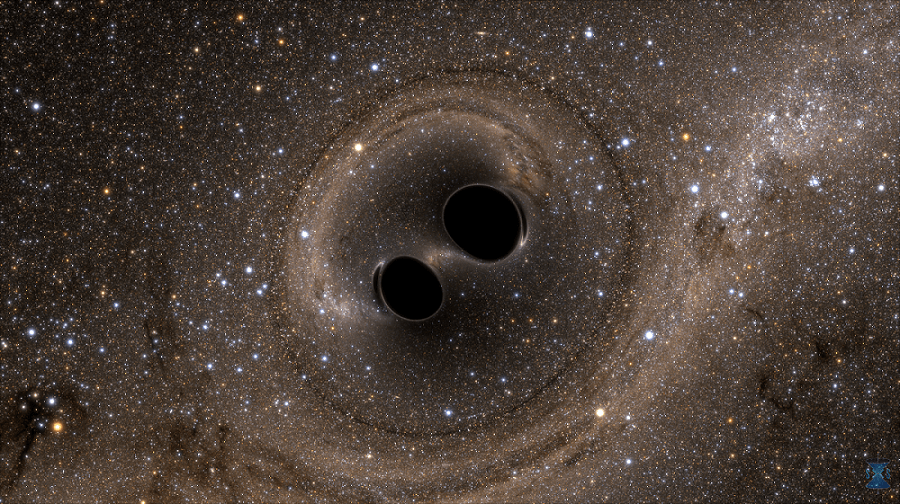
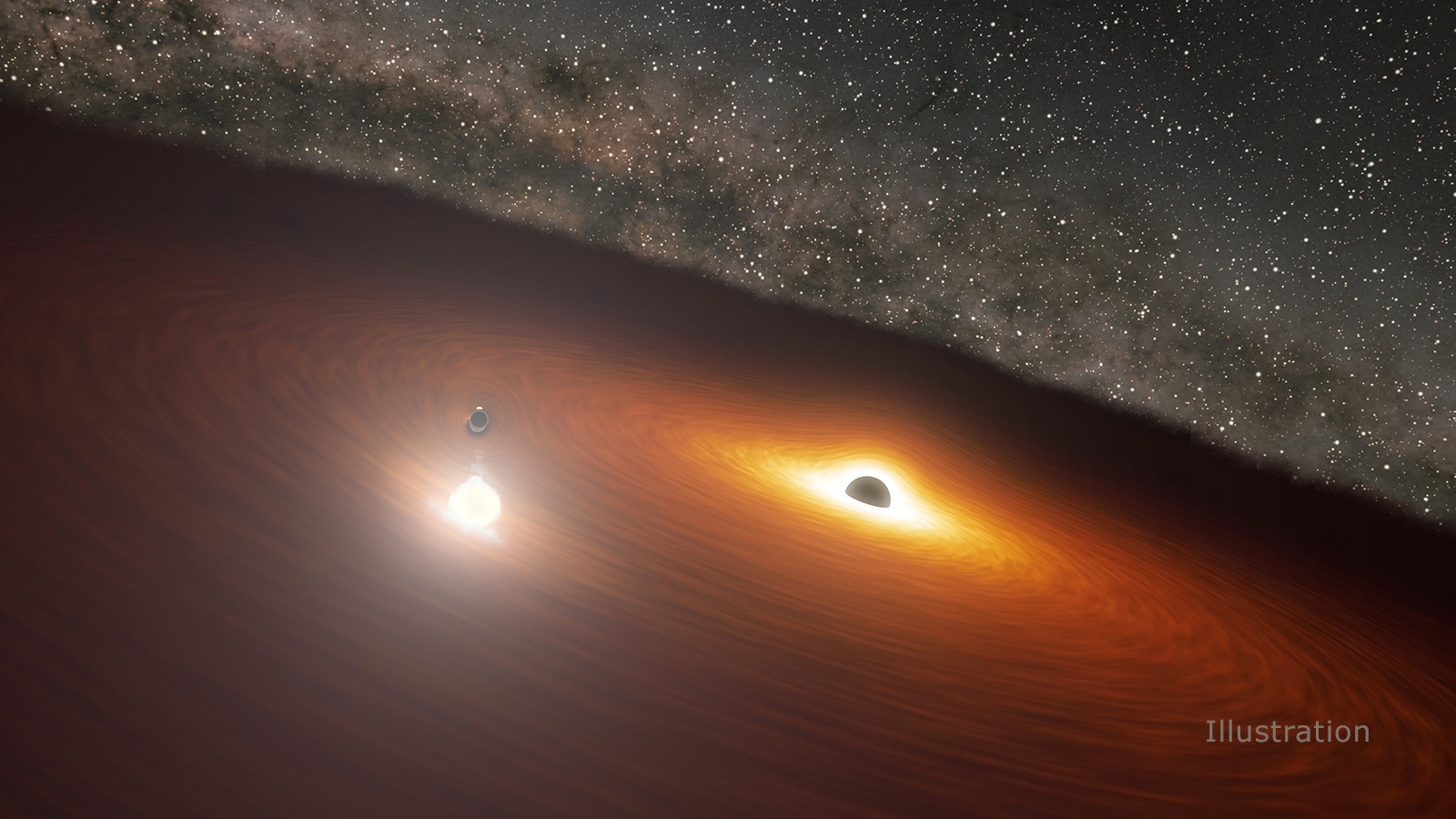
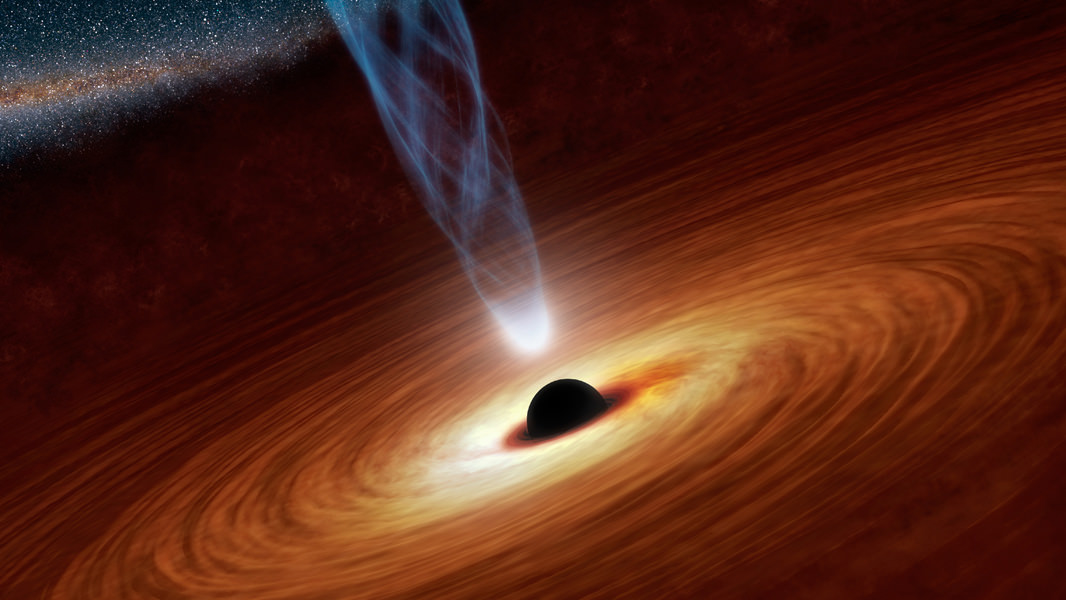
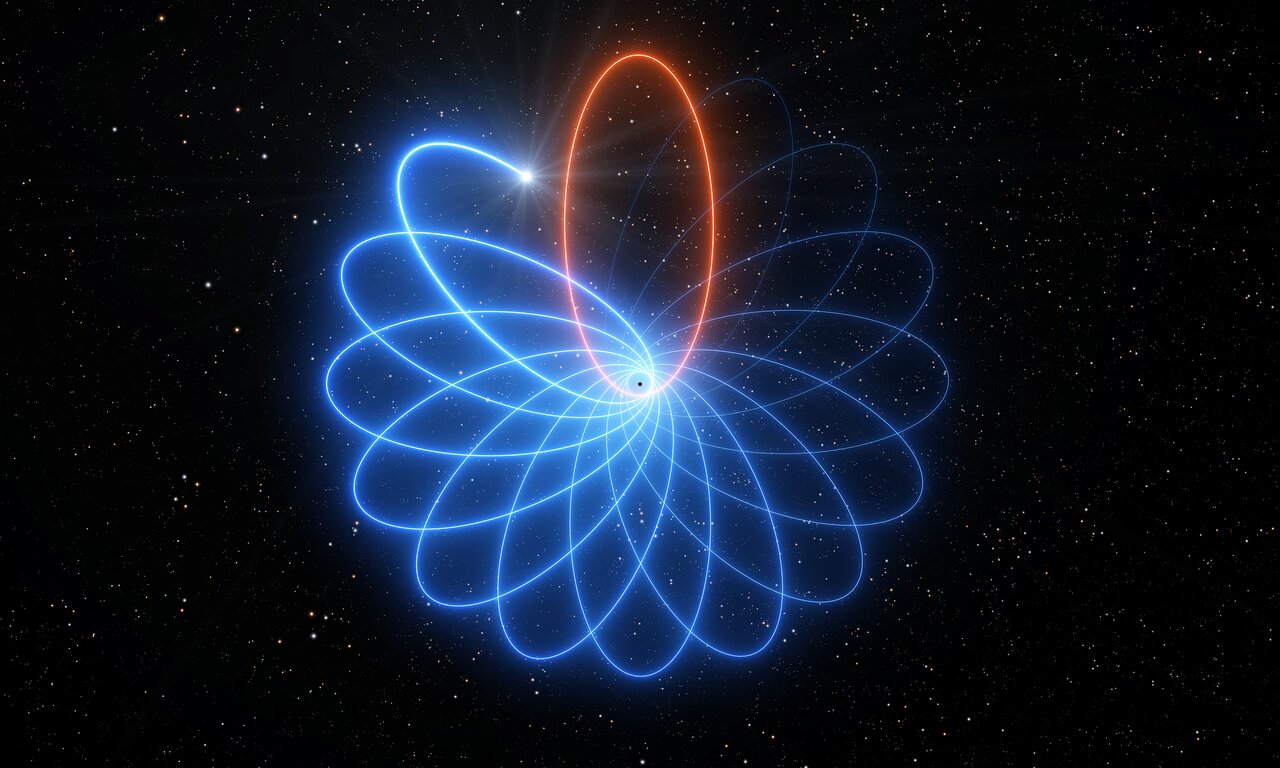
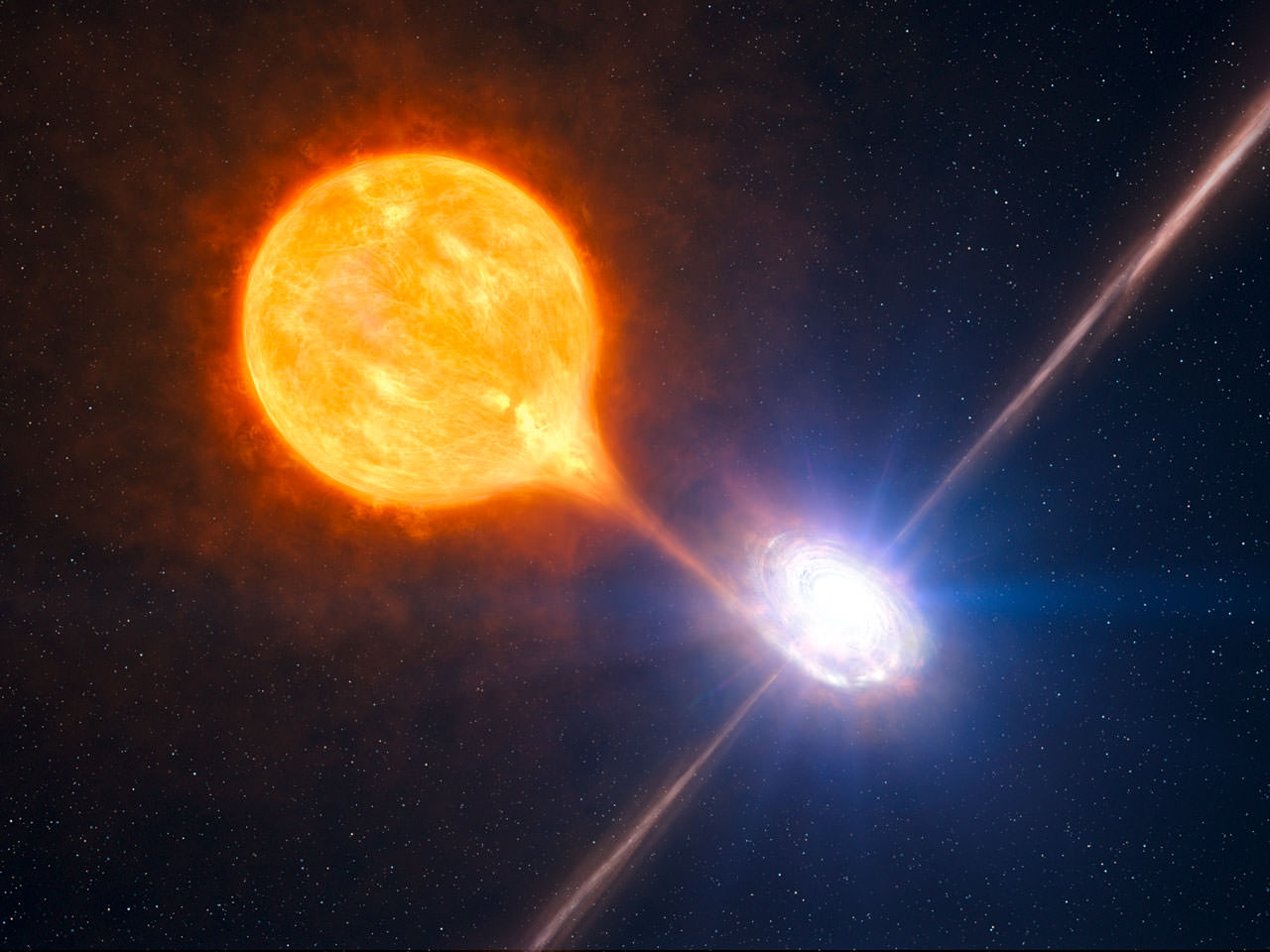
One of the most pressing questions in astronomy concerns black holes. We know that massive stars that explode as supernovae can leave stellar mass black holes as remnants. And astrophysicists understand that process. But what about the supermassive black holes (SMBHs) like Sagittarius A-star (Sgr A*,) at the heart of the Milky Way?
SMBHs can have a billion solar masses. How do they get so big?
Continue reading “New Simulations Show How Black Holes Grow, Through Mergers and Accretion”