[/caption]
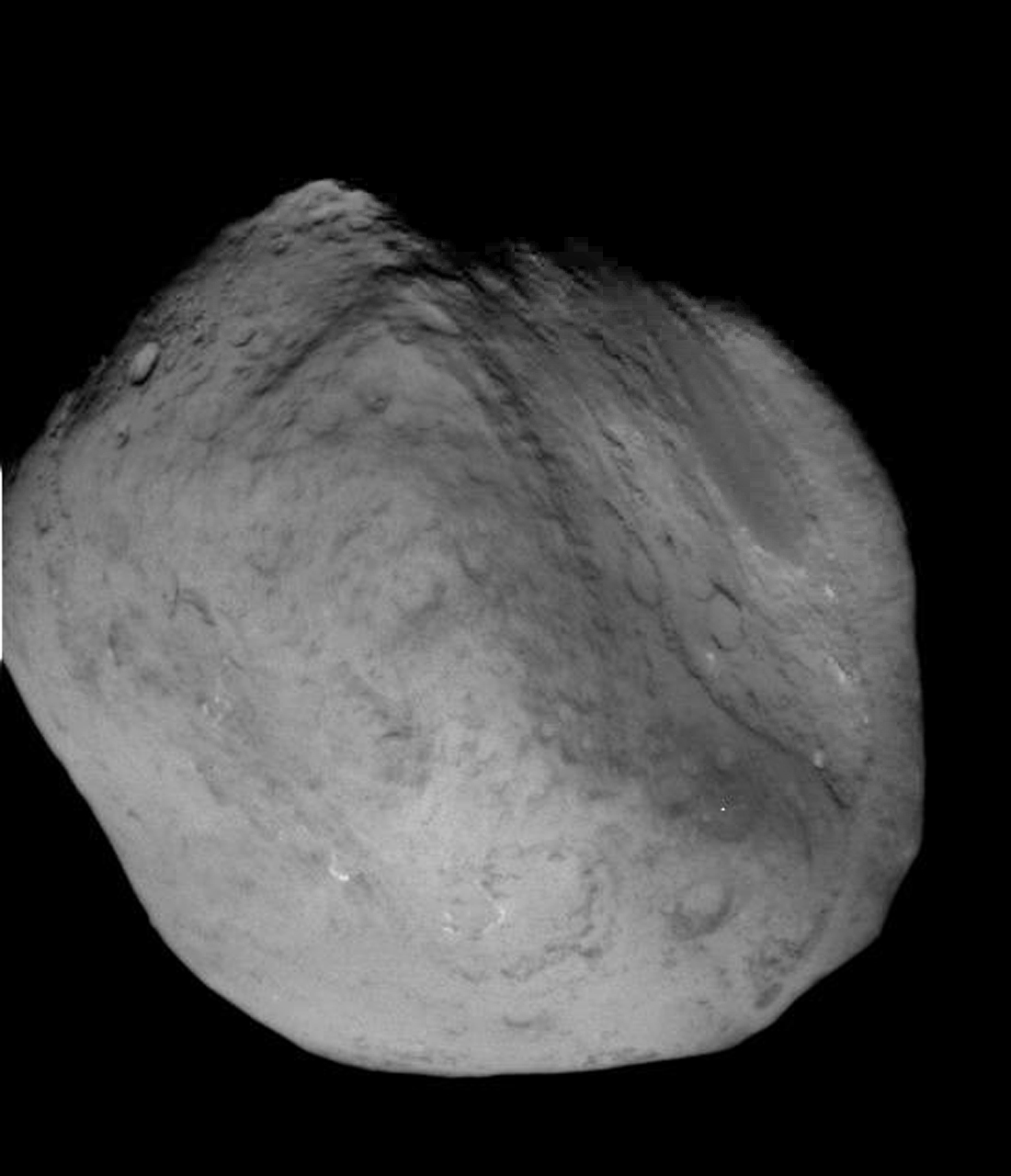
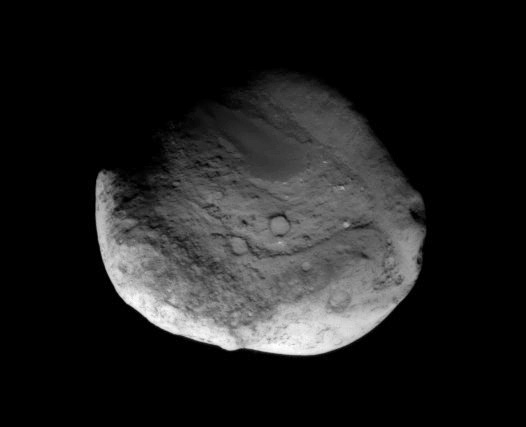
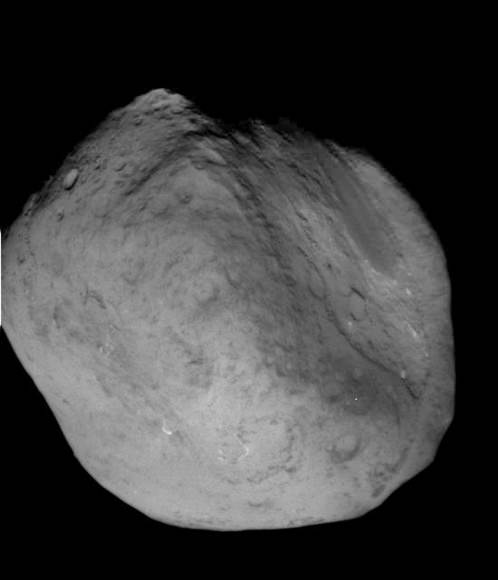
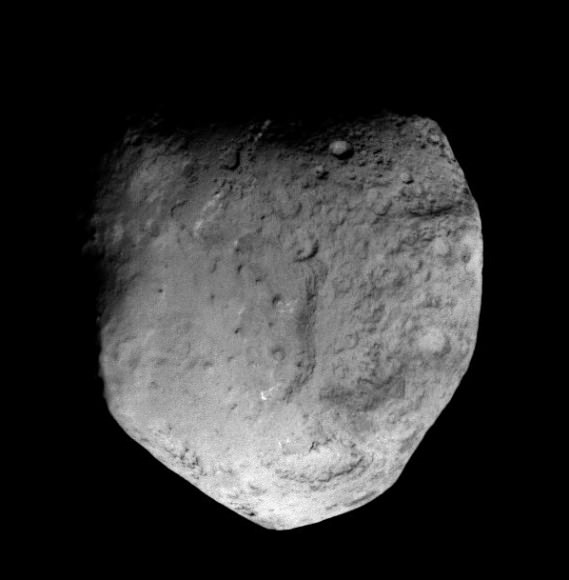
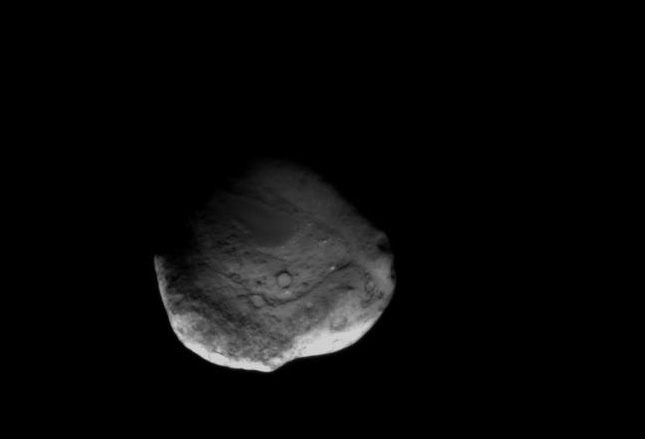
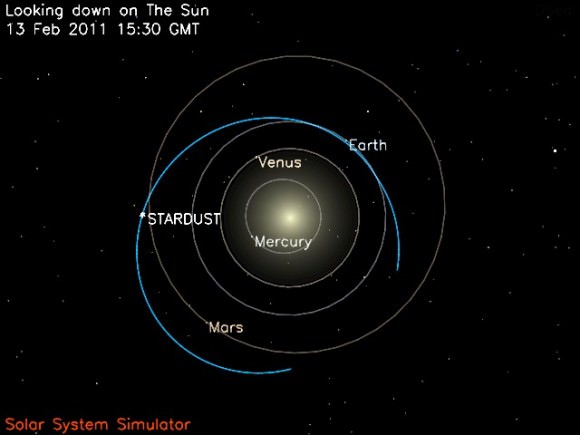
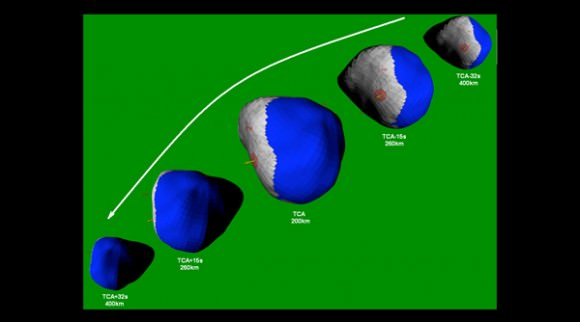
NASA’s aging and amazing Stardust space probe has at last discovered the human made crater created on Comet Tempel 1 in 2005 by the history making cosmic smash up with NASA’s Deep Impact penetrator. Stardust streaked past the comet on Feb. 14 at 10.9 km/sec, or 24,000 MPH, and succeeded in briefly photographing the crater as it approached within 178 km (111 mi) during the fleeting moments of the probes closest approach.
