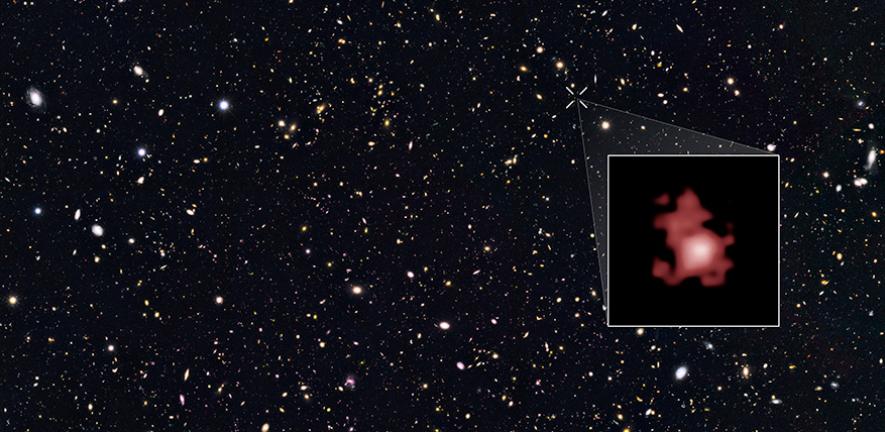
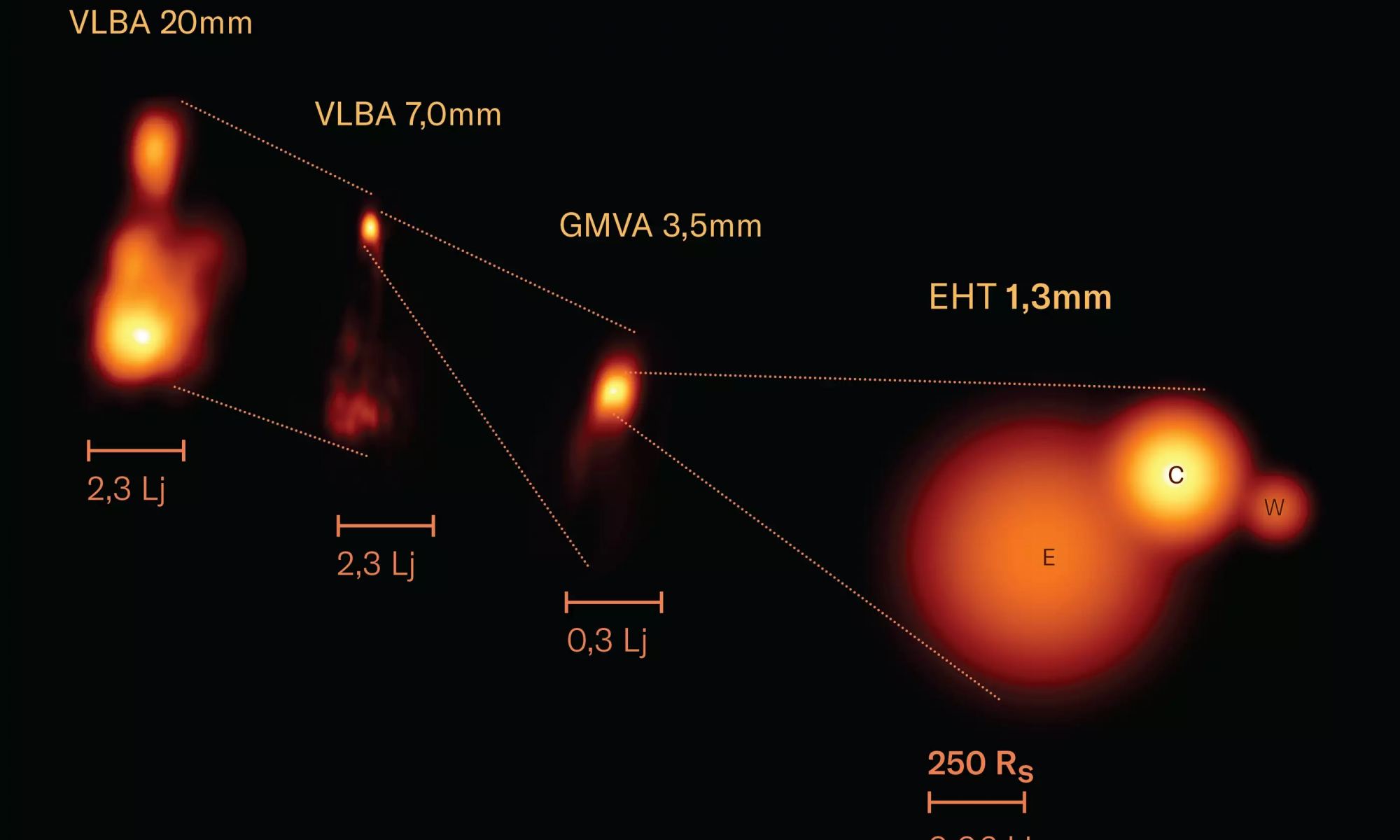
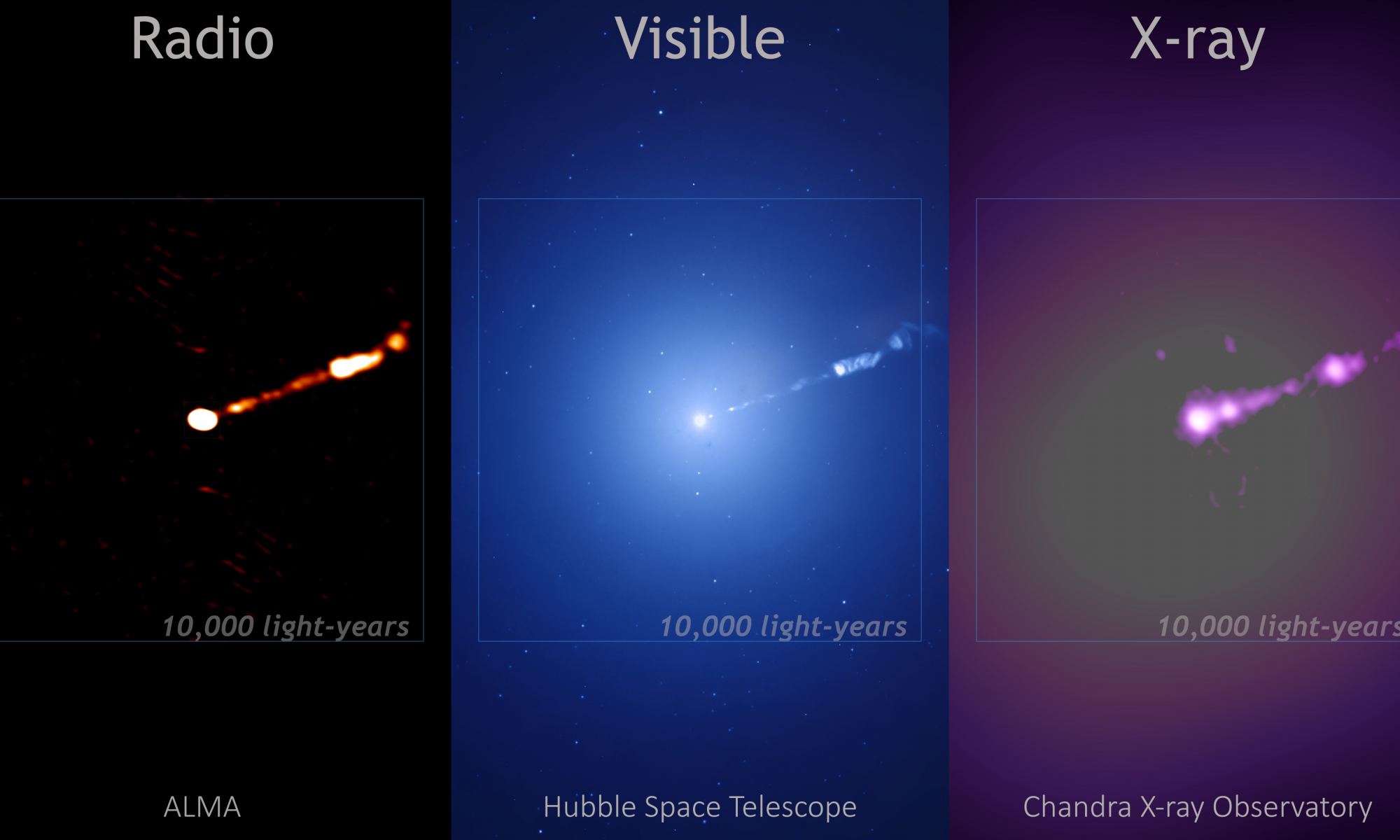
Although supermassive black holes are common throughout the Universe, we don’t have many direct images of them. The problem is that while they can have a mass of millions or billions of stars, even the nearest supermassive black holes have tiny apparent sizes. The only direct images we have are those of M87* and Sag A*, and it took a virtual telescope the size of Earth to capture them. But we are still in the early days of the Event Horizon Telescope (EHT), and improvements are being made to the virtual telescope all the time. Which means we are starting to look at more supermassive black holes.
Continue reading “The Event Horizon Telescope Zooms in on a Black Hole's Jet”The Event Horizon Telescope Zooms in on a Black Hole's Jet