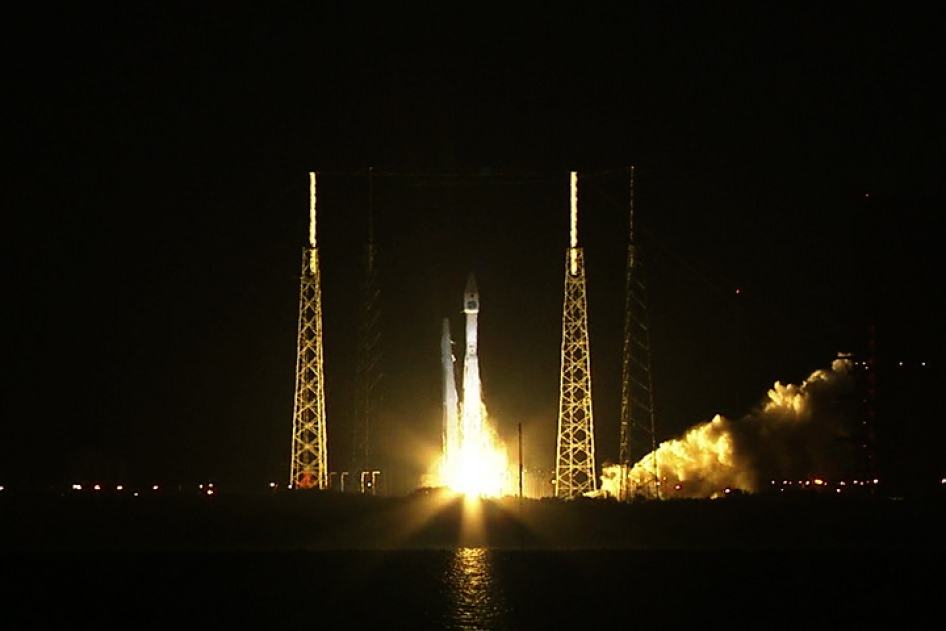
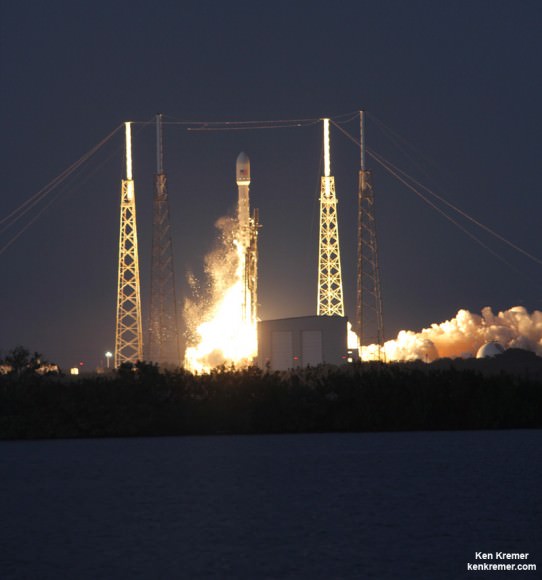
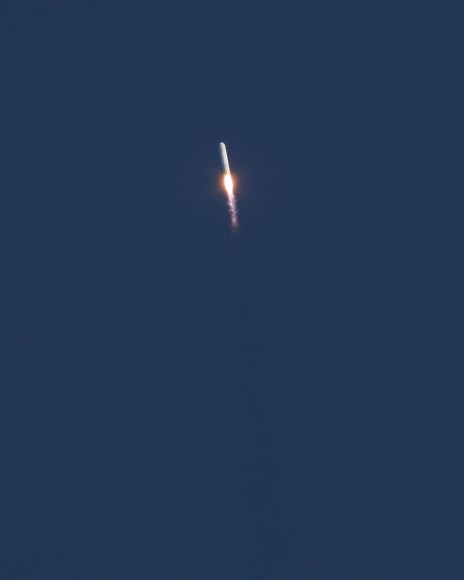
The dual Atlas V rocket engines roar to life on a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket at Cape Canaveral Air Force Station’s Space Launch Complex 41. The launch vehicle will boost NASA’s Tracking and Data Relay Satellite, or TDRS-L, spacecraft to Earth orbit. Liftoff was at 9:33 p.m. EST on Jan. 23, 2014.
Credit: NASA
Story updated[/caption]
A spectacular nighttime blastoff lit up the evening skies for hundreds of miles around the Florida Space coast on a mission that sent a critical NASA communications relay satellite to orbit this evening, Jan. 23.
NASA’s huge Tracking and Data Relay Satellite L (TDRS-L) is now safely in orbit following tonight’s successful launch aboard a United Launch Alliance Atlas V rocket from Cape Canaveral Air Force Station in Florida.
The Atlas V rocket was launched at 9:33 p.m. EST from Space Launch Complex 41 into crystal clear skies that gave excited spectators an uncommonly long and stunning launch spectacle that was well worth the wait.
The 3.8 ton TDRS-L satellite will become part of a network providing high-data-rate communications to the International Space Station (ISS), Hubble Space Telescope, launch vehicles and a host of other research spacecraft that relay absolutely critical flight, telemetry and science data.

