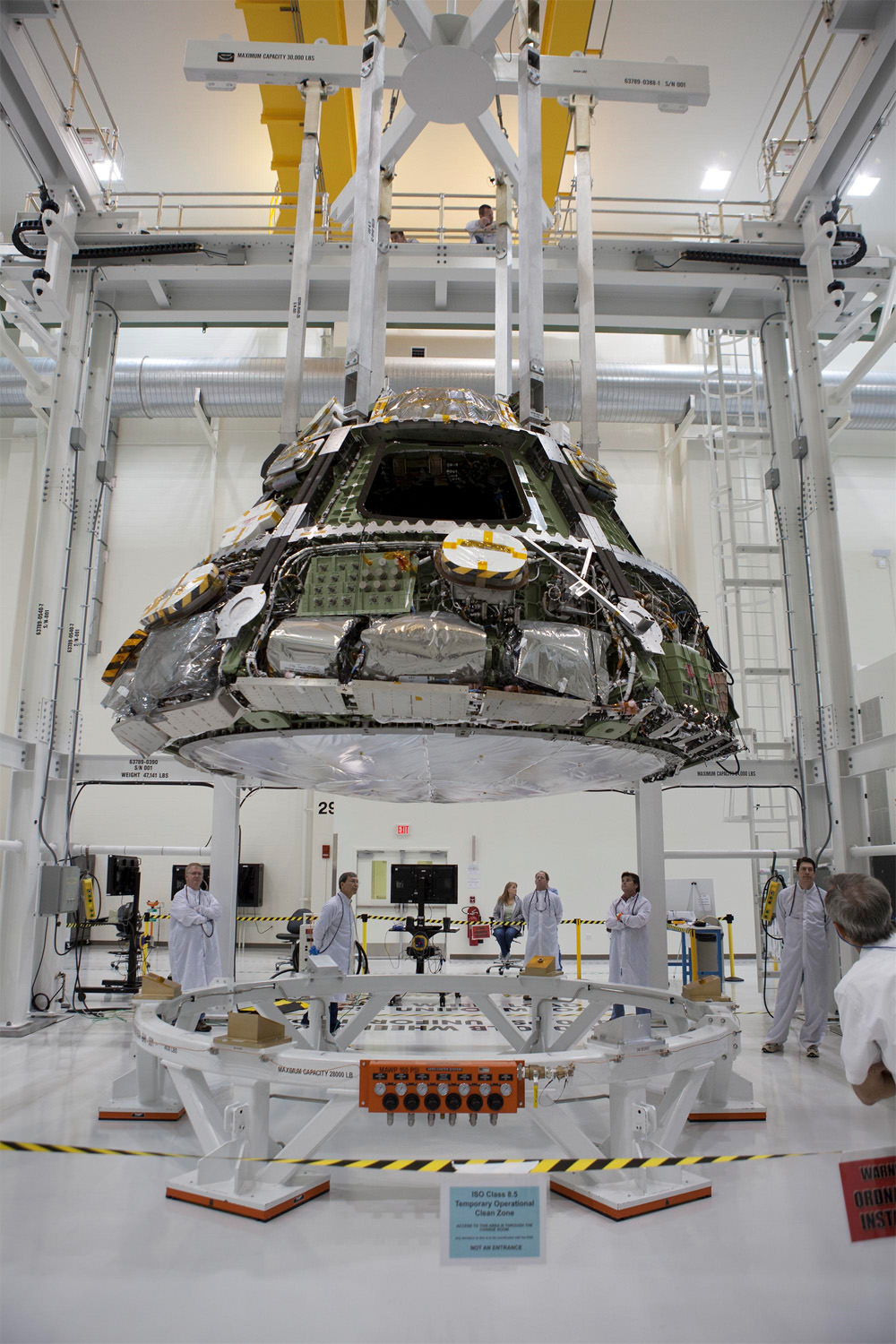
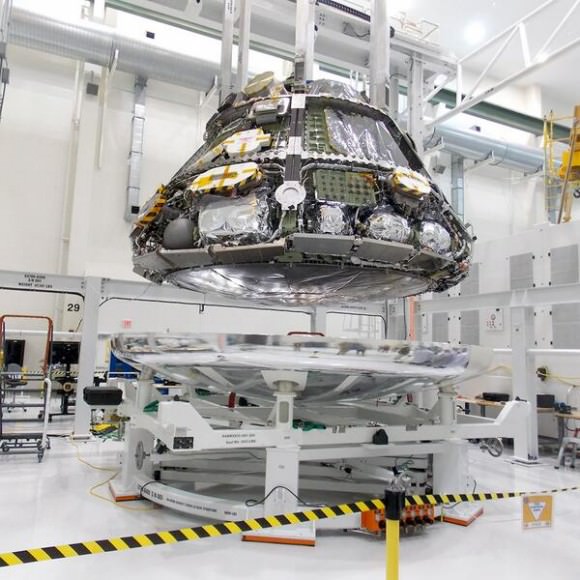
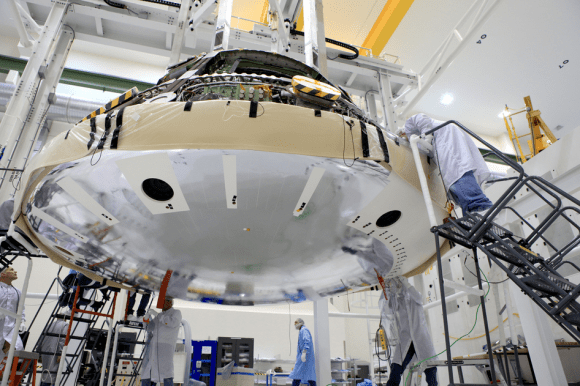
Lockheed Martin and NASA engineers are installing the largest heat shield ever built onto the Orion EFT-1 spacecraft’s crew module at the Kennedy Space Center. Liftoff is slated for late Fall 2014. Credit: Lockheed Martin
Story updated[/caption]
In a key milestone, technicians at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) in Florida have attached the world’s largest heat shield to a pathfinding version of NASA’s Orion crew capsule edging ever closer to its inaugural unmanned test flight later this Fall on a crucial mission dubbed Exploration Flight Test-1 (EFT-1).