The intentional celestial collision in 2005 was designed to violently unleash the buried remnants of the early solar system into an enormous ejecta cloud of dusty debris that scientists could sift for clues to help unlock the secrets of how we all formed and evolved some 4.5 Billion Years ago.
Tempel 1 is the first comet to receive a second visit by probes from Earth.
Comets have continuously smashed into Earth over the eons and delivered vast quantities of key ingredients – such as water and organic molecules – that may have sparked the formation of life on the early Earth.
NASA approved the use of the already orbiting Stardust-NExT spacecraft to follow up on the science discoveries by Deep Impact as the best and most economical way to try and locate the crater blast site, image new terrain and look for changes on the comets surface since the 2005 mission as the comet also completed another orbit around our Sun and eroded due to solar heating.
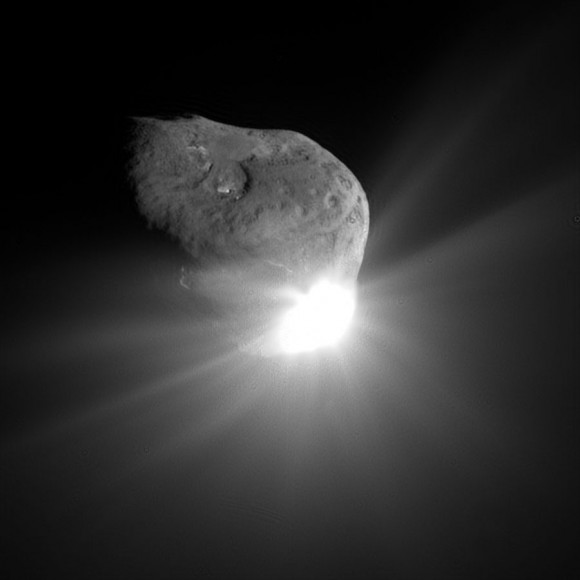
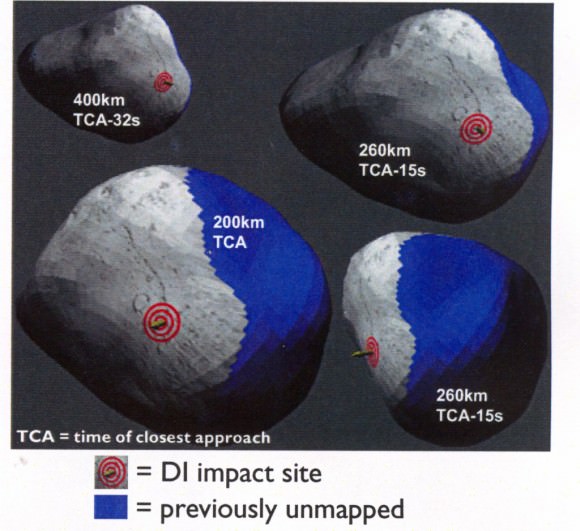
The human made crater is about 150 meters wide and was formed by a 375 kilogram (800 pound) projectile propelled into the speeding path of Comet Tempel 1 by the Deep Impact mothership in 2005.
