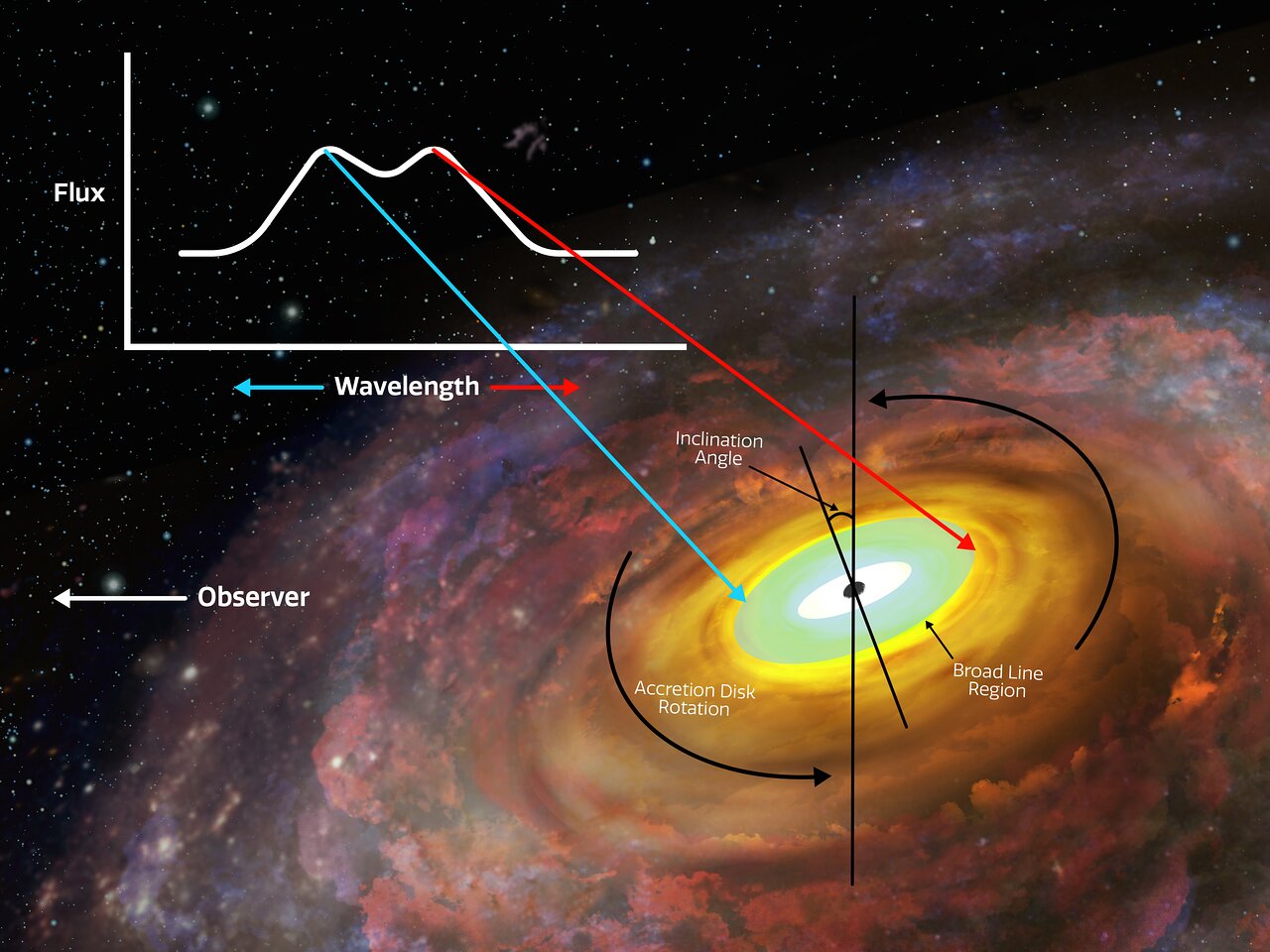
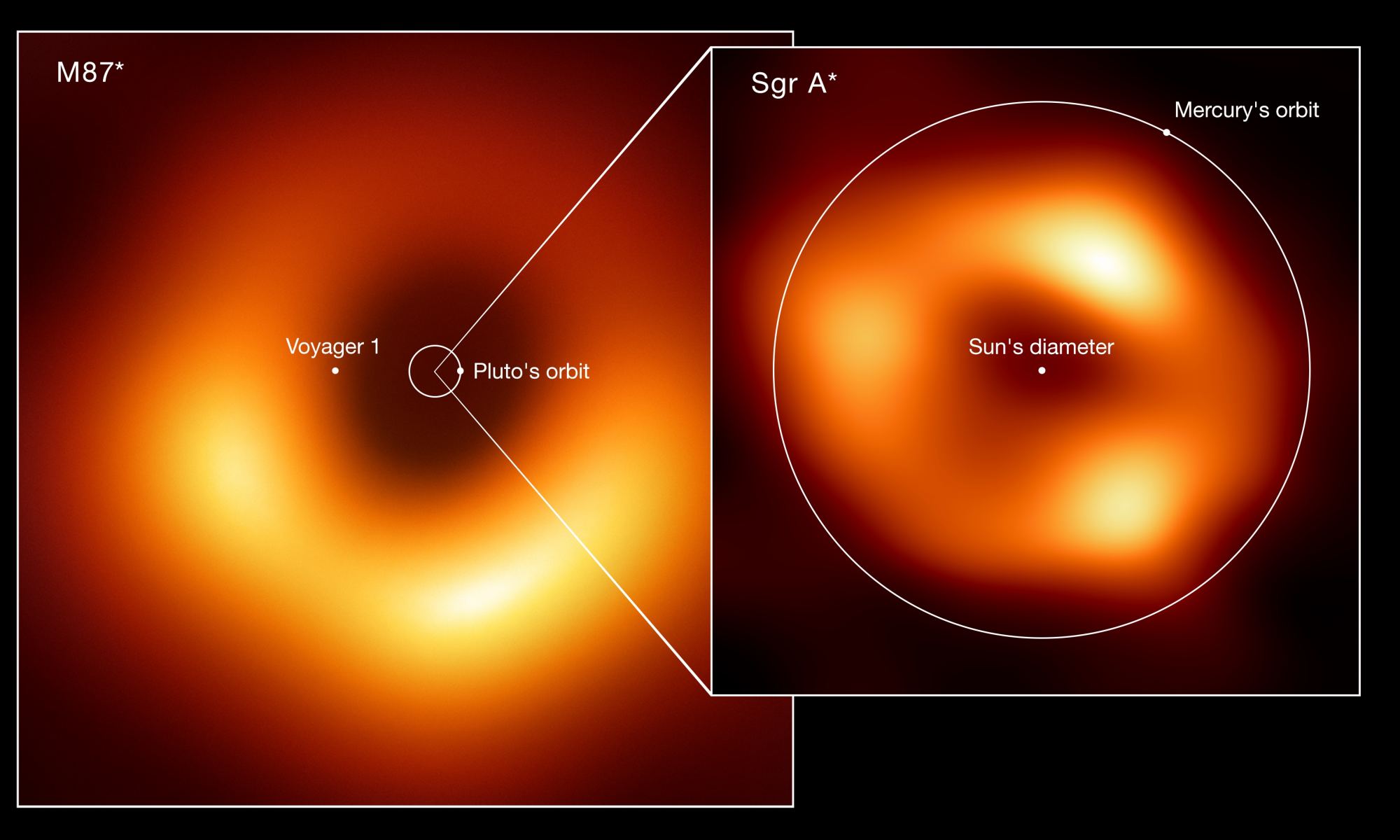
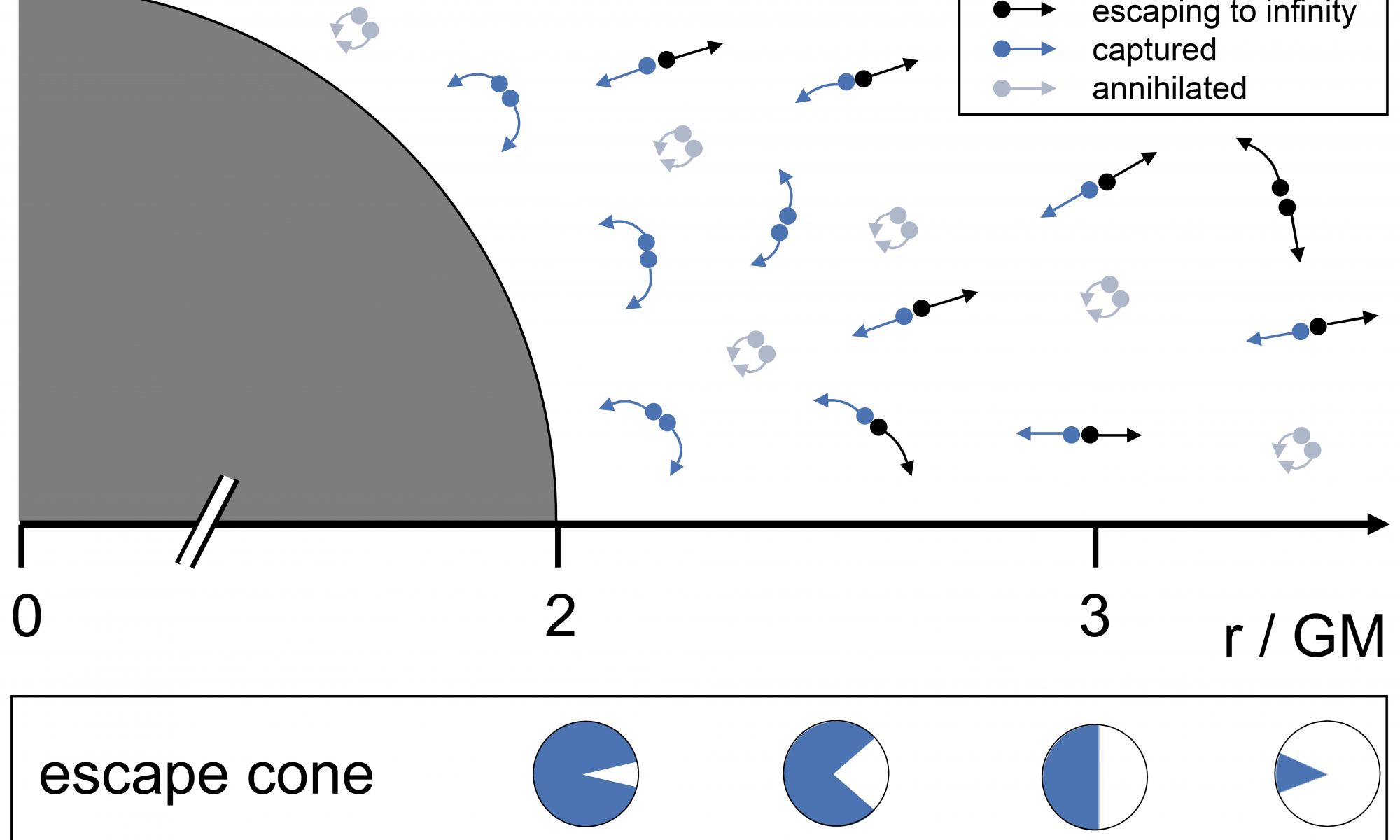
When you think of a black hole, you might think its defining feature is its event horizon. That point of no return not even light can escape. While it’s true that all black holes have an event horizon, a more critical feature is the disk of hot gas and dust circling it, known as the accretion disk. And a team of astronomers have made the first direct measure of one.
Continue reading “Astronomers Precisely Measure a Black Hole's Accretion Disk”Could This Supermassive Black Hole Only Have Formed by Direct Collapse?

Nearly every galaxy in the universe contains a supermassive black hole. Even galaxies that are billions of light years away. This means supermassive black holes form early in the development of a galaxy. They are possibly even the gravitational seeds around which a galaxy forms. But astronomers are still unclear about just how these massive gravitational beasts first appeared.
Continue reading “Could This Supermassive Black Hole Only Have Formed by Direct Collapse?”Does the Milky Way's Supermassive Black Hole Have a Companion?
At the heart of our galaxy, there is a monster black hole. Known as Sagittarius A*, it has a mass of 4.2 million Suns, and it’s only about 27,000 light-years from Earth. Sag A* is the closest supermassive black hole, and one of only two that we’ve observed directly. It is so close that we can even see stars closely orbiting it. Some of those stars we’ve been observing for more than 20 years, which means we have a very good handle on their orbits. We’ve used those orbits to determine the mass of Sag A*, but a new study looks at a different question: does our galaxy’s black hole have a companion?