One of the primary goals of NASA’s eagerly anticipated Orion EFT-1 uncrewed test flight is to test the efficacy of the heat shield in protecting the vehicle – and future human astronauts – from excruciating temperatures reaching 4000 degrees Fahrenheit (2200 C) during scorching re-entry heating.
A trio of parachutes will then unfurl to slow Orion down for a splashdown in the Pacific Ocean.
Orion is NASA’s next generation human rated vehicle now under development to replace the now retired space shuttle. The state-of-the-art spacecraft will carry America’s astronauts on voyages venturing farther into deep space than ever before – past the Moon to Asteroids, Mars and Beyond!
“The Orion heat shield is the largest of its kind ever built. Its wider than the Apollo and Mars Science Lab heat shields,” Todd Sullivan told Universe Today. Sullivan is the heat shield senior manager at Lockheed Martin, Orion’s prime contractor.
The heat shield measures 16.5 feet (5 m) in diameter.
Lockheed Martin and NASA technicians mated the heat shield to the bottom of the capsule during assembly work inside the Operations and Checkout High Bay facility at KSC.
“Holes were drilled into the heat shield from the inside to the outside at the structural attached points at the underside of the crew module,” said Jules Schneider, Orion Project manager for Lockheed Martin at KSC, during a recent exclusive interview by Universe Today inside the Orion clean room at KSC.
“Then its opened up from the outside and bolted in place underneath. Closeout plugs made of Avcoat are then installed to close it up and seal the gaps,” Schneider explained.
The heat shield is constructed from a single seamless piece of Avcoat ablator, that was applied by engineers at Textron Defense System near Boston, Mass.
“They applied the Avcoat ablater material to the outside. That’s what protects the spacecraft from the heat of reentry,” Sullivan explained.
The ablative material will wear away as it heats up during the capsules atmospheric re-entry thereby preventing the 4000 degree F heat from being transferred to the rest of the capsule and saving it and the human crew from utter destruction.

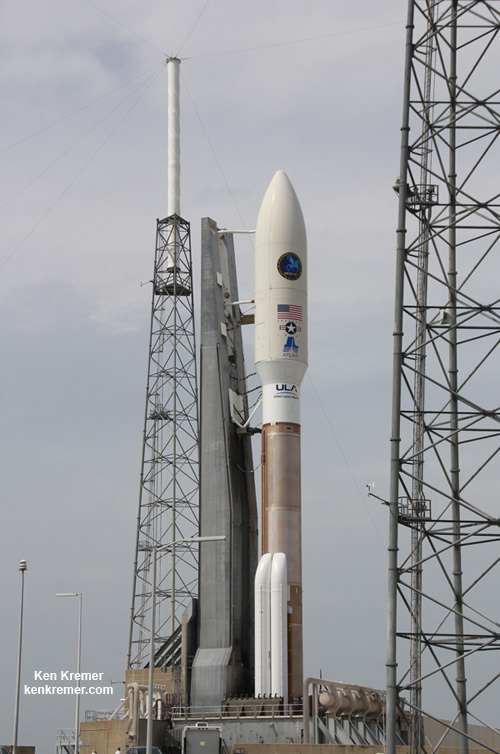
Orion EFT-1 is slated to launch in December 2014 atop the mammoth, triple barreled United Launch Alliance (ULA) Delta IV Heavy rocket, currently the most powerful booster in America’s fleet.
