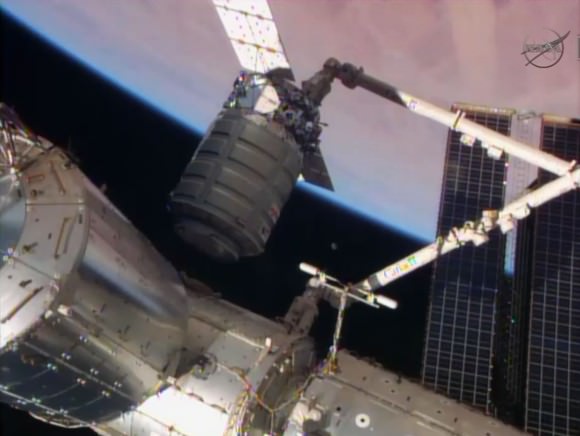
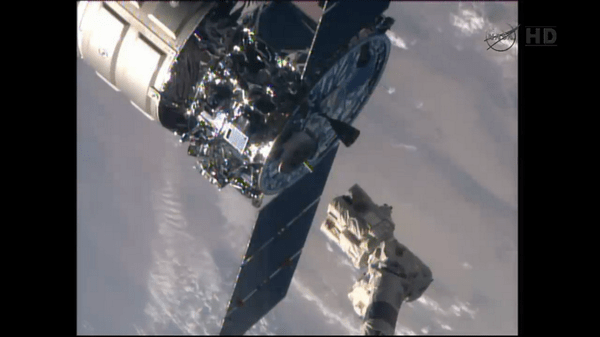
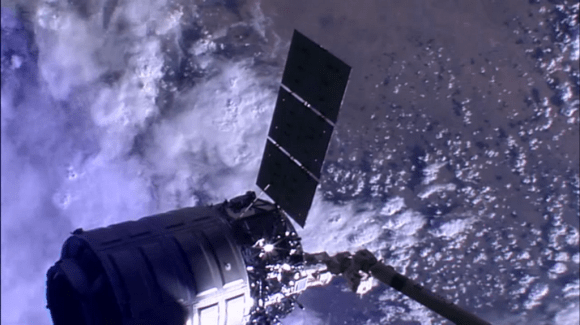
The Cygnus commercial cargo ship ‘Janice Voss’ built by Orbital Sciences finished it’s month-long resupply mission and bid farewell to the International Space Station (ISS) this morning, Friday, Aug. 15, after station astronauts released the vessel from the snares of the Canadarm2 robotic arm at 6:40 a.m. EDT.
The on time release and departure took place as the massive orbiting lab complex was soaring 260 miles (400 km) above the west coast of Africa over the coastline of Namibia.
Expedition 40 Flight Engineer and ESA astronaut Alexander Gerst was in charge of commanding the vessels actual release from the snares on the end effector firmly grasping Cygnus at the terminus of the 58-foot (17-meter) long Canadian robotic arm.
Gerst was working at the robotics work station inside the seven windowed cupola, backed by fellow station crew member and NASA astronaut Reid Wiseman.
About two minutes later, Cygnus fired its thrusters to depart the million pound station and head toward a destructive fiery reentry into the Earth’s atmosphere over the Pacific Ocean on Sunday, Aug. 17.
Ground controllers at Mission Control, Houston had paved the way for Cygnus release earlier this morning when they unberthed the cargo ship from the Earth-facing port of the Harmony module at about 5:14 a.m. EDT.
This mission dubbed Orbital-2, or Orb-2, marks the second of at least eight operational cargo resupply missions to the ISS under Orbital’s Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA.
