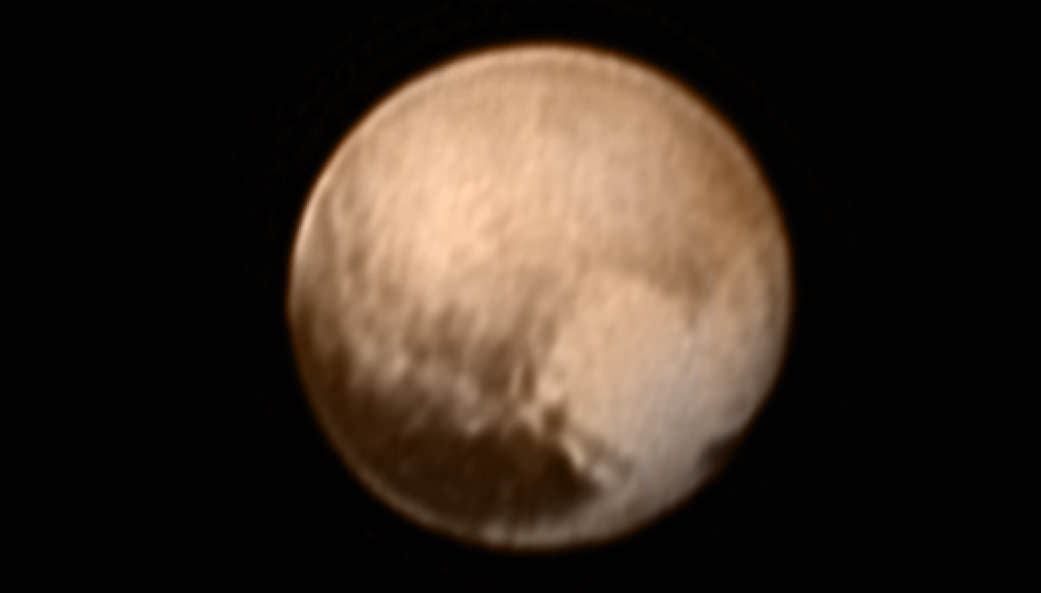
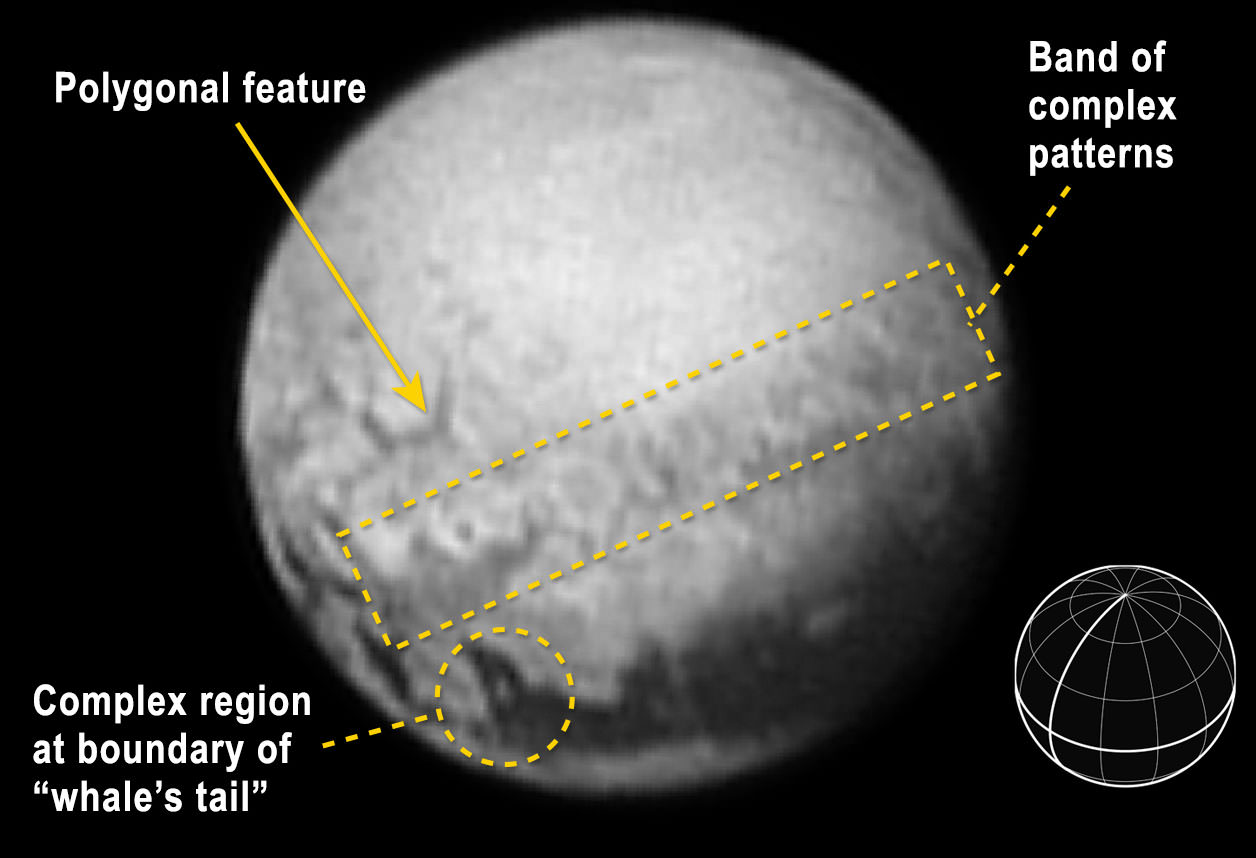
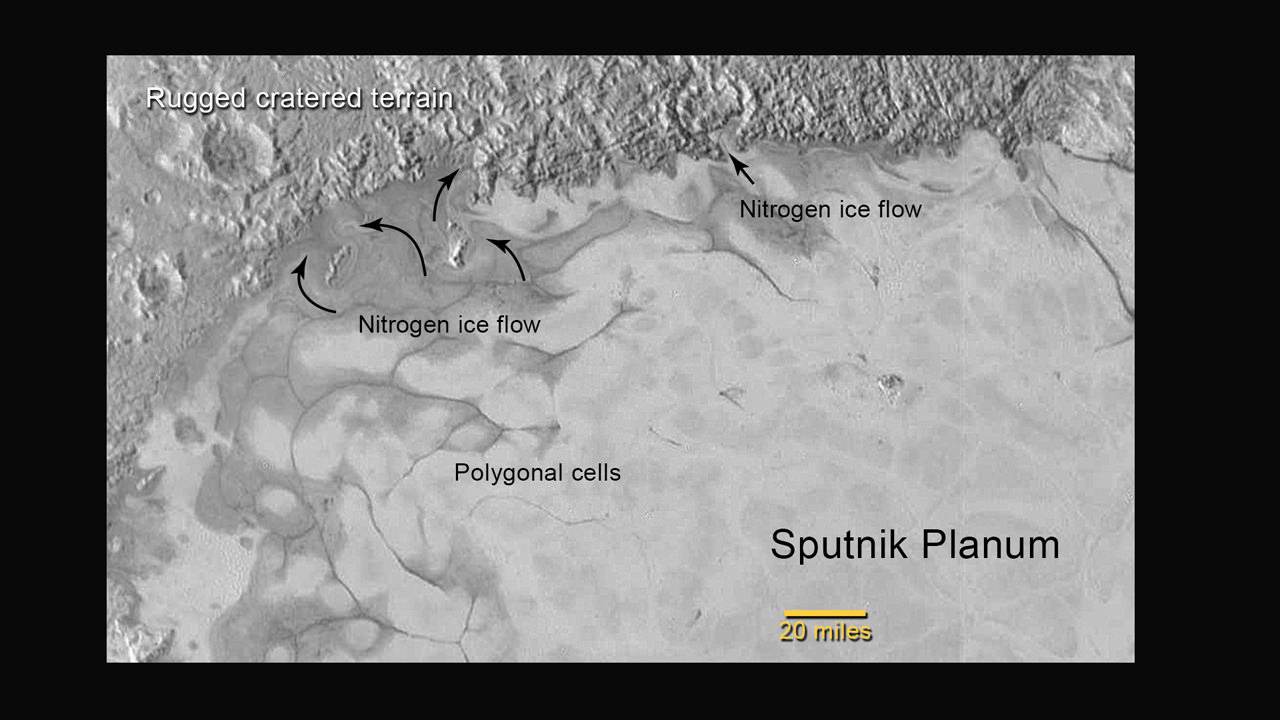
The team also released new LORRI images showing “extensive evidence of exotic ices flowing across Pluto’s surface and revealing signs of recent geologic activity, something scientists hoped to find but didn’t expect.”
The images focuses on Sputnik Planum, a Texas-sized plain, which lies on the western, left half of Pluto’s bilobed and bright heart-shaped feature, known as Tombaugh Regio.

