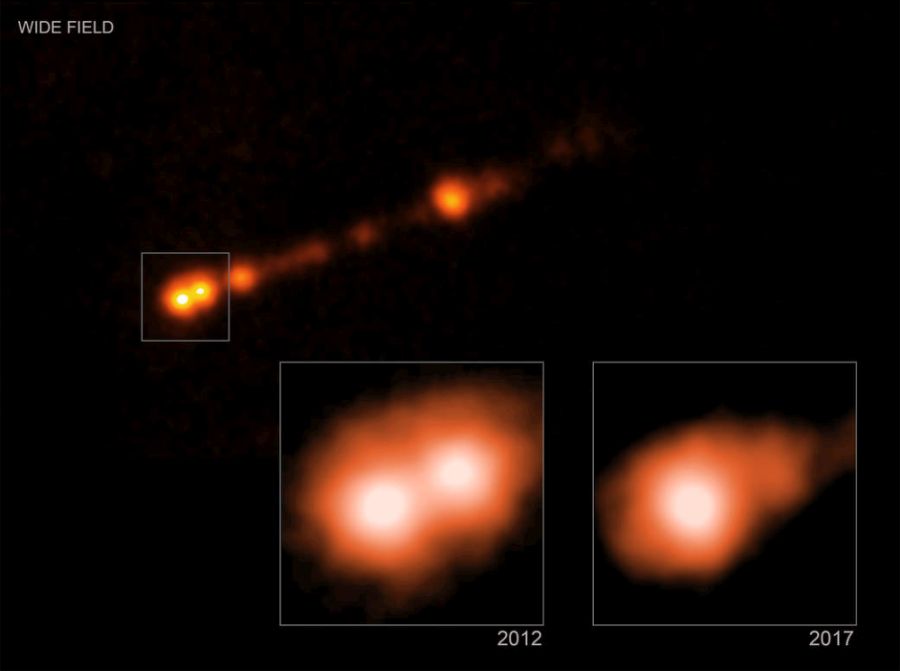
Perhaps the greatest discovery to come from the “Golden Age of General Relativity” (ca. 1960 to 1975) was the realization that a supermassive black hole (SMBH) exists at the center of our galaxy. In time, scientists came to realize that similarly massive black holes were responsible for the extreme amounts of energy emanating from the active galactic nuclei (AGNs) of distant quasars.
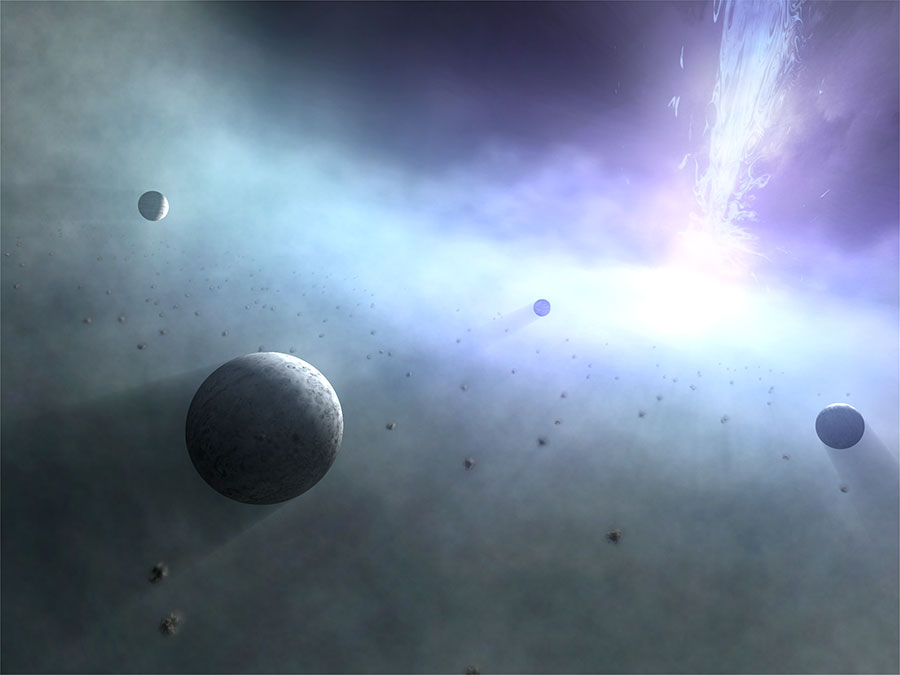
Given their sheer size, mass, and energetic nature, scientists have known for some time that some pretty awesome things take place beyond the event horizon of an SMBH. But according to a recent study by a team of Japanese researchers, it is possible that SMBHs can actually form a system of planets! In fact, the research team concluded that SMBHs can form planetary systems that would put our Solar System to shame!
Continue reading “There Could be Planets Orbiting Around Supermassive Black Holes”