Continue reading “Does the Milky Way's Supermassive Black Hole Have a Companion?”How Did Supermassive Black Holes Grow So Quickly, So Early?

Supermassive black holes haunt the cores of many galaxies. Yet for all we know about black holes (not nearly enough!), the big ones remain a mystery, particularly when they began forming. Interestingly, astronomers see them in the early epochs of cosmic history. That raises the question: how did they get so big when the Universe was still just a baby?
Continue reading “How Did Supermassive Black Holes Grow So Quickly, So Early?”The Milky Way’s Supermassive Black Hole had a Burst of Activity 200 Years Ago. We Just Saw the Echo.
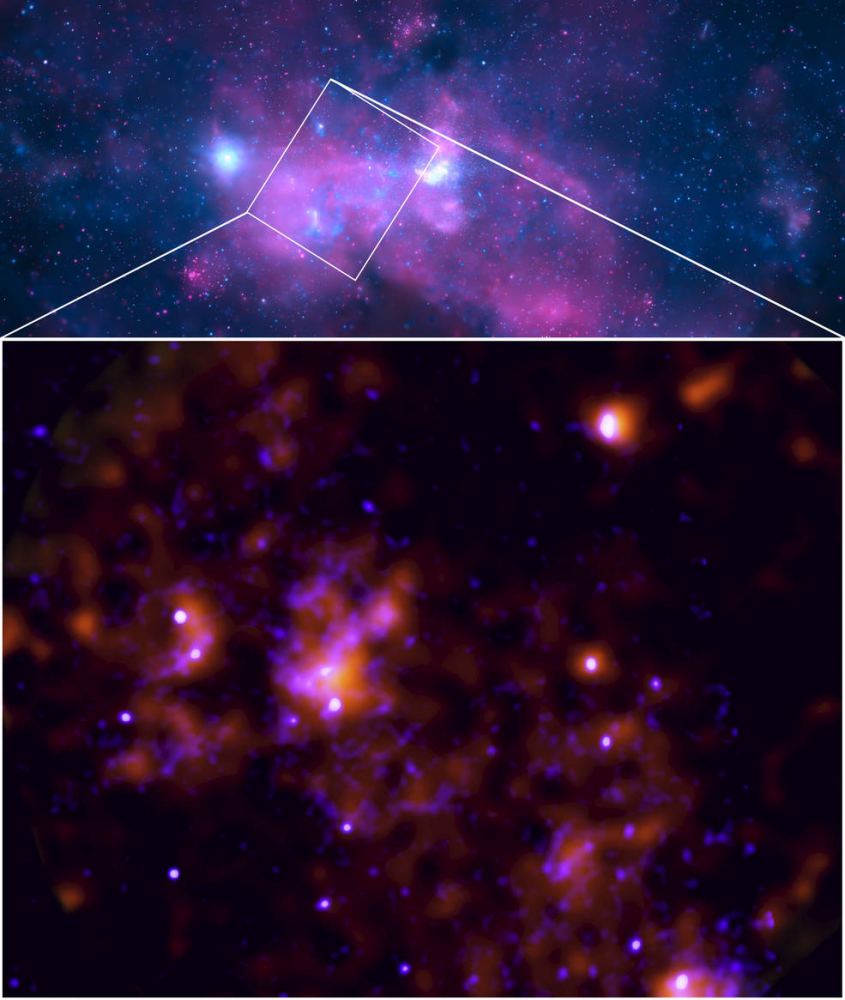

We in the Milky Way Galaxy are pretty lucky to have a fairly quiet central supermassive black hole in Sgr A*. It’s not loud and bright like an active galactic nucleus. It appears to be active for brief periods before going to sleep. Two hundred years ago, it “woke up” for about a year and a half and had a bite to eat.
