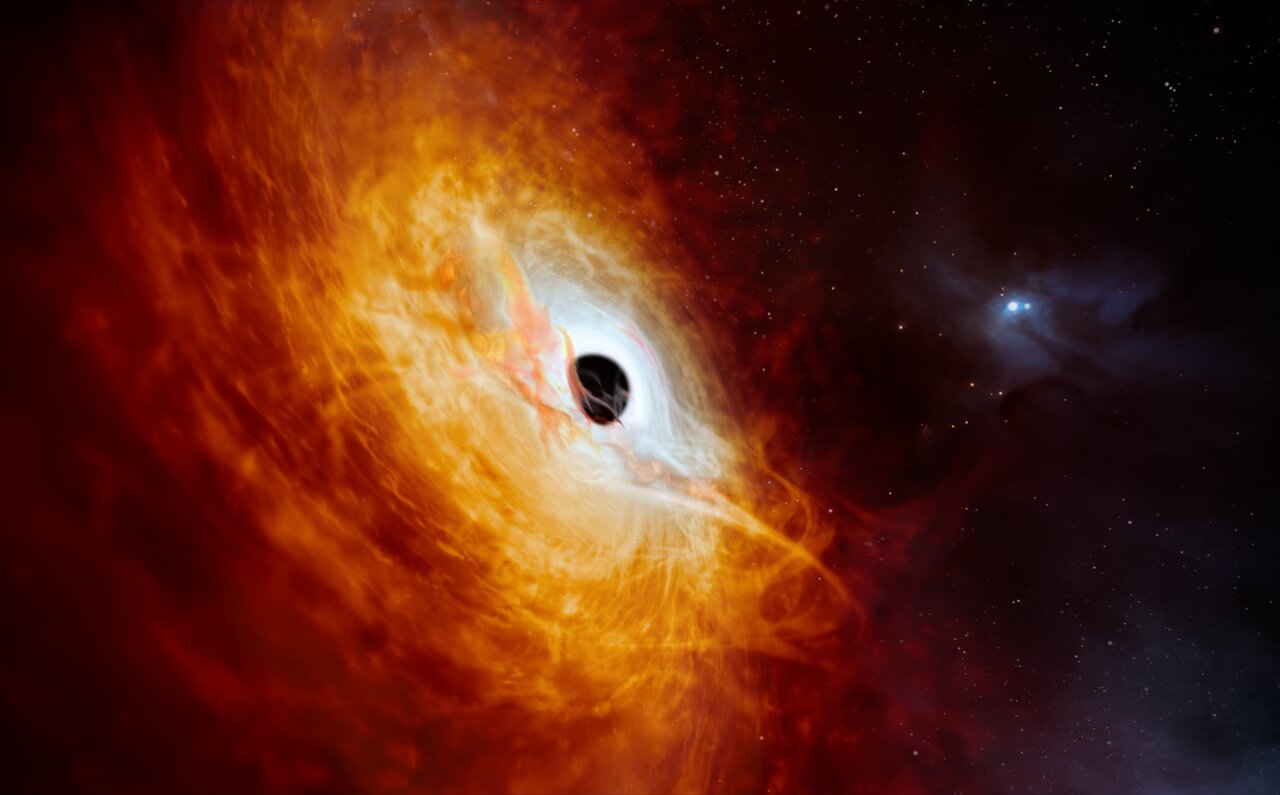
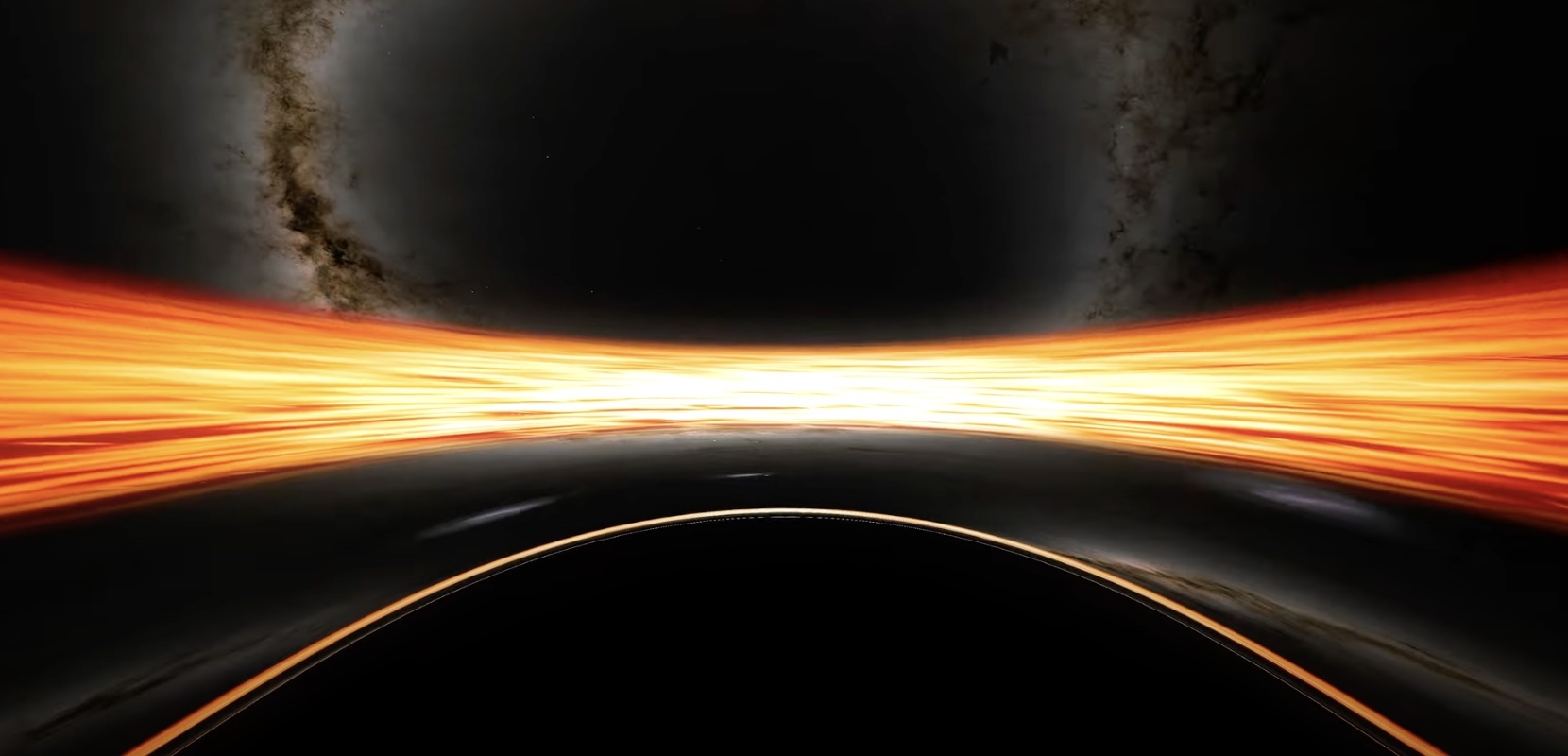
The lifecycle of a star is regularly articulated as formation taking place inside vast clouds of gas and dust and then ending either as a planetary nebula or supernova explosion. In the last 70 years however, there seems to be a number of massive stars that are just disappearing! According to stellar evolution models, they should be exploding as supernova but instead, they just seem to vanish. A team of researchers have studied the behaviour of star VFTS 243 – a main sequence star with a black hole companion – and now believe it, like the others, have just collapsed, imploding into a black hole!
Continue reading “Hundreds of Massive Stars Have Simply Disappeared”Hundreds of Massive Stars Have Simply Disappeared