The recently launched Orbital Sciences Cygnus cargo carrier also relays data via the TDRS system.
The ISS, Hubble and all these other spacecraft could not function without the TDRS network of relay satellites.

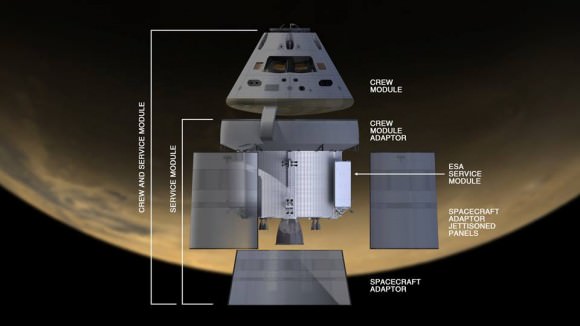
The TDRS-L satellite will also be used to track and relay vital information for the maiden launch of NASA’s next generation Orion human spaceflight capsule slated for Fall 2014.
Read my latest Orion update – here.
“TDRS-L and the entire TDRS fleet provide a vital service to America’s space program by supporting missions that range from Earth-observation to deep space discoveries,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden.
“TDRS also will support the first test of NASA’s new deep space spacecraft, the Orion crew module, in September. This test will see Orion travel farther into space than any human spacecraft has gone in more than 40 years.”
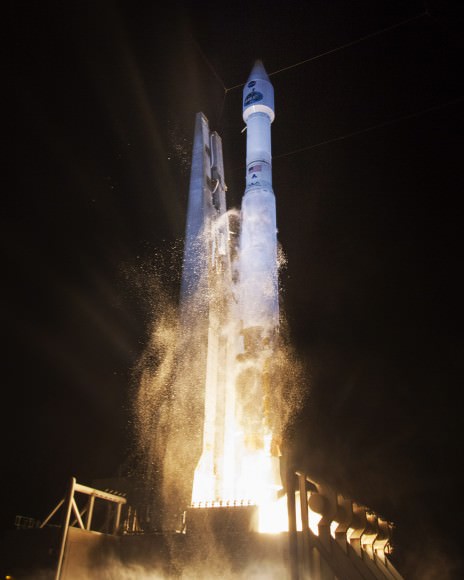

TDRS-L arrived in geosynchronous transfer orbit about two hours after liftoff. It will orbit at an altitude of 22,300 miles.
The venerable Atlas V rocket is one of the most reliable and well built rockets in the world.
Indeed the Atlas V has been entrusted to launch many high value missions for NASA and the Defense Department- such as Curiosity, JUNO and the X-37 B.

The last Atlas V launch from the Cape occurred in November 2013 and sent NASA’s MAVEN Mars orbiter on a voyage to the Red Planet.
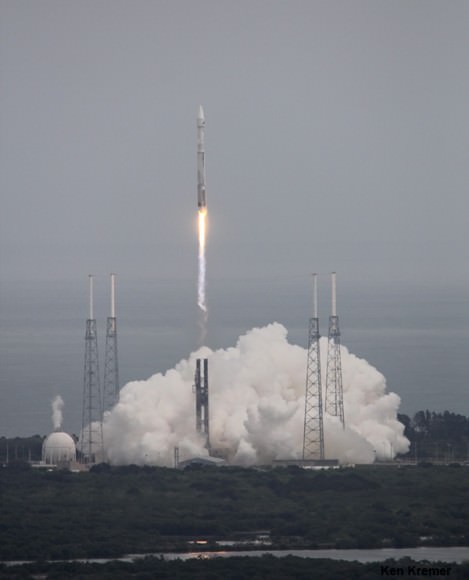

And the two stage rocket is being man-rated right now to launch humans to low Earth orbit in the near future.
The Atlas V has been chosen to launch two of the upcoming astronaut ‘space taxis’ as part of NASA’s commercial crew initiative to launch human crews to the International Space Station.
Just today, Sierra Nevada Corp announced that their Dream Chaser mini shuttle will launch to orbit on its first flight on Nov. 1, 2016.
TDRS-L is the 12th in this series of communications satellites.
It is identical to the TDRS-K spacecraft launched in 2013, which was the first of the third generation of TDRS satellites.
They were built by Boeing Space and Intelligence Systems of El Segundo, Calif., and have a 15 year design lifetime.
NASA will now conduct a three month in orbit checkout.
TDRS-M, the next spacecraft in this series, is on track to be ready for launch in late 2015.

This is the third generation of TDRS satellites.
“The TDRS fleet began operating during the space shuttle era with the launch of TDRS-1 in 1983. Of the 11 TDRS spacecraft placed in service to date, eight still are operational. Four of the eight have exceeded their design life,” said NASA.
The Atlas V launched in the 401 configuration vehicle, which includes a 4-meter diameter payload fairing and no solid rocket motors. The first stage was powered by the RD AMROSS RD-180 engine. The Centaur upper stage was powered by a single Aerojet Rocketdyne RL10A-4 engine.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, Chang’e-3, Orbital Sciences, SpaceX, commercial space, LADEE, Mars and more news.