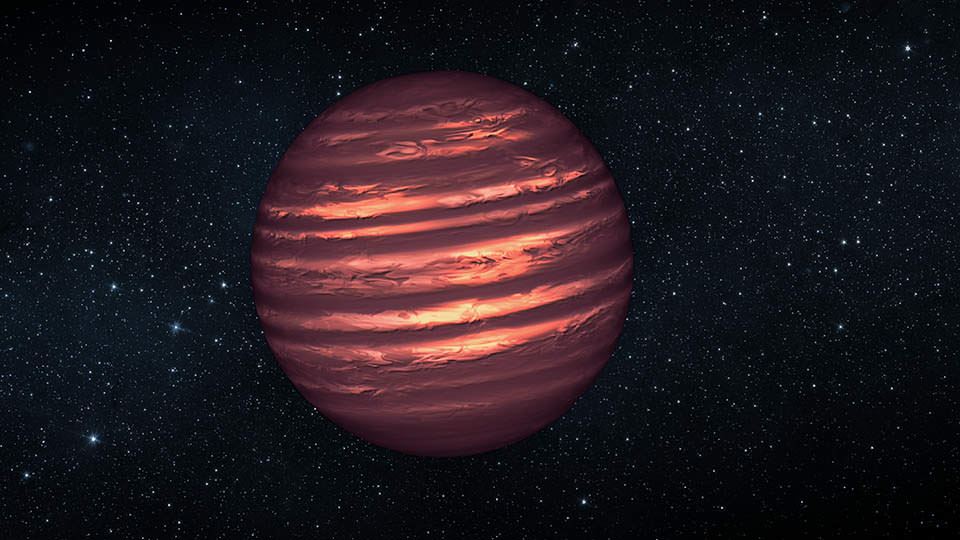
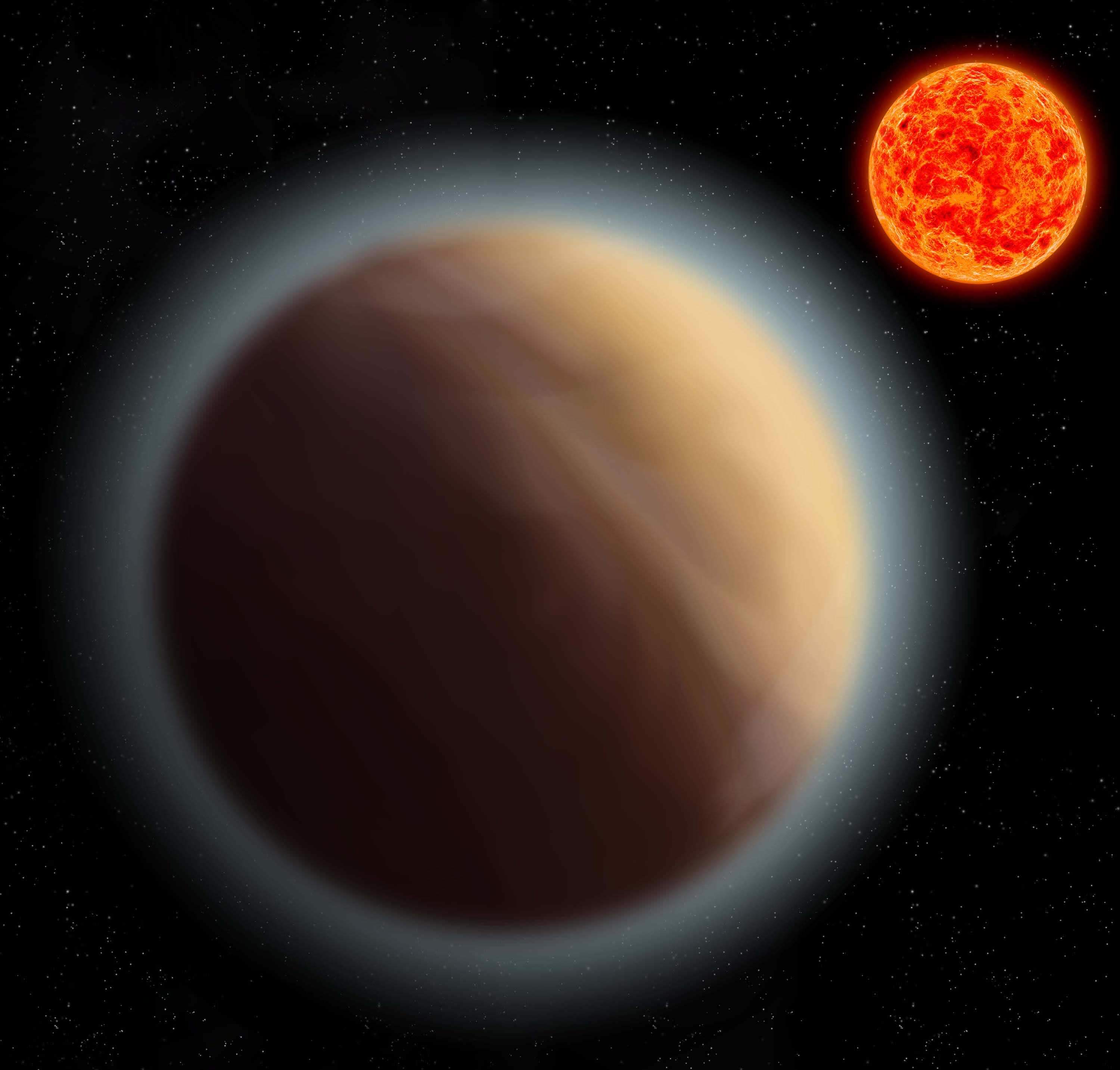
Thanks to the success of the Kepler mission, we know that there are multitudes of exoplanets of a type called “Hot Jupiters.” These are gas giants that orbit so close to their stars that they reach extremely high temperatures. They also have exotic atmospheres, and those atmospheres contain a lot of strangeness, like clouds made of aluminum oxide, and titanium rain.
A team of astronomers has created a cloud atlas for Hot Jupiters, detailing which type of clouds and atmospheres we’ll see when we observe different Hot Jupiters.
Continue reading “Extremely Hot Exoplanets Can Have Extreme Weather, Like Clouds of Aluminum Oxide and Titanium Rain”