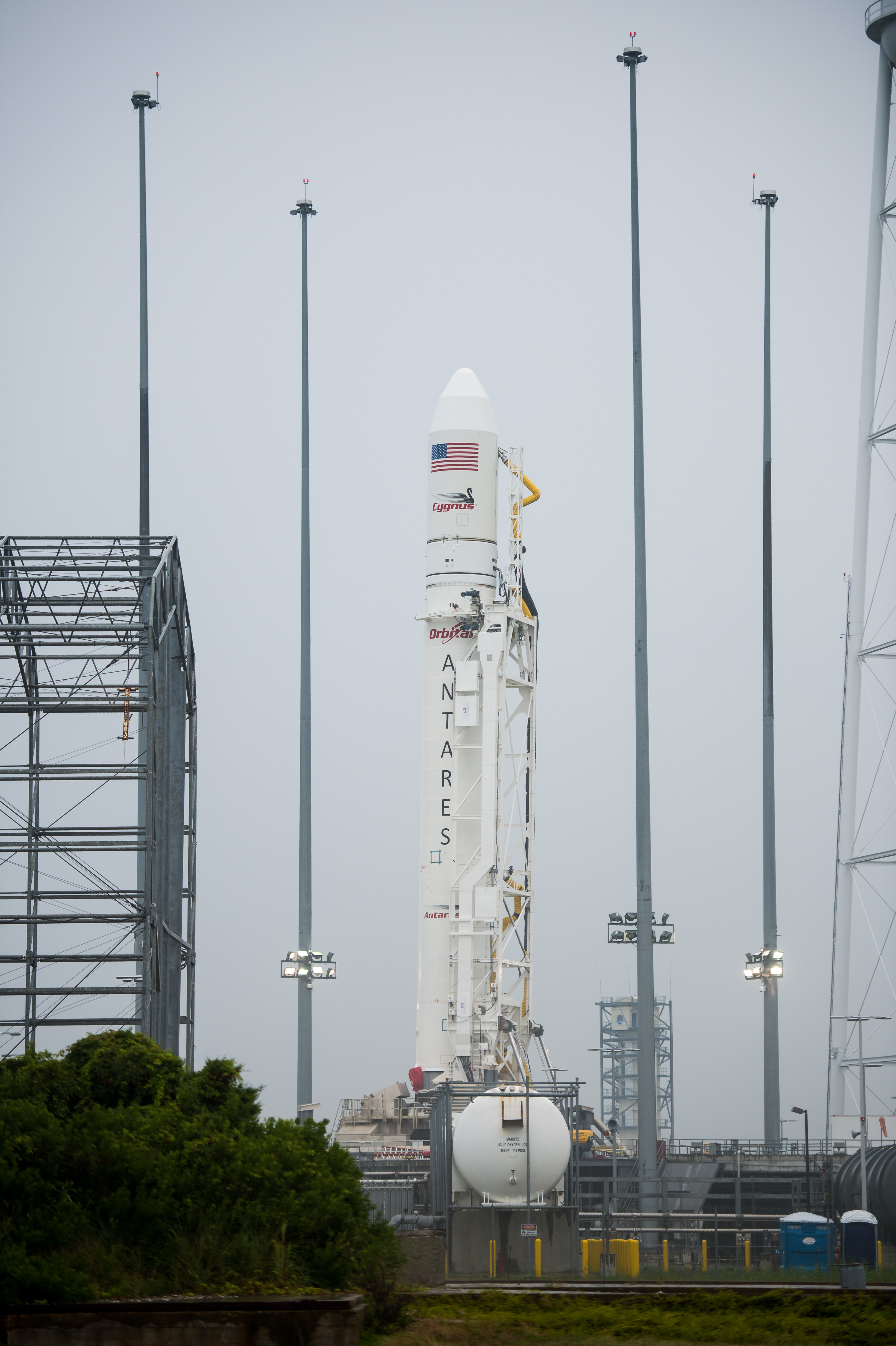
The Cygnus spacecraft was christened “SS Janice Voss” in honor of Janice Voss who flew five shuttle missions during her prolific astronaut carrier, worked for both NASA and Orbital Sciences and passed away in February 2012.