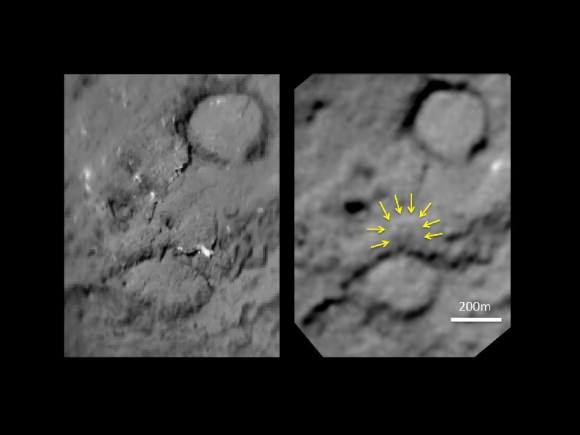

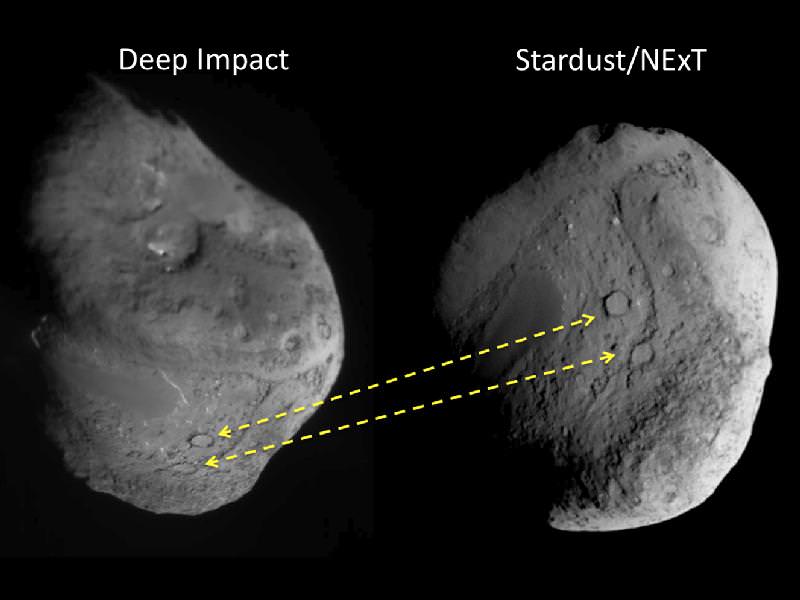
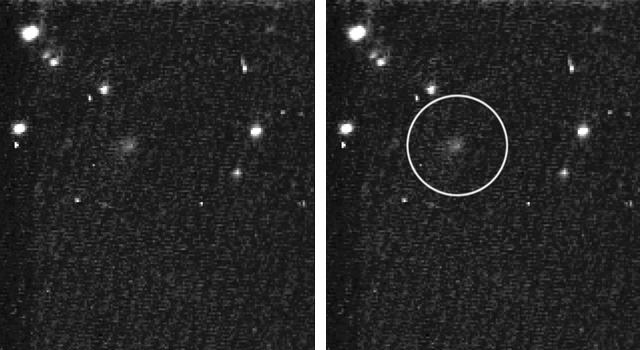
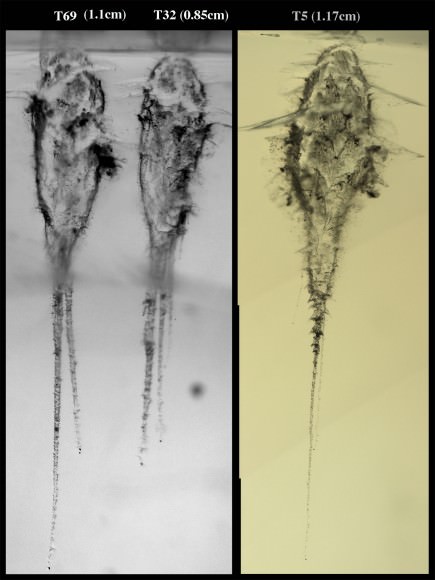
This pair of images shows the before-and-after comparison of the part of comet Tempel 1 that was hit by the impactor from NASA's Deep Impact spacecraft. The left-hand image is a composite made from images obtained by Deep Impact in July 2005. The right-hand image shows arrows identifying the rim of the crater caused by the impactor. The crater is estimated to be 150 meters (500 feet) in diameter. This image also shows a brighter mound in the center of the crater likely created when material from the impact fell back into the crater. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Maryland/Cornell
Stardust-NExT took 72 high resolution science images of the comet during the Valentine’s Day encounter flyby on Feb, 14 at 11:40 p.m. EST (8:40 p.m. PST). The probe absolutely had to be precisely navigated to exactly hit the aim point for sequencing the images to match the right moment in the erratic rotation of the volatile comet.
