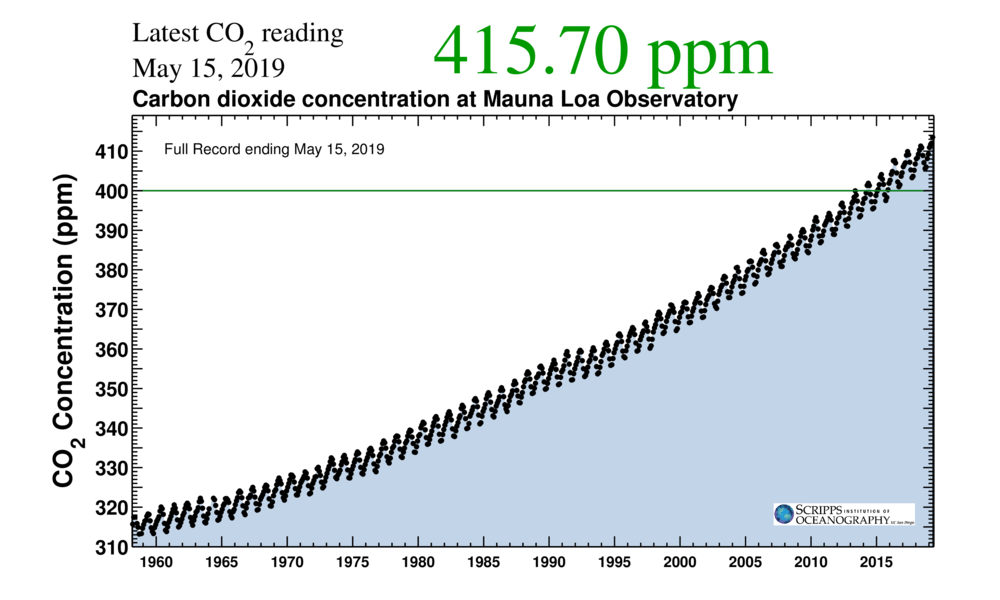
Between the scientific community, governments, humanitarian organizations, and even military planners, climate change is considered to be the single greatest threat facing humanity today. Between the increases in famine, disease, flooding, displacement, extreme weather, and chaos that result, it is clear that the way we are causing our planet to get warmer is having dire consequences.
But there a number of scenarios where the harm being done now could result in a runaway effect leading to mass extinctions. This possibility was illustrated in a recent study conducted by MIT professor Daniel Rothman with the support of NASA and the National Science Foundation (NSF). According to Rothman, we are in danger of breaching a “carbon threshold” that could lead to a runaway effect with Earth’s oceans.
Continue reading “New Study Shows How Breaching “Carbon Threshold” Could Trigger Mass Extinction in Earth’s Oceans”