Continue reading “The Milky Way’s Supermassive Black Hole had a Burst of Activity 200 Years Ago. We Just Saw the Echo.”Astronomers Have Never Detected Merging Supermassive Black Holes. That Might Be About to Change
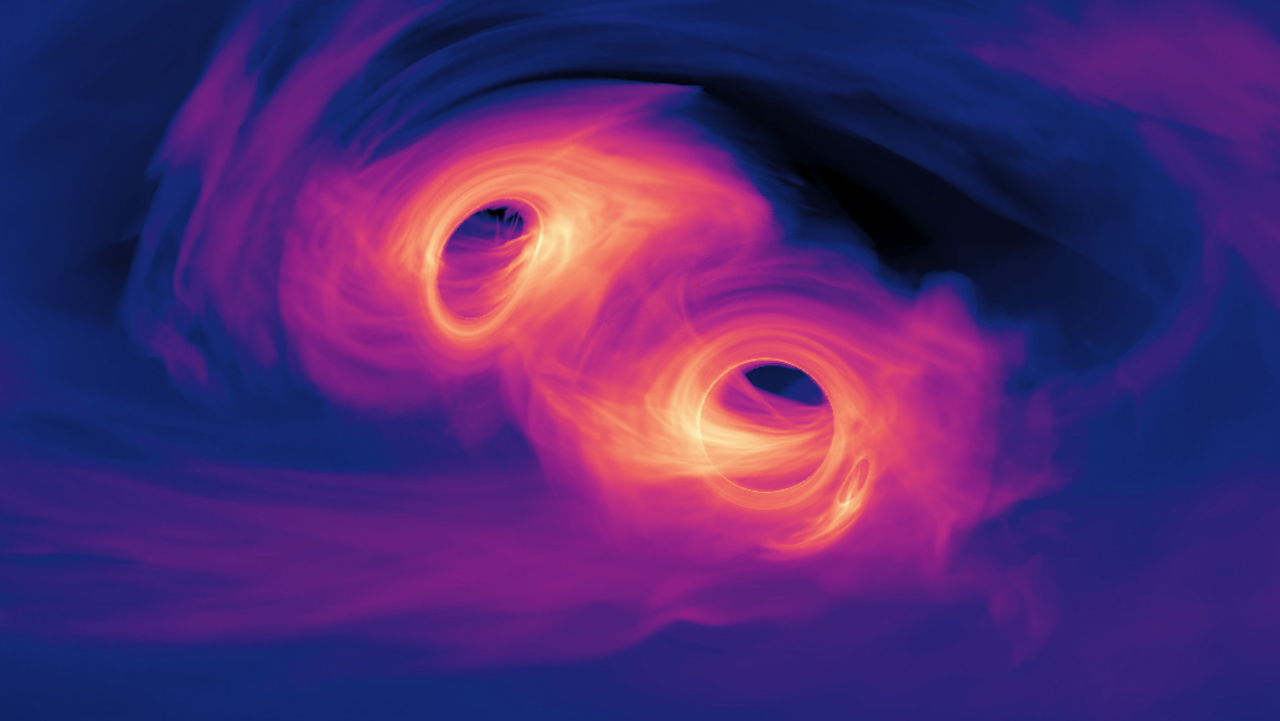
Gravitational wave astronomy currently can only detect powerful rapid events, such as the mergers of neutron stars or stellar mass black holes. We’ve been very successful in detecting the mergers of stellar mass black holes, but a long-term goal is to detect the mergers of supermassive black holes.
Continue reading “Astronomers Have Never Detected Merging Supermassive Black Holes. That Might Be About to Change”Pulsars Could Help Map the Black Hole at the Center of the Milky Way
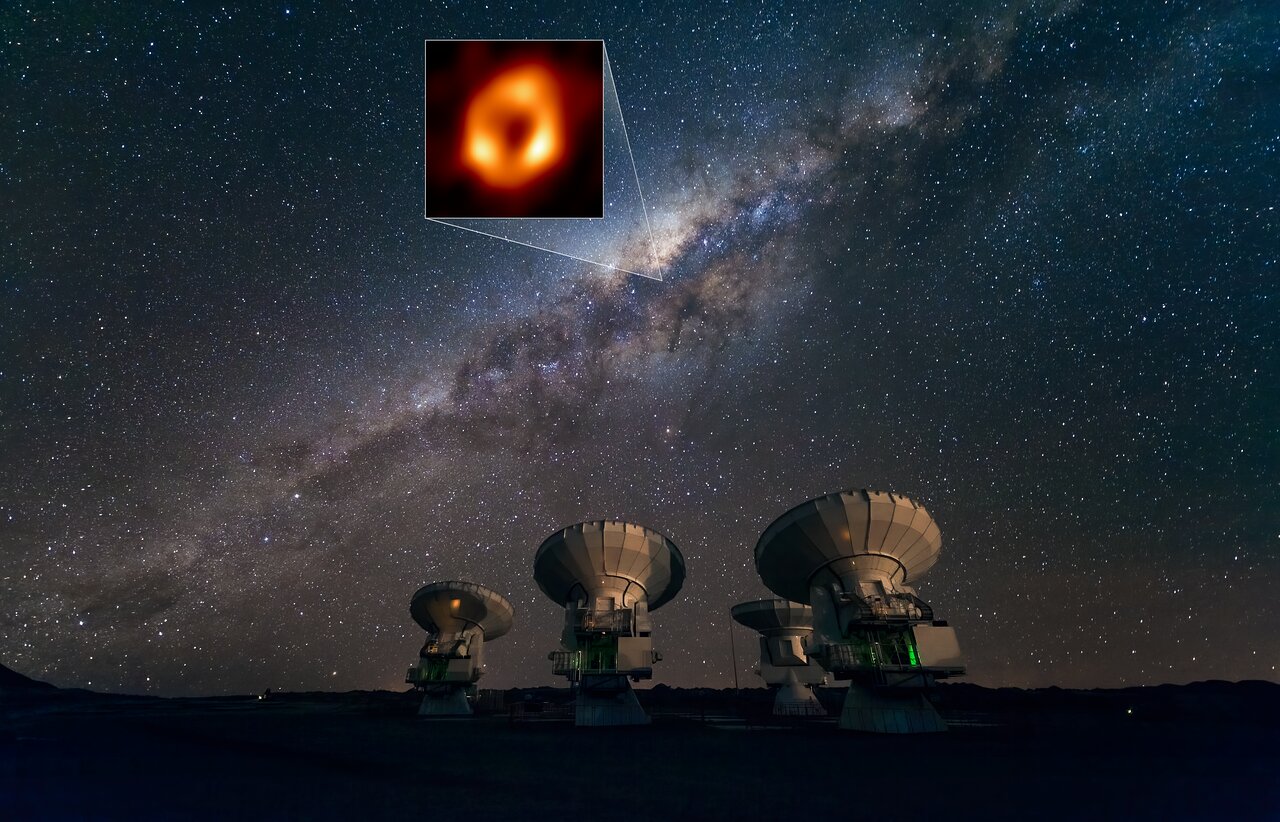

The Theory of General Relativity (GR), proposed by Einstein over a century ago, remains one of the most well-known scientific postulates of all time. This theory, which explains how spacetime curvature is altered in the presence of massive objects, remains the cornerstone of our most widely-accepted cosmological models. This should come as no surprise since GR has been verified nine ways from Sunday and under the most extreme conditions imaginable. In particular, scientists have mounted several observation campaigns to test GR using Sagittarius A* (Sgr A*), the supermassive black hole at the center of the Milky Way.