The results of the Stardust-NExT mission were announced at a post encounter new briefing after most of the images and science data had streamed back to Earth. The science team and NASA said that all the mission objectives were accomplished.
“If you ask me was this mission 100 percent successful in terms of the science, I’d have to say no. It was 1000 percent successful!” said Stardust-NExT principal investigator Joe Veverka of Cornell University, Ithaca, N.Y., at the news briefing.
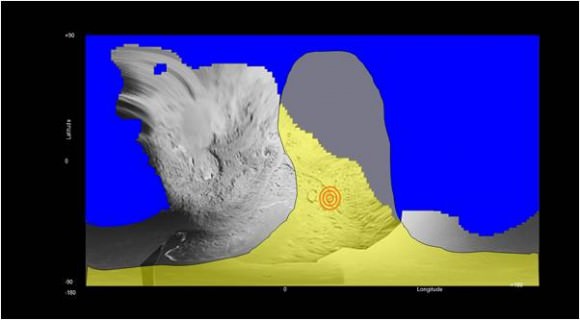
“We found the Deep Impact crater. We see erosion in comparison to 2005. So we do see changes. Erosion on the scale of 20 to 30 meters of material has occurred in the five or six years since we took the first picture. We are seeing a change, but we have to spend time quantifying the changes and understanding what they mean.”
“We saw a lot of new territory. It’s amazing with lots of layers. There is lots of surface sublimation. We had to arrive at precisely the right time in order to see new and old territory.”
“We had monitored the comets rotation for several years. And we got the longitude almost perfect within 1 or 2 degrees,” Veverka said.
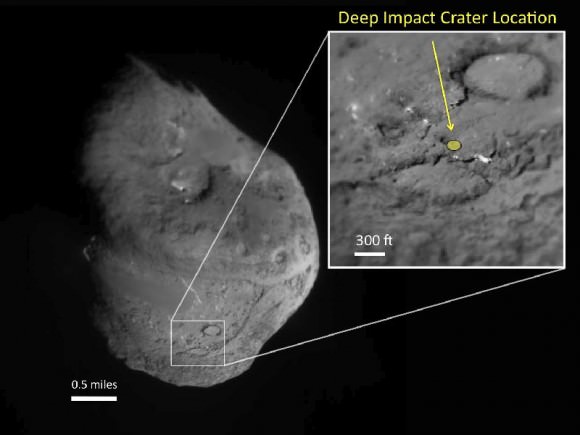

Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Maryland/Cornell
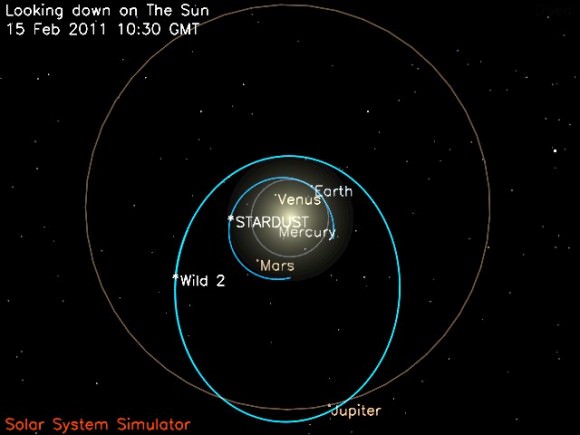
It took a few years of careful study to deduce the comets complex rotational patterns which change as the body orbits in a wide orbital path between Mars and Jupiter and is heated by the sun.
Peter Schultz, a science team co-investigator agreed and showed the comparison images.
