[/caption]
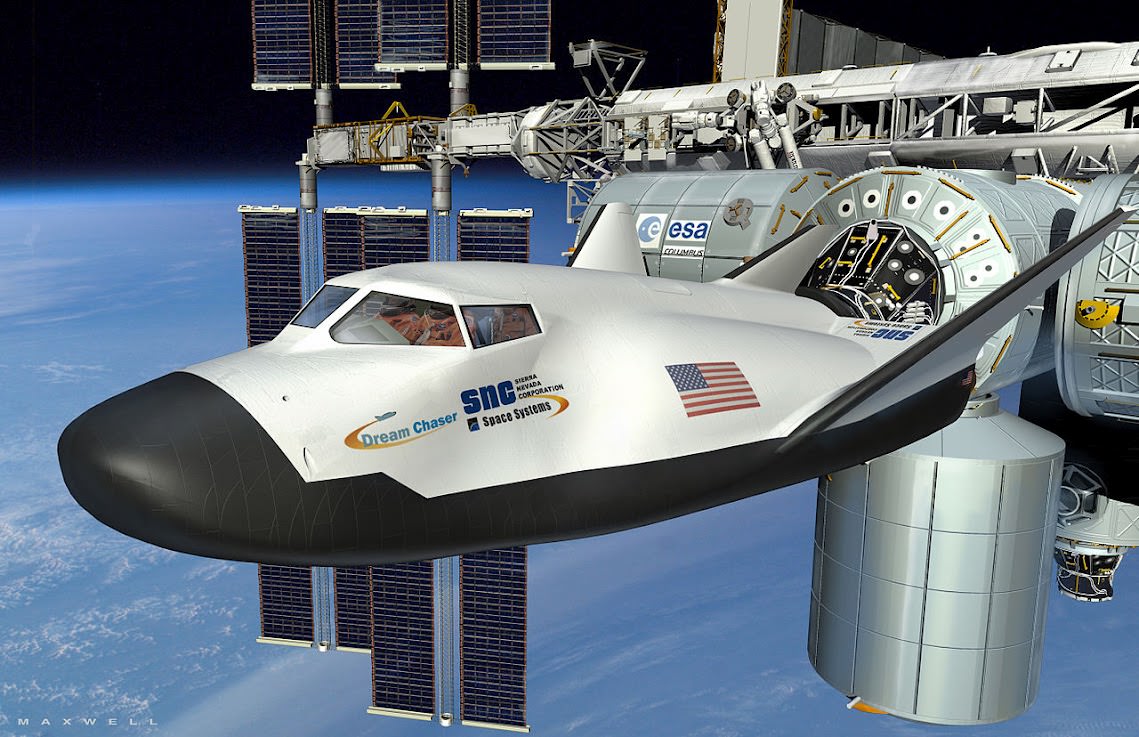
Image Caption: Dream Chaser commercial crew vehicle built by Sierra Nevada Corp docks at ISS
Commercial test pilots, not NASA astronauts, will fly the first crewed missions that NASA hopes will at last restore America’s capability to blast humans to Earth orbit from American soil – perhaps as early as 2015 – which was totally lost following the forced shuttle shutdown.
At a news briefing this week, NASA managers at the Kennedy Space Center (KSC) said the agency is implementing a new way of doing business in human spaceflight and purposely wants private companies to assume the flight risk first with their crews before exposing NASA crews as a revolutionary new flight requirement. Both NASA and the companies strongly emphasized that there will be no shortcuts to flying safe.
A trio of American aerospace firms – Boeing, SpaceX and Sierra Nevada Corp – are leading the charge to develop and launch the new commercially built human-rated spacecraft that will launch Americans to LEO atop American rockets from American bases.
The goal is to ensure the nation has safe, reliable and affordable crew transportation systems for low-Earth orbit (LEO) and International Space Station (ISS) missions around the middle of this decade.
The test launch schedule hinges completely on scarce Federal dollars from NASA for which there is no guarantee in the current tough fiscal environment.
The three companies are working with NASA in a public-private partnership using a combination of NASA seed money and company funds. Each company was awarded contracts under NASA’s Commercial Crew Integrated Capability Initiative, or CCiCap, program, the third in a series of contracts aimed at kick starting the development of the so-called private sector ‘space taxis’ to fly astronauts to and from the ISS.
