Do you get the feeling that Elon Musk likes making bold announcements?
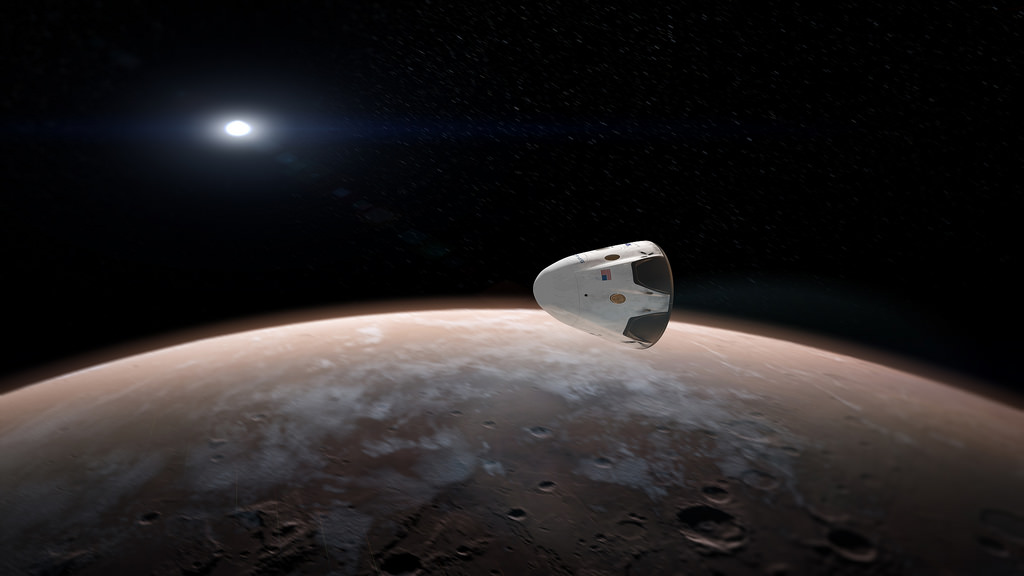
Every space enthusiast’s favorite billionaire-turned-space-entrepreneur has just announced that he hopes