“We saw the crater,” said Schultz, of University. “It’s subdued; it’s about 150 meters across and has a small central mound in the center. It looks as if from the impact, the stuff went up and came back down. So we did get it, there’s no doubt. I think one of the bottom-line messages is that this surface of the comet where we hit is very weak. It’s fragile. So the crater partly healed itself.”
“It was about the size we expected. But more subdued.”
The probes mission is almost complete since it has very little fuel left. The remaining science data from the flyby is being sent back and some outbound data is being collected.
“This spacecraft has logged over 3.5 billion miles since launch, and while its last close encounter is complete, its mission of discovery is not,” said Tim Larson, Stardust-NExT project manager at JPL. “We’ll continue imaging the comet as long as the science team can gain useful information, and then Stardust will get its well-deserved rest.”
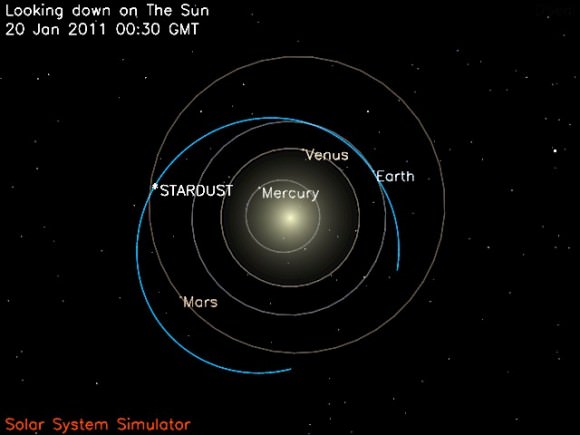
Stardust-NExT is a repurposed spacecraft that has journeyed nearly 6 billion kilometers since it was launched in 1999.
Initially christened as Stardust, the spaceships original task was to fly by Comet Wild 2 in 2004. It also collected priceless cometary dust particles from the coma which was safely parachuted back to Earth inside a return canister in 2006. High powered science analysis of the precious comet dust will help researchers discern the origin and evolution of our solar system.
This was humanities first revisit to a comet and at a bargain basement price by using an old spacecraft already in space.
“The cost was just $29 Million dollars. A new Discovery class mission costs $300 to 500 Million. So that’s maybe 6% the cost of developing and launching a new mission,” said Ed Weiler, the associate administrator for NASA’s Science Mission Directorate at NASA HQ in Washington, DC.
Read more about the Stardust-NExT Flyby and mission in my earlier stories here, here, here and here
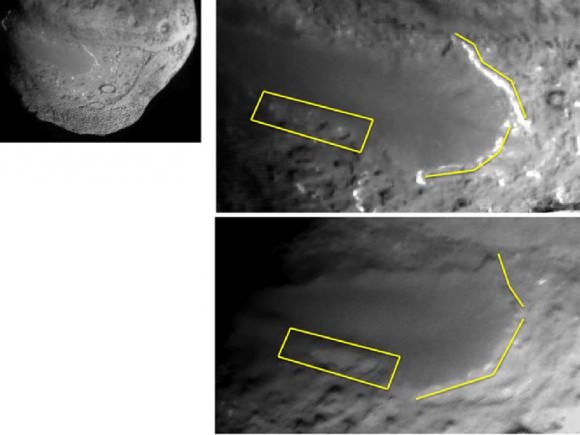
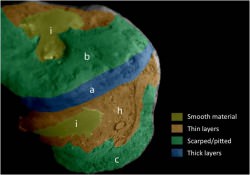
This image layout depicts changes in the surface of comet Tempel 1, observed first by NASA's Deep Impact Mission in 2005 (top right) and again by NASA's Stardust-NExT mission on Feb. 14, 2011 (bottom right). Between the two visits, the comet made one trip around the sun. The image at top left is a wider shot from Deep Impact. The smooth terrain is at a higher elevation than the more textured surface around it. Scientists think that cliffs, illustrated with yellow lines to the right, are being eroded back to the left in this view. The cliffs appear to have eroded as much as 20 to 30 meters (66 to 100 feet) in some places, since Deep Impact took the initial image. The box shows depressions that have merged together over time, also from erosion. This erosion is caused by volatile substances evaporating away from the comet. Credit: NASA/JPL-Caltech/University of Maryland/Cornell