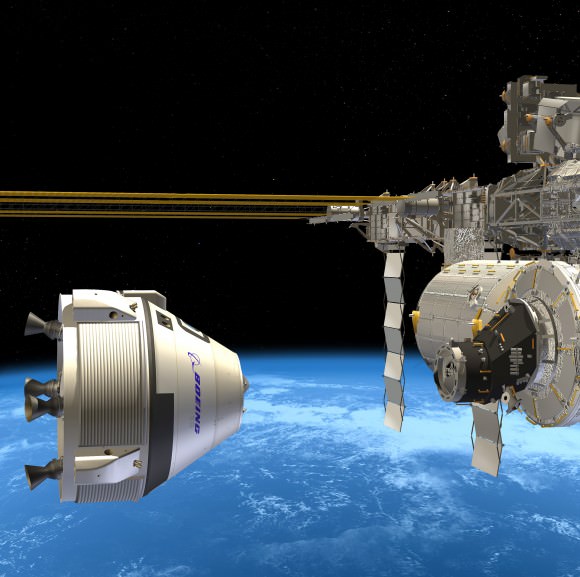
Caption: Boeing CST-100 crew vehicle docks at the ISS
The combined value of NASA’s Phase 1 CCiCap contracts is about $1.1 Billion and runs through March 2014 said Ed Mango, NASA’s Commercial Crew Program manager. Phase 2 contract awards will follow and eventually lead to the actual flight units after a down selection to one or more of the companies, depending on NASA’s approved budget.
Since the premature retirement of NASA’s shuttle fleet in 2011, US astronauts have been 100% reliant on the Russians to hitch a ride to the ISS – at a price tag of over $60 Million per seat. This is taking place while American aerospace workers sit on the unemployment line and American expertise and billions of dollars of hi-tech space hardware rots away or sits idly by with each passing day.
Boeing, SpaceX and Sierra Nevada Corp seek to go where no private company has gone before – to low Earth orbit with their private sector manned spacecraft. And representatives from all three told reporters they are all eager to move forward.
All three commercial vehicles – the Boeing CST-100; SpaceX Dragon and Sierra Nevada Dream Chaser – are designed to carry a crew of up to 7 astronauts and remain docked at the ISS for more than 6 months.
“For well over a year now, since Atlantis [flew the last space shuttle mission], the United States of America no longer has the capability to launch people into space. And that’s something that we are not happy about,” said Garrett Reisman, a former space shuttle astronaut who is now the SpaceX Commercial Crew project manager leading their development effort. “We’re very proud to be part of the group that’s going to do something about that and get Americans back into space.”

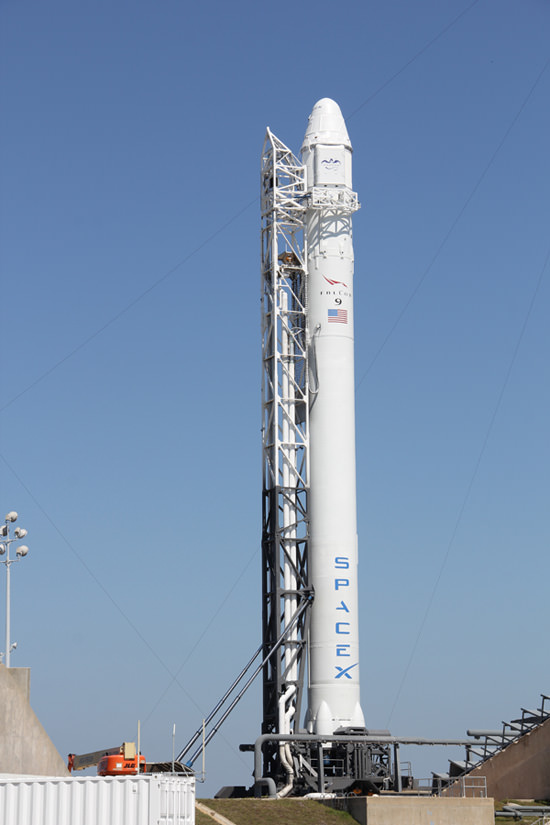