The Delta IV Heavy is the only rocket with sufficient thrust to launch the Orion EFT-1 capsule and its attached upper stage to its intended orbit of 3600 miles altitude above Earth – about 15 times higher than the International Space Station (ISS) and farther than any human spacecraft has journeyed in 40 years.
At the conclusion of the two-orbit, four- hour EFT-1 flight, the detached Orion capsule plunges back and re-enters the Earth’s atmosphere at 20,000 MPH (32,000 kilometers per hour).
“That’s about 80% of the reentry speed experienced by the Apollo capsule after returning from the Apollo moon landing missions,” Scott Wilson, NASA’s Orion Manager of Production Operations at KSC, told me during an interview at KSC.
“The big reason to get to those high speeds during EFT-1 is to be able to test out the thermal protection system, and the heat shield is the biggest part of that.”
“Numerous sensors and instrumentation have been specially installed on the EFT-1 heat shield and the back shell tiles to collect measurements of things like temperatures, pressures and stresses during the extreme conditions of atmospheric reentry,” Wilson explained.
The heat shield arrived at KSC in December 2013 loaded inside NASA’s Super Guppy aircraft while I was onsite. Read my story – here.
The data gathered during the unmanned EFT-1 flight will aid in confirming. or refuting, design decisions and computer models as the program moves forward to the first flight atop NASA’s mammoth SLS booster in late 2017 on the EM-1 mission and more human crewed missions thereafter.

Recently, the EFT-1 launch was postponed three months from its long planned slot in mid-September to December 2014 when NASA was ordered to make way for the accelerated launch of recently declassified US Air Force Space Surveillance satellites that were given a higher priority.
The covert Geosynchronous Space Situational Awareness Program, or GSSAP, satellites were only unveiled in Feb. 2014 during a speech by General William Shelton, commander of the US Air Force Space Command.
Despite the EFT-1 launch postponement, Kennedy Space Center Director Bob Cabana said technicians are pressing forward and continue to work around the clock at KSC in order to still be ready in time to launch by the original launch window that opens in mid- September 2014.
“The contractor teams are working to get the Orion spacecraft done on time for the December 2017 launch,” said Cabana.
“They are working seven days a week in the Operations and Checkout High Bay facility to get the vehicle ready to roll out for the EFT-1 mission and be mounted on top of the Delta IV Heavy.”
“I can assure you the Orion will be ready to go on time, as soon as we get our opportunity to launch that vehicle on its first flight test and that is pretty darn amazing.”
“Our plan is to have the Orion spacecraft ready because we want to get EFT-1 out so we can start getting the hardware in for Exploration Mission-1 (EM-1) and start processing for that vehicle that will launch on the Space Launch System (SLS) rocket in 2017,” Cabana told me
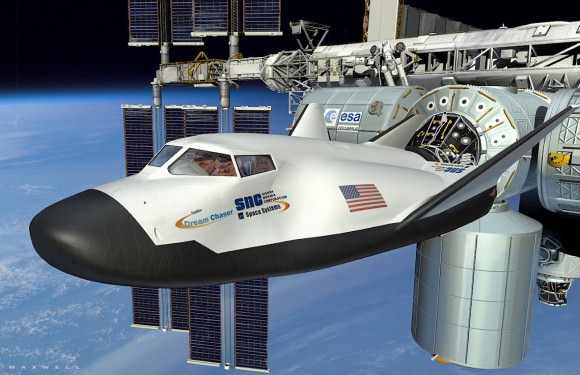
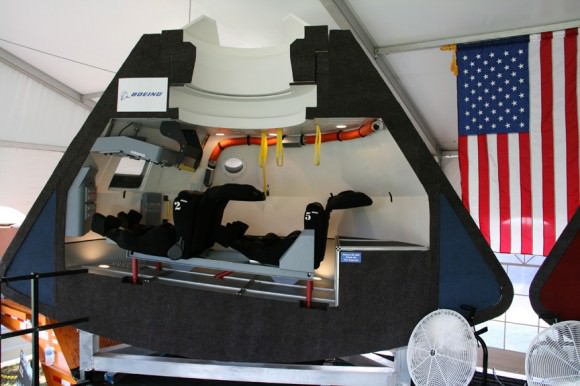
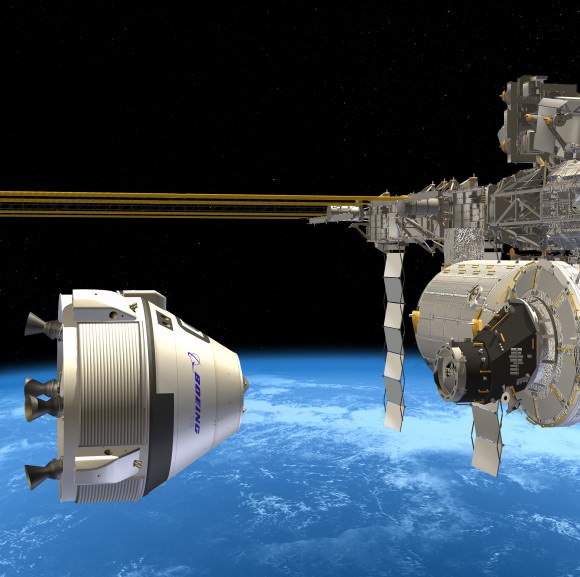
Concurrently, new American-made private crewed spaceships are under development by SpaceX, Boeing and Sierra Nevada – with funding from NASA’s Commercial Crew Program (CCP) – to restore US capability to ferry US astronauts to the International Space Station (ISS) and back to Earth by late 2017.