his company, SpaceX, will send humans to Mars in 2024. If this sounds outrageous, you’re not keeping up with developments in commercial space. If this sounds a little bit ambitious, you’re probably right. But ambition is what Musk is all about.
“I think, if things go according to plan, we should be able to launch people probably in 2024, with arrival in 2025,” Musk said.
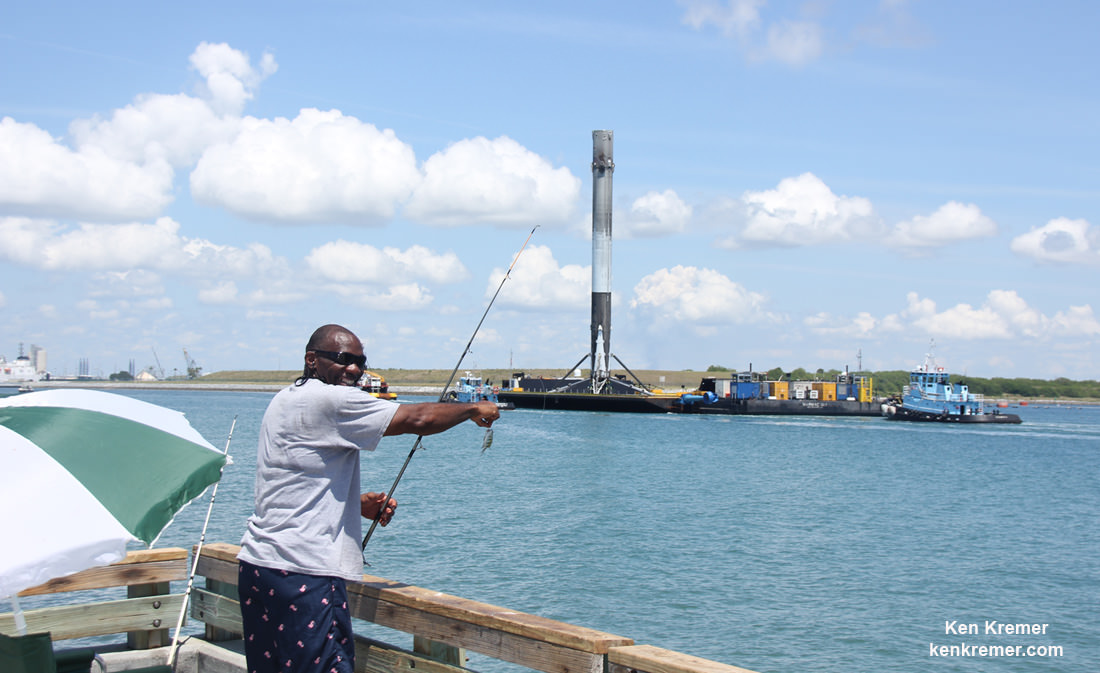
