NEW JERSEY – Record breaking snow from the ‘Blizzard of 2015’ hit vast regions of the US Northeast today, Jan. 27, 2015, stretching from Long Island to New England.
NASA and NOAA Earth orbiting satellites are keeping track of the storm affecting millions of residents.
This afternoon the agencies provided a new set of night-time and daytime views of the Blizzard of 2015 taken by the Suomi NPP and the GOES-East satellites.
The crippling blizzard is causing misery, extensive destruction to homes and businesses in localized areas, power outages, traffic accidents, breaks in some sea walls and deaths.
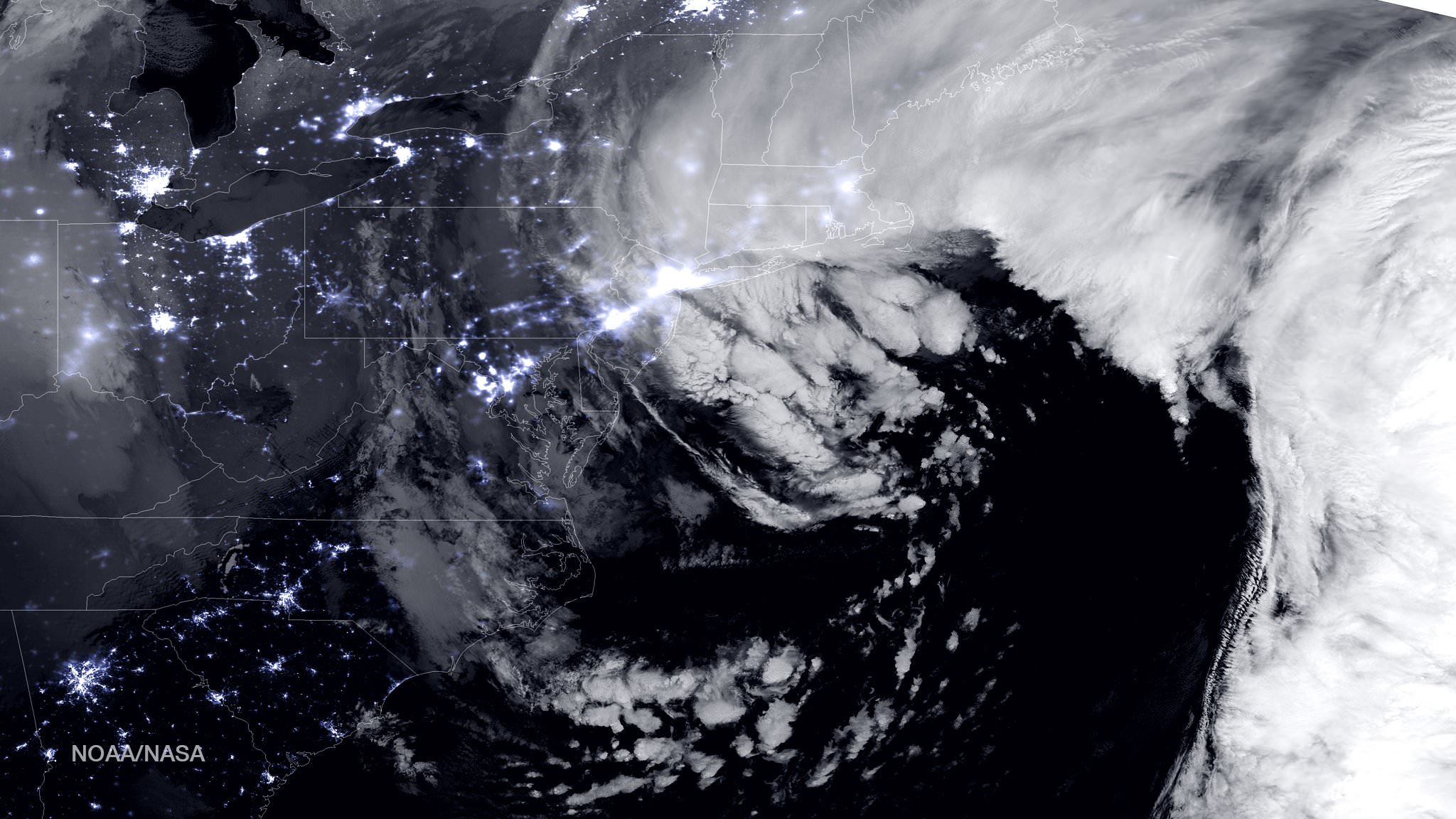
The satellite image above shows a combination of the day-night band and high resolution infrared imagery from the NASA-NOAA’s Suomi NPP satellite.
