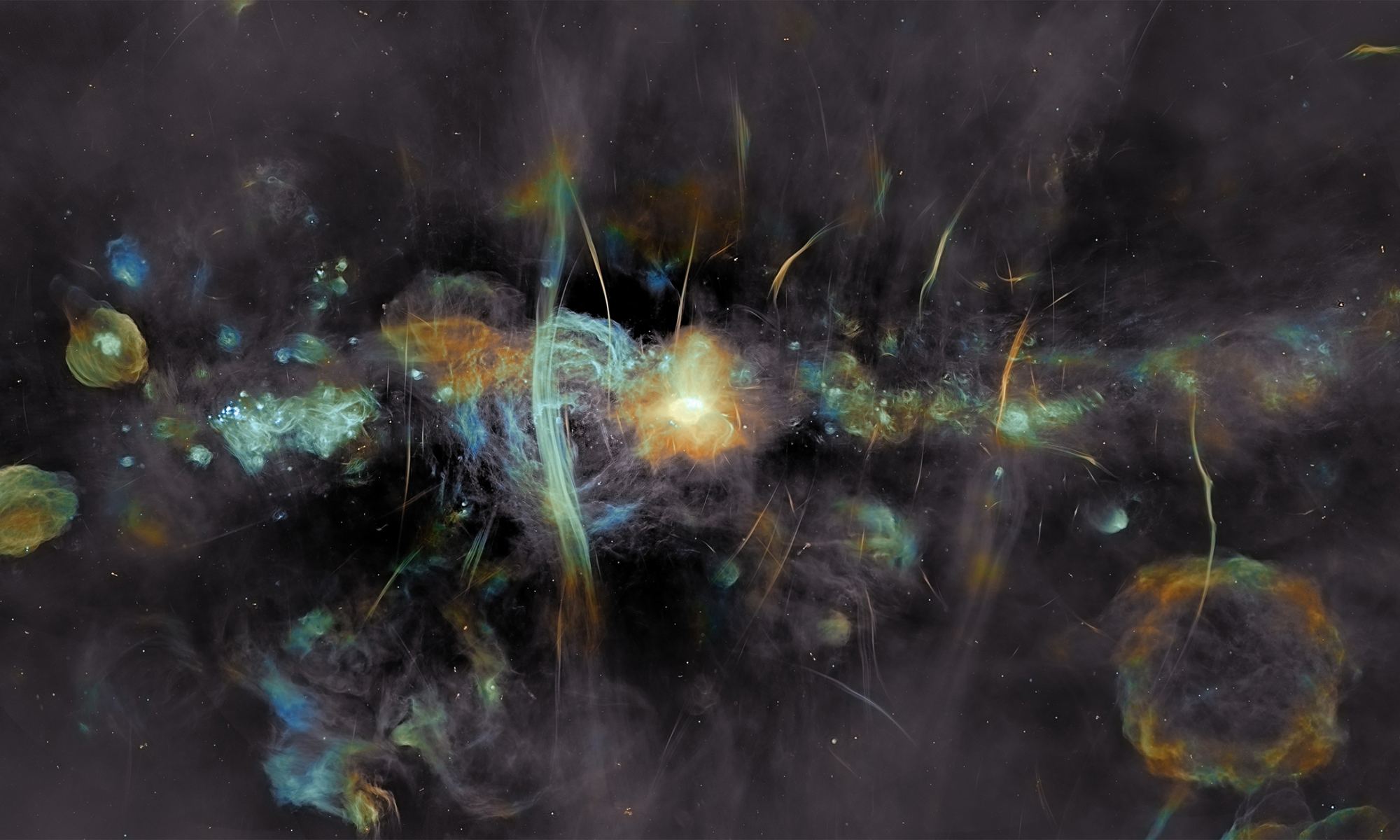
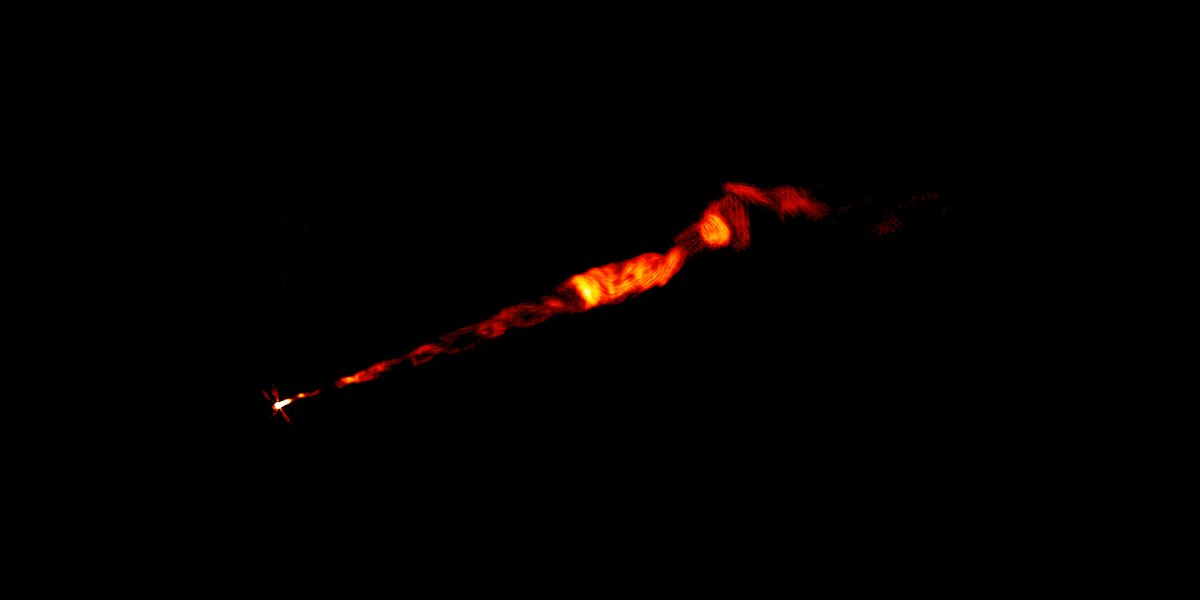
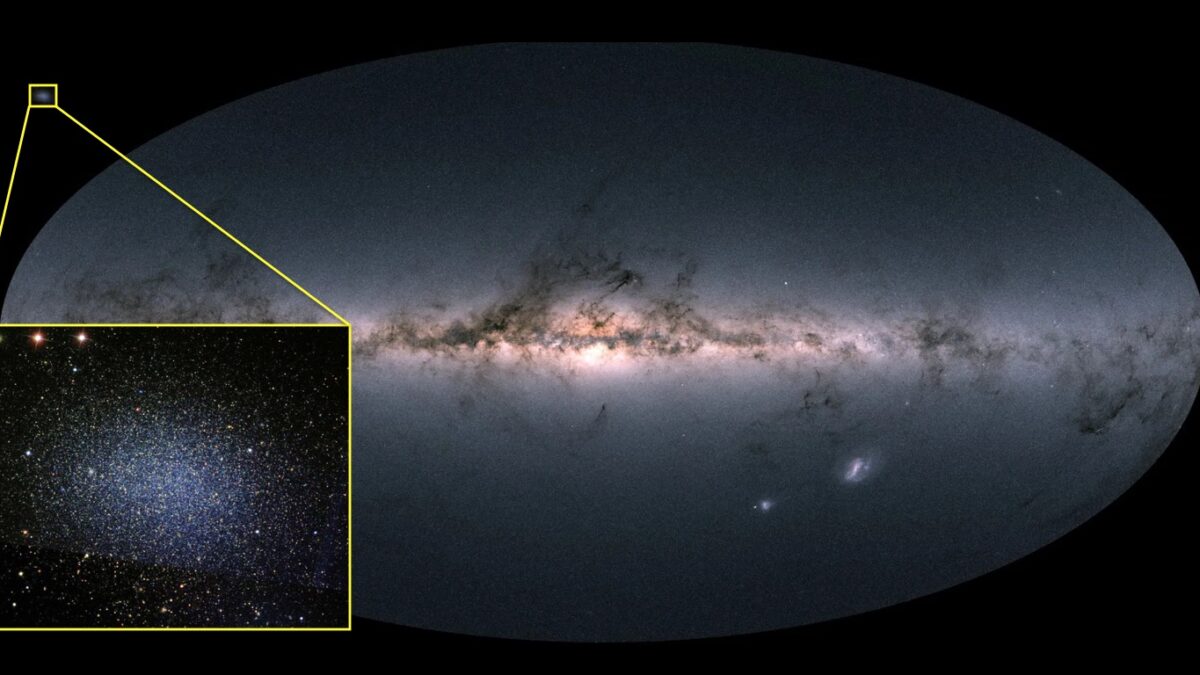
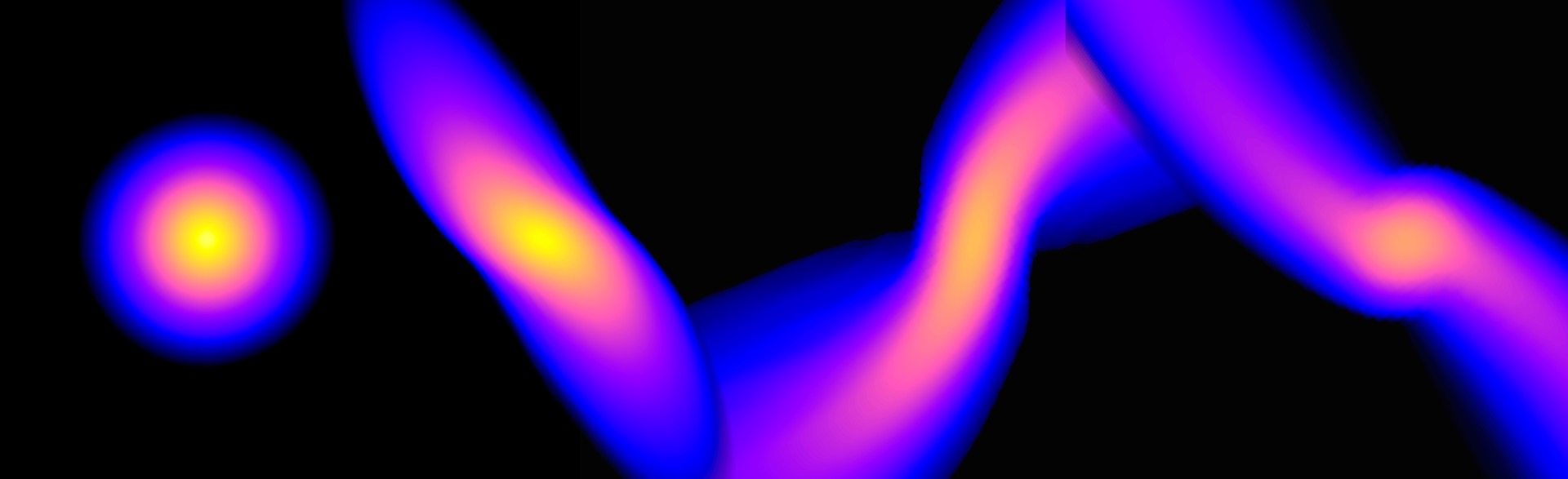
The inner 600 light years of our galaxy is a maelstrom of cosmic radiation, turbulent swirling gas clouds, intense star formation, supernovae, huge bubbles of radio energy, and of course a giant supermassive black hole. This bustling downtown of the Milky Way is a potential treasure trove of discovery but has been difficult to study as the galaxy’s central regions are obscured by dust and glaring radiation. But a new image of this region with unprecedented detail reveals more than we’ve ever seen before. We find some familiar objects like supernovae but also some mysterious structures – gaseous filaments dozens of light years long channeling electrons at near light speed.
Behold, the galaxy’s centre as never seen before: