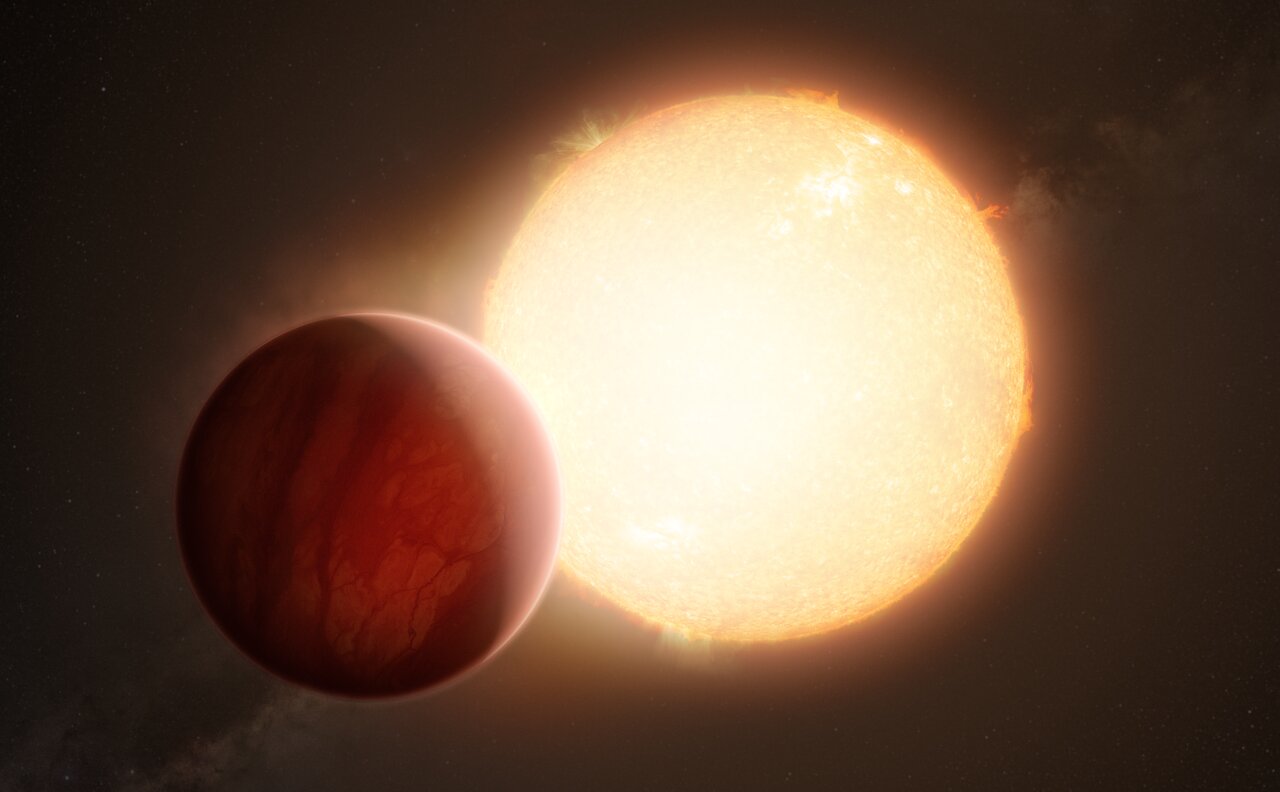
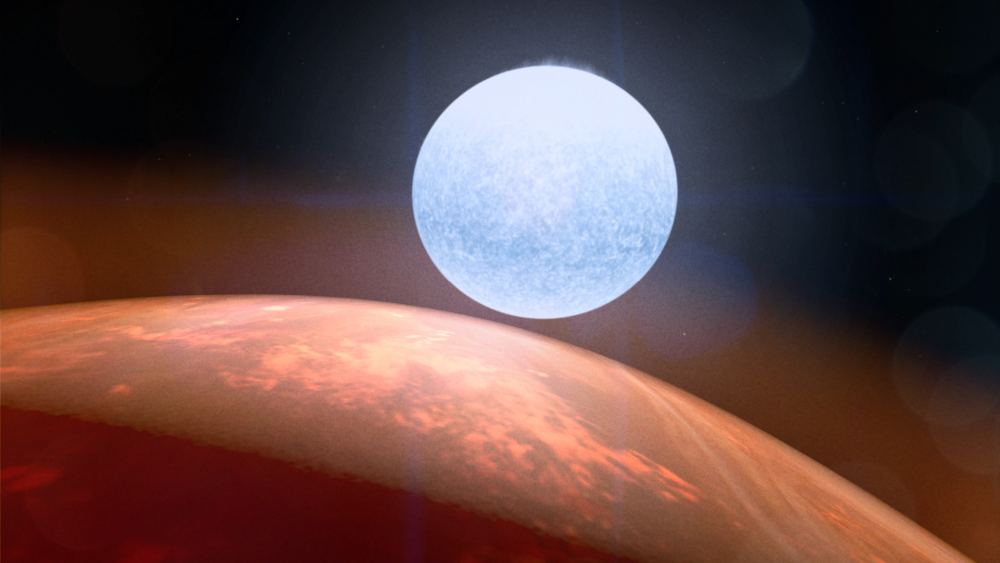
Astronomers have spotted barium in the atmosphere of a distant exoplanet. With its 56 protons, you have to run your finger further down the periodic table than astronomers usually do to find barium. What does finding such a heavy element in an exoplanet atmosphere mean?
It means we’re still learning how strange exoplanets can be.
Continue reading “The Heaviest Element Ever Seen in an Exoplanet’s Atmosphere: Barium”