Read my exclusive new interview with NASA Administrator Charles Bolden explaining the importance of getting Commercial Crew online – here.

Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Orion, Boeing, SpaceX, Orbital Sciences, commercial space, Curiosity, Mars rover, MAVEN, MOM and more planetary and human spaceflight news.
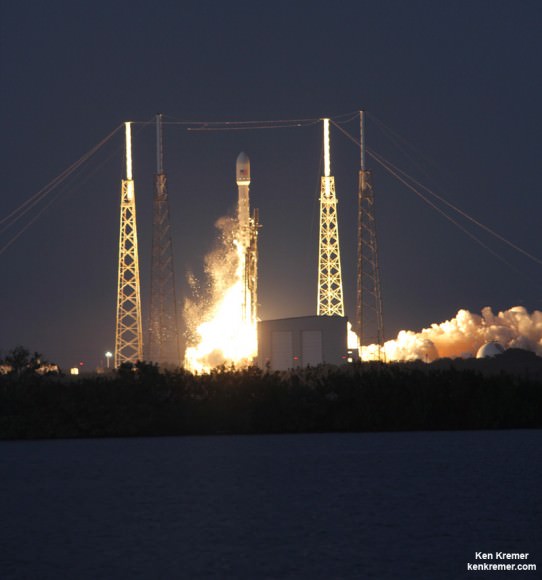
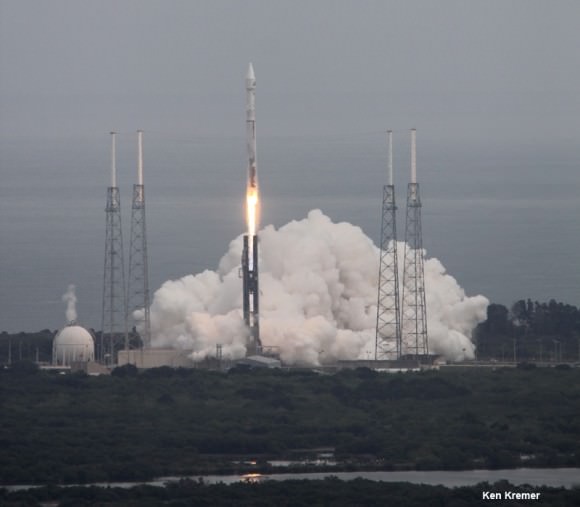
Ken Kremer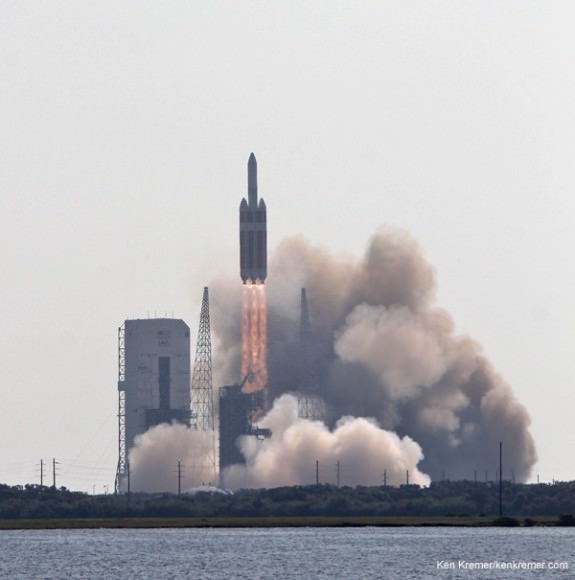 Delta 4 Heavy rocket and super secret US spy satellite roar off Pad 37 on June 29, 2012 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Orion EFT-1 capsule will blastoff atop a similar Delta 4 Heavy Booster in December 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com[/caption]
Delta 4 Heavy rocket and super secret US spy satellite roar off Pad 37 on June 29, 2012 from Cape Canaveral, Florida. NASA’s Orion EFT-1 capsule will blastoff atop a similar Delta 4 Heavy Booster in December 2014. Credit: Ken Kremer- kenkremer.com[/caption]