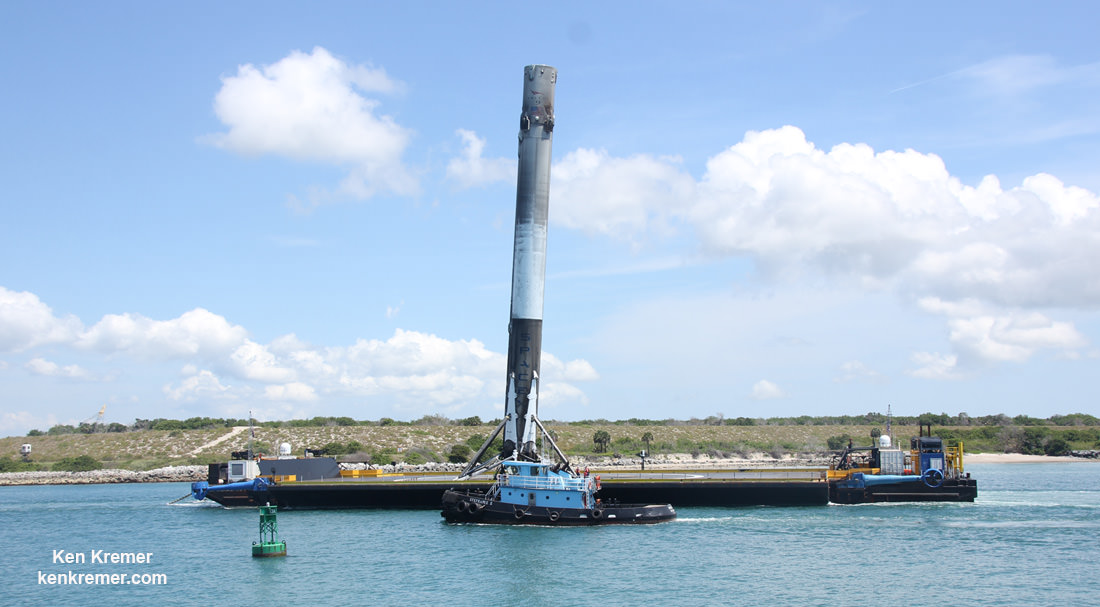
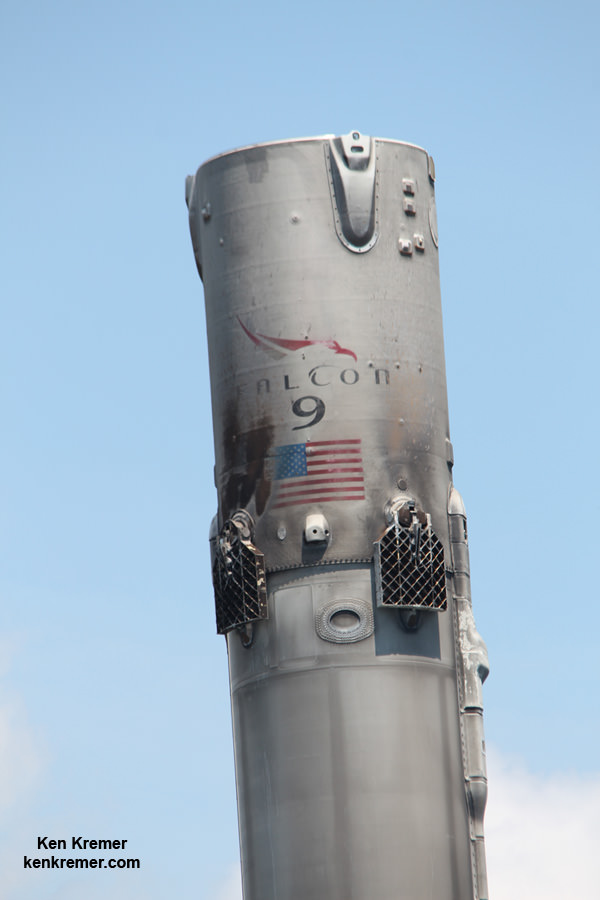
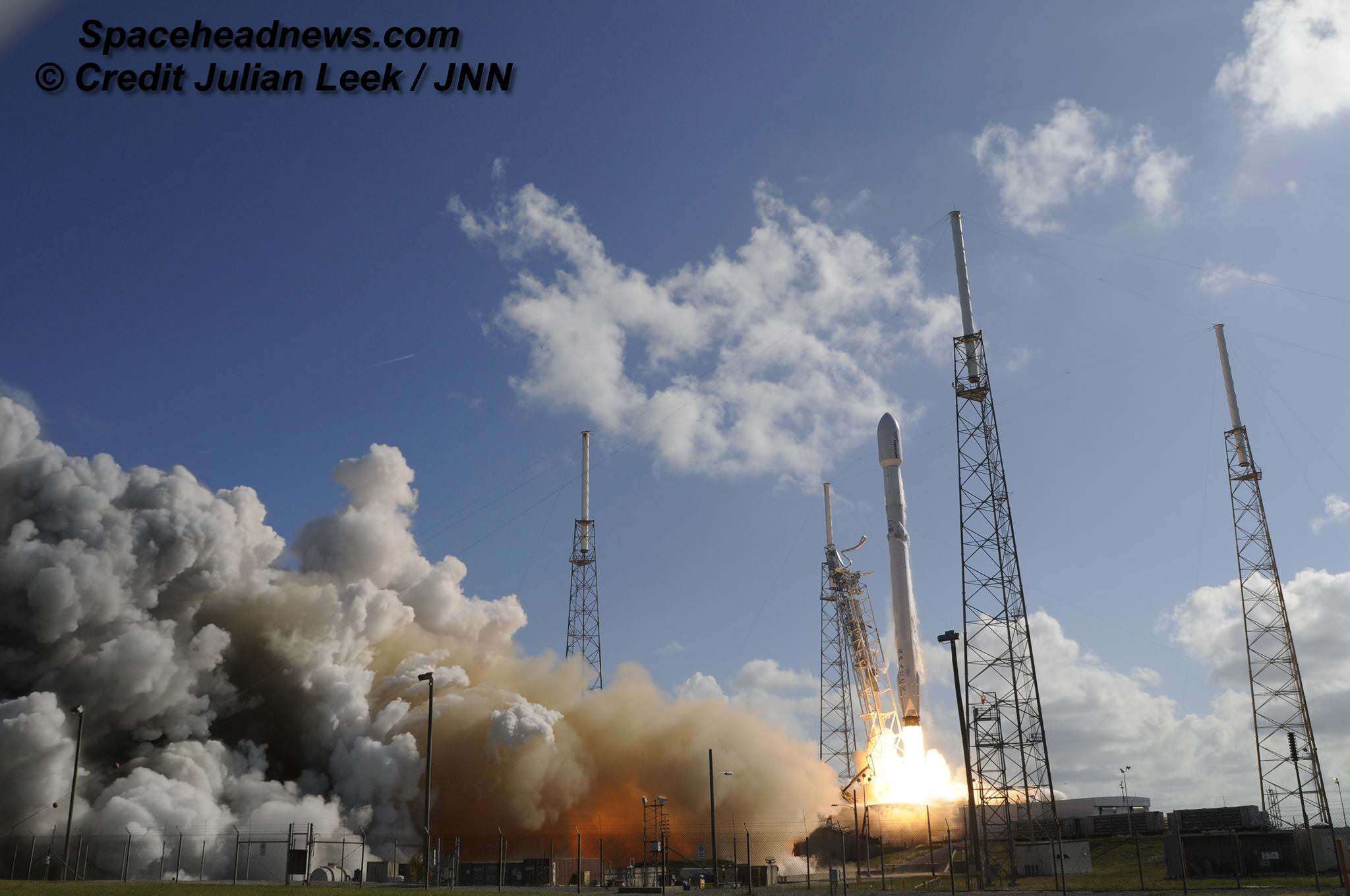
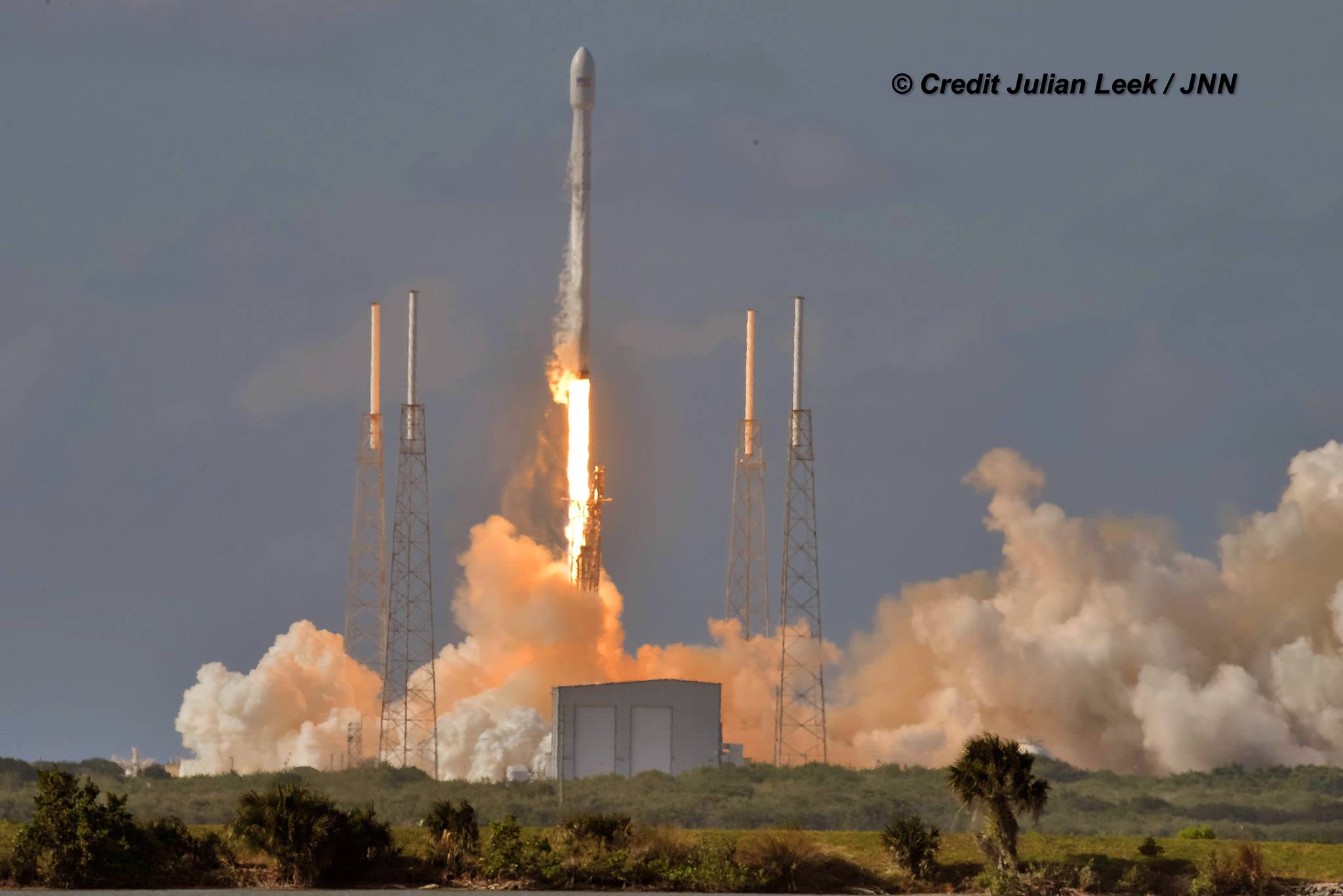
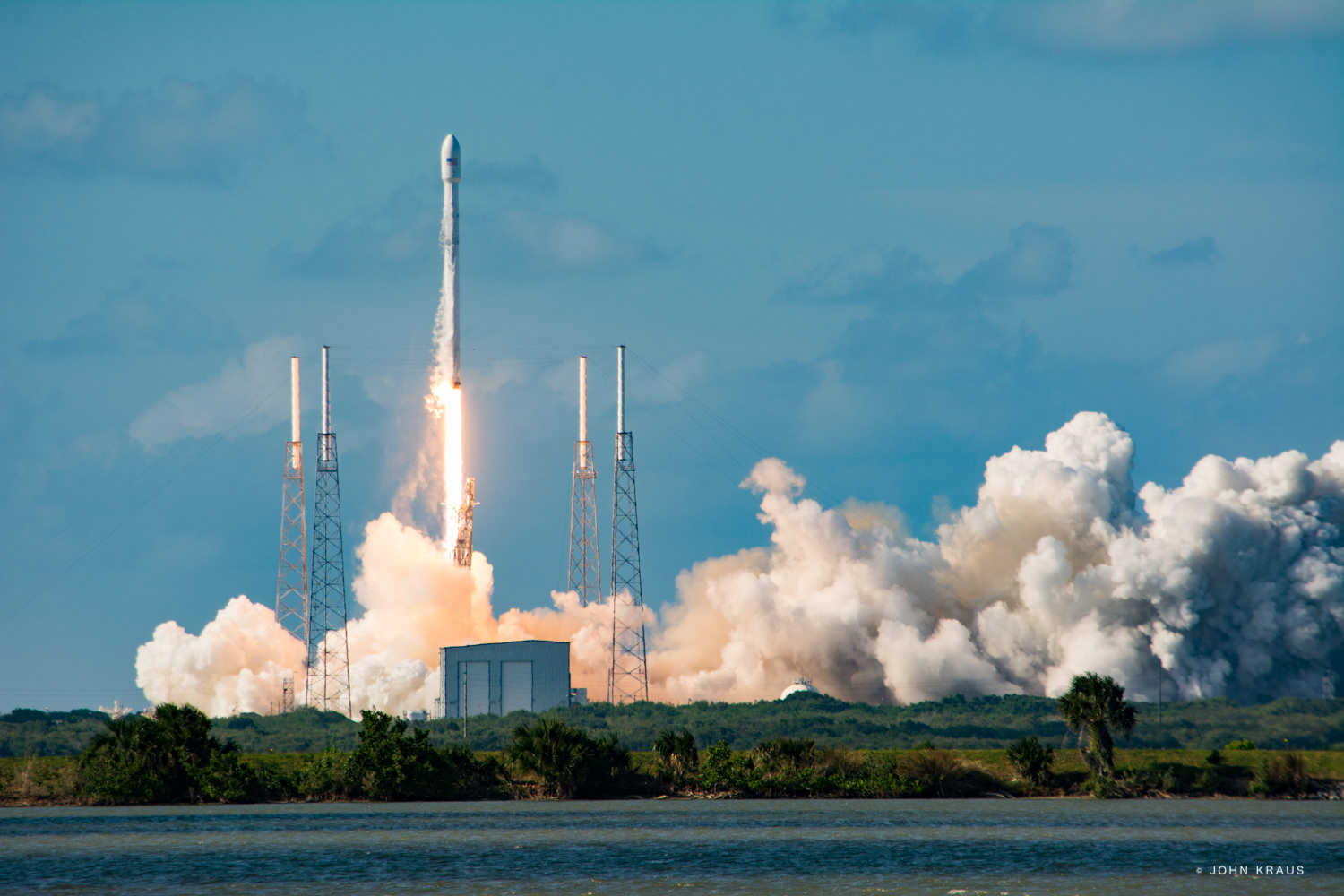
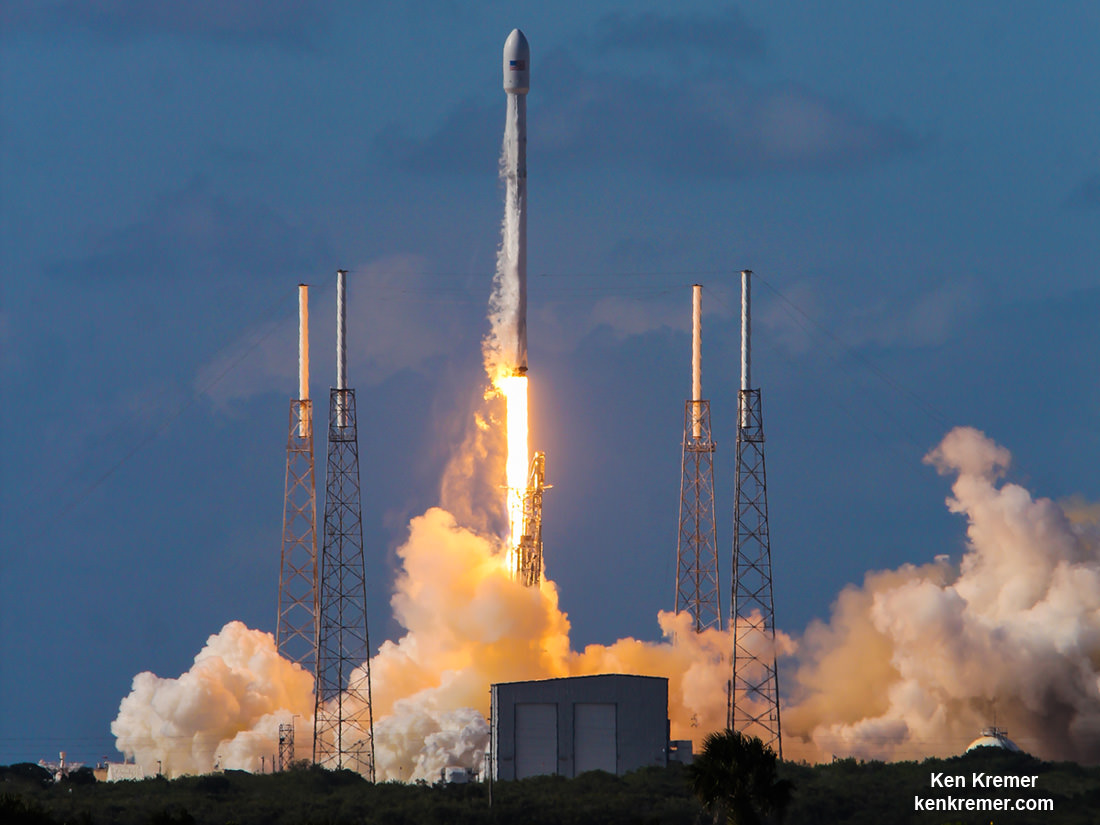
Musk, of course, is the Paypal co-founder who went on to start the Tesla electric car company, and SpaceX, the private space company. SpaceX has achieved a lot in its short time, including developing the Falcon re-usable rocket and the Dragon delivery and re-supply craft. With an even more powerful rocket in development, the Falcon Heavy, it’s fair to say that Musk has a track record of delivering on ambitious projects.