It was taken as the historic blizzard neared peak intensity as it moved over the New York area and through the Boston Metropolitan areas at 06:45Z (1:45 a.m. EST) on January 27, 2015.
The high cloud tops from the most intense parts of the storm blurred the regions normally bright nighttime lights in the satellite image.
Although the snow totals were about half the over two feet forecast for the New York Metropolitan region, many areas to the north and east were inundated with very heavy to historic snow fall totals, as bad or worse than the forecasters predicted.
Over two feet of snow fell on areas of New York’s Long Island and stretching north to vast regions of Connecticut, Massachusetts, New Hampshire and into Maine.
Near hurricane force waves are crashing into some coastal towns along the Massachusetts shoreline. Wind gusts as high as 78 mph have been recorded.
“Highest snowfall report has been Auburn, MA with 32.5 inches! Wind gust reports as high as 78 mph in Nantucket, MA,” according to a tweet this evening from the National Weather Service (NWS).
Worchester, Mass had a record breaking 31 inches of snow. And it’s still falling this evening in the 2nd largest city in New England.
A flood emergency is in effect in Marshfield, Mass., where an 80 foot section of the seawall was smashed by crashing waves and is destroying homes as shown on NBC Nightly News.
Blinding snow is raging in Portland, Maine this evening according on a live NBC News report.
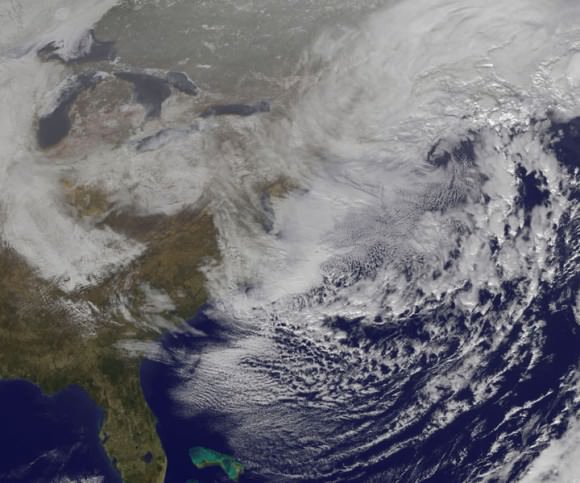

“At 10 a.m. EST, the National Weather Service noted “the powerful nor’easter that brought moderate to heavy snowfall and blizzard conditions to the Northeast on Monday will continue to affect the region on Tuesday, with heavy snow and blizzard conditions expected from eastern Long Island to Maine as the system slowly moves to the northeast. Snow and strong winds will being tapering off from south to north Tuesday night into Wednesday morning,” wrote NASA’s Rob Gutro of NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in an update.
“Later on January 27, 2015 at 17:35 UTC (12:35 p.m. EST) NOAA’s Geostationary Operational Environmental or GOES-East satellite captured an image of the nor’easter over New England. The image was created by the NASA/NOAA GOES Project and showed the clouds associated with the nor’easter blanketing New England. An occluded front extended north and eastward out of the low pressure area’s center out into the Atlantic Ocean.”
The latest NOAA forecast as of 4 PM, Jan. 27 states:
HIGH WINDS AND HEAVY SNOW WILL BEGIN TO GRADUALLY TAPER OFF FROM SOUTH TO NORTH TONIGHT…BUT WILL LAST INTO EARLY WEDNESDAY MORNING ACROSS PORTIONS OF MAINE. HEAVY SNOWFALL WILL COMBINE WITH SUSTAINED WINDS OF 30 TO 40 MPH…AND GUSTS IN EXCESS OF 50 MPH…TO CREATE LIFE-THREATENING WHITEOUT OR BLIZZARD CONDITIONS. THESE WINDS MAY LEAD TO DOWNED TREES AND POWER LINES RESULTING IN POWER OUTAGES. TRAVEL WILL BE IMPOSSIBLE AND LIFE-THREATENING IN MANY AREAS. ALONG THE IMMEDIATE COASTLINE…WIND GUSTS TO NEAR 65 MPH WILL BE POSSIBLE. COASTAL FLOODING AND SEVERE BEACH EROSION WILL ALSO BE A POSSIBILITY…AND VULNERABLE ROADS AND STRUCTURES MAY BE FLOODED OR DAMAGED.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.
Reporting from snowy New Jersey.