Last year, the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) – an international consortium of astronomers and observatories – announced they had taken the first images of Sag A*, which came just two years after the release of the first-ever images of an SMBH (M87). In 2014, the European members of the EHT launched another initiative known as BlackHoleCam to gain a better understanding of SMBHs using a combination of radio imaging, pulsar observations, astrometry, and GR. In a recent paper, the BHC initiative described how they tested GR by observing pulsars orbiting Sgr A*.
Continue reading “Pulsars Could Help Map the Black Hole at the Center of the Milky Way”If Black Holes Evaporate, Everything Evaporates
Hawking radiation is one of the most famous physical processes in astronomy. Through Hawking radiation, the mass, and energy of a black hole escape over time. It’s a brilliant theory, and it means that black holes have a finite lifetime. If Hawking radiation is true. Because as famous as it is, Hawking radiation is unproven. The theory is not even theoretically proven.
Continue reading “If Black Holes Evaporate, Everything Evaporates”When Black Holes Merge, They'll Ring Like a Bell

When two black holes collide, they don’t smash into each other the way two stars might. A black hole is an intensely curved region of space that can be described by only its mass, rotation, and electric charge, so two black holes release violent gravitational ripples as merge into a single black hole. The new black hole continues to emit gravitational waves until it settles down into a simple rotating black hole. That settling down period is known as the ring down, and its pattern holds clues to some of the deepest mysteries of gravitational physics.