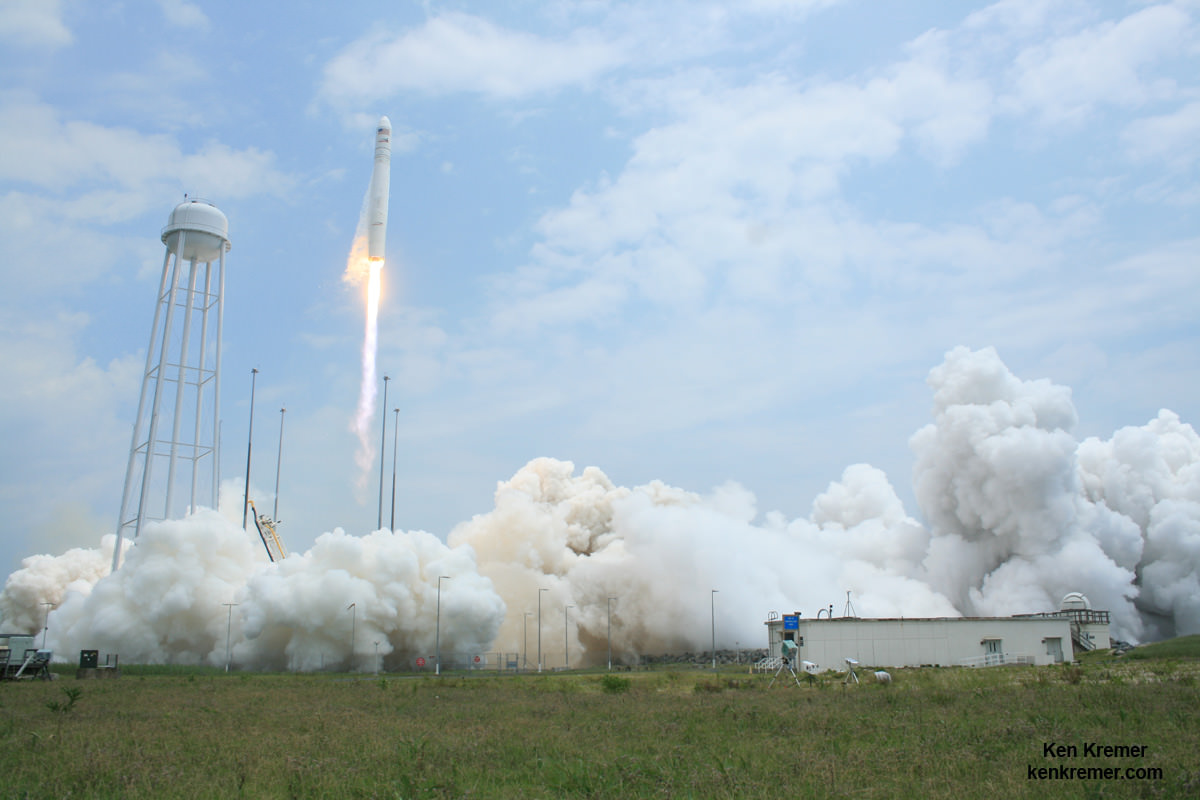
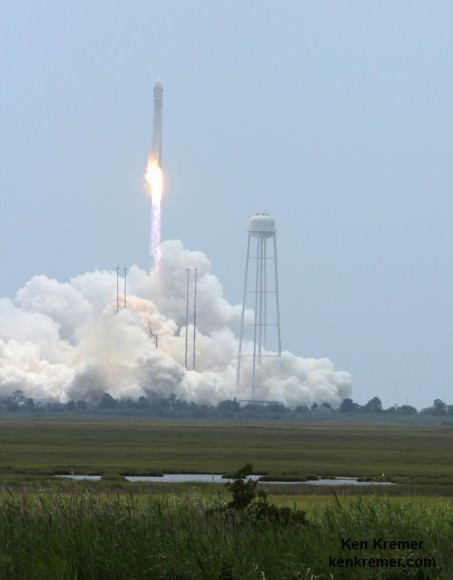
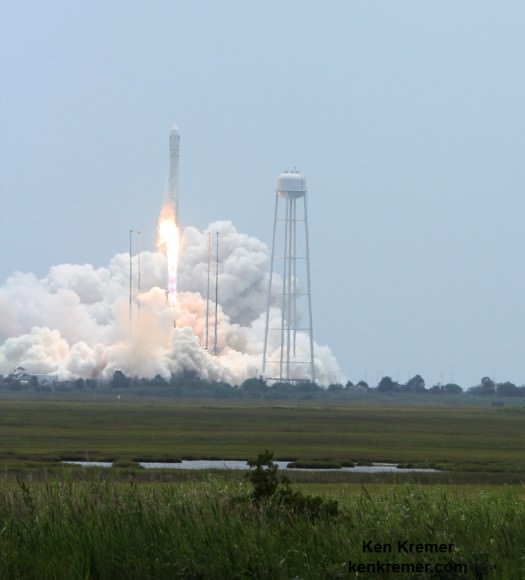
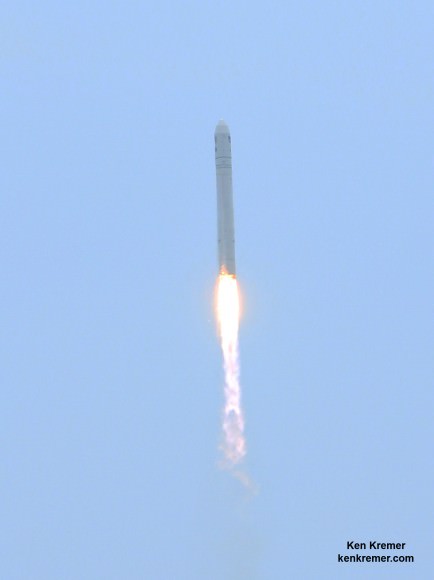
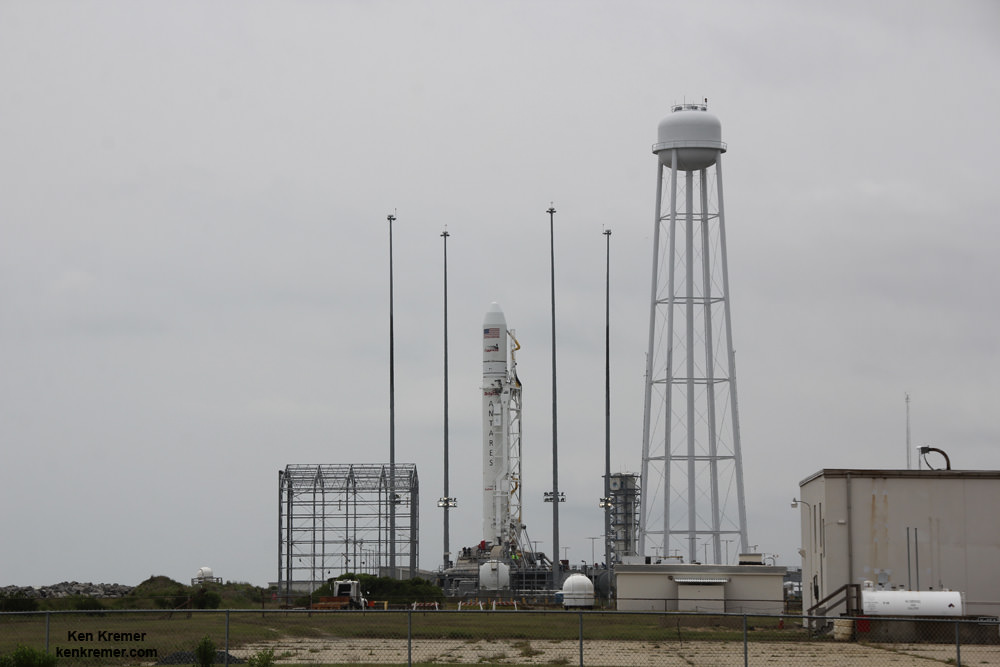
Cygnus roared to orbit during a spectacular blastoff on July 13 atop an Orbital Sciences Corp. Antares rocket on the Orb-2 mission at 12:52 p.m. (EDT) from the beachside Pad 0A at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport on NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility on the Eastern Shore of Virginia.

The US/Italian built pressurized Cygnus cargo freighter delivered 1,657 kg (3653 lbs) of cargo to the ISS Expedition 40 crew including over 700 pounds (300 kg) of science experiments and instruments, crew supplies, food, water, computer equipment, spacewalk tools and student research experiments.
The supplies are critical to keep the station flying and humming with research investigations.
The wide ranging science cargo and experiments includes a flock of 28 Earth imaging nanosatellites and deployers, student science experiments and small cubesat prototypes that may one day fly to Mars.
The “Dove” flock of nanosatellites will be deployed from the Kibo laboratory module’s airlock beginning next week. “They will collect continuous Earth imagery documenting natural and man-made conditions of the environment to improve disaster relief and increase agricultural yields” says NASA.

Cygnus arrived at the station after a three day chase. It was captured in open space on July 16, 2014 at 6:36 a.m. EDT by Commander Steve Swanson working at a robotics workstation in the cupola.
The by the book arrival coincided with the 45th anniversary of the launch of Apollo 11 on July 16, 1969 on America’s first manned moon landing mission by Neil Armstrong, Buzz Aldrin and Michael Collins.
Orbital Sciences was awarded a $1.9 Billion supply contract by NASA to deliver 20,000 kilograms (44,000 pounds) of research experiments, crew provisions, spare parts and hardware for 8 flights to the ISS through 2016 under the Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) initiative.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing ISS, Rosetta, OCO-2, GPM, Curiosity, Opportunity, Orion, SpaceX, Boeing, Orbital Sciences, MAVEN, MOM, Mars and more Earth & Planetary science and human spaceflight news.