Musk’s announcement, at the Code Conference 2016 in Los Angeles, is definitely exciting news. It comes on the heels of an announcement earlier this spring stating that SpaceX will send a Dragon capsule to Mars in 2018, albeit one with no personnel on board. Musk founded SpaceX in 2002 with the goal of advancing the technologies required to establish a human colony on Mars, so everything seems to be going according to plan.
But a colony needs supplies, and with that in mind Musk also announced the intention of sending a craft to Mars every two years, in order to establish a supply line.
“The basic game plan is we’re going to send a mission to Mars with every Mars opportunity from 2018 onwards,” Musk said Wednesday night. “They occur approximately every 26 months. We’re establishing cargo flights to Mars that people can count on for cargo.”
“That’s what’s necessary to create a self-sustaining, or a growing, city on Mars,” he added.
Of course, there’s lots of work to be done yet. Currently, there is no rocket powerful enough for a mission like this. The most powerful rocket ever built was the Saturn V, used to get the Apollo mission to the Moon. That was 50 years ago.

NASA’s Space Launch System will have the power for a Mars mission, but that’s a ways away, and they probably won’t be giving SpaceX one. SpaceX has developed the Falcon rocket, and are working on the Falcon Heavy, but it won’t be enough to establish and maintain a presence on Mars. Still, this obstacle is anything but insurmountable, even though there has been no announcement on the building of this required rocket.
This whole endeavour will be enormously expensive, of course. But with a growing customer base for SpaceX, including the US military, NASA, and commercial communications customers, it seems like the money will be there.
As for the timeline, Musk acknowledges that it is a fairly aggressive one. “When I cite a schedule, it’s actually a schedule I think is true,” Musk said. “It’s not some fake schedule I don’t think is true. I may be delusional. That is entirely possible, and maybe it’s happened from time to time, but it’s never some knowingly fake deadline ever.”
The announcement itself sounds so simple. But Musk knows, as does everyone else involved in planning these kinds of missions, that there is an enormous amount of complex detail behind it all. The food required, the energy needed, and all of the other things that a sustained human presence on Mars will require in order to succeed, are all waiting to be addressed. Musk plans to address some of these details in September at the International Astronautical Congress in Guadalajara, Mexico.

Musk generates a lot of headlines when he makes these announcements. That’s as it should be. But there are other plans to reach Mars, too.
NASA is planning to get to Mars, but they’re going about it differently. They plan on using their SLS and the Orion to explore what’s called cis-lunar space, near the Moon, to test deep space operations, life support systems, solar-electric thrusters, and habitats. All of this activity could start as soon as 2021, and would support an eventual round-trip mission to Mars in the 2030s.
For a long time, it seemed that a mission to Mars was out of reach, off the table, and nobody was really talking about it. Now, we have two separate programs aiming toward an eventual mission to Mars.
Could this be the new space race? But instead of capitalism versus communism, as in the original space race, it’s government versus private?
In the end, it won’t really matter. We just want someone to get there. And we want an established presence. A colony.
Our survival may depend on it.