Continue reading “When Black Holes Merge, They'll Ring Like a Bell”Where Are the Missing Black Holes? The Hubble May Have Helped Find One
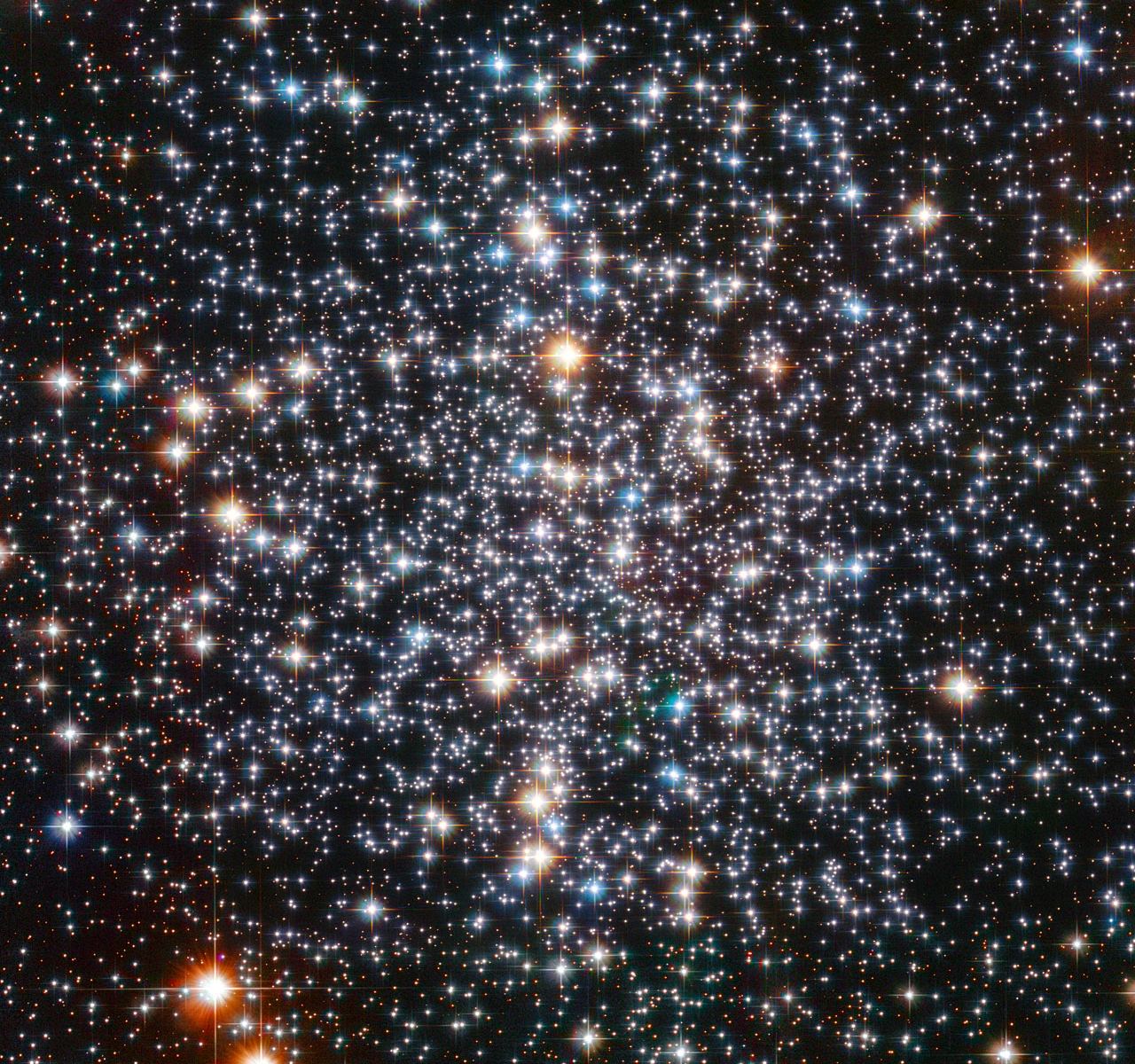

Most black holes are stellar mass black holes. They’re created when a star several times more massive than our Sun reaches the end and collapses in on itself. There are also supermassive black holes (SMBH,) the behemoths at the center of galaxies that can boast billions of times more mass than the Sun.
But where are the intermediate-mass black holes?
Continue reading “Where Are the Missing Black Holes? The Hubble May Have Helped Find One”