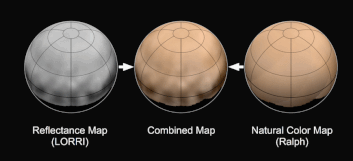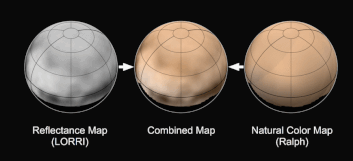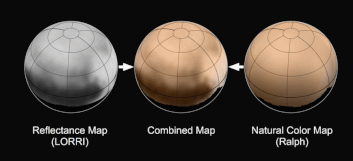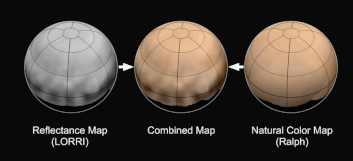
New imagery and spectral evidence from the Ralph instrument was presented that appears to show the flow of nitrogen ices in geologically recent times across a vast region. They appear to flow similar to glaciers on Earth. There are also carbon monoxide and methane ices mixed in with the water ices.
“We’ve only seen surfaces like this on active worlds like Earth and Mars,” said mission co-investigator John Spencer of SwRI. “I’m really smiling.”
“At Pluto’s temperatures of minus-390 degrees Fahrenheit, these ices can flow like a glacier,” said Bill McKinnon, deputy leader of the New Horizons Geology, Geophysics and Imaging team at Washington University in St. Louis.
“In the southernmost region of the heart, adjacent to the dark equatorial region, it appears that ancient, heavily-cratered terrain has been invaded by much newer icy deposits.”
“We see the flow of viscous ice that looks like glacial flow.”
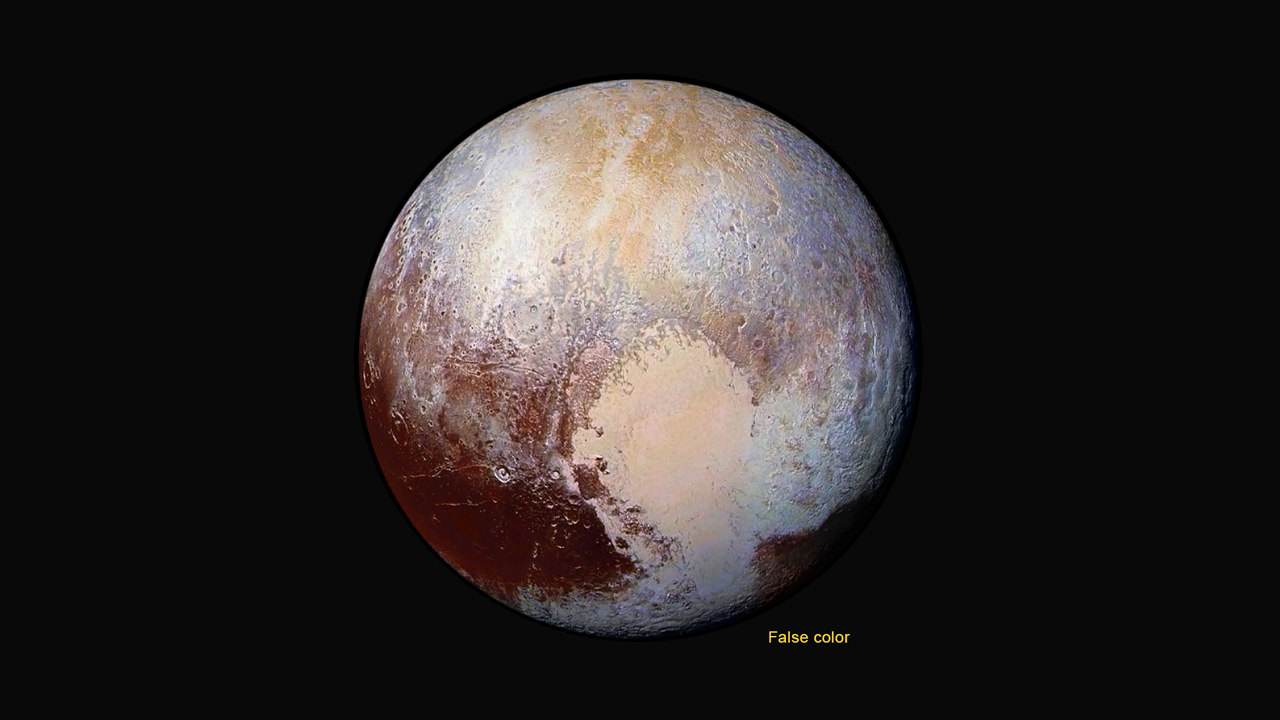

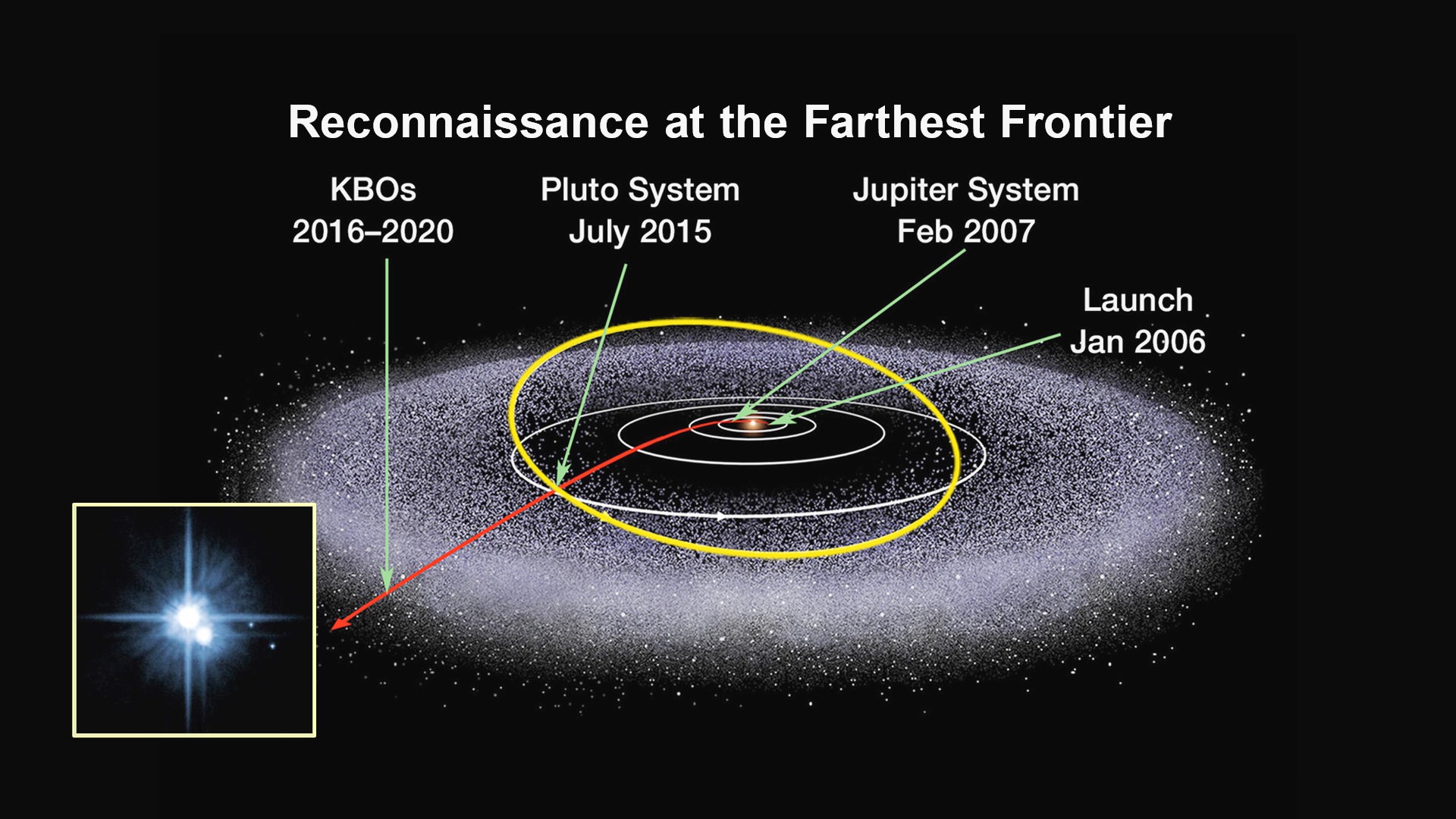
If the spacecraft remains healthy as expected, the science team plans to target New Horizons to fly by another smaller Kuiper Belt Object (KBO) as soon as 2018.
Watch for Ken’s continuing coverage of the Pluto flyby. He was onsite reporting live on the flyby and media briefings for Universe Today from the Johns Hopkins University Applied Physics Laboratory (APL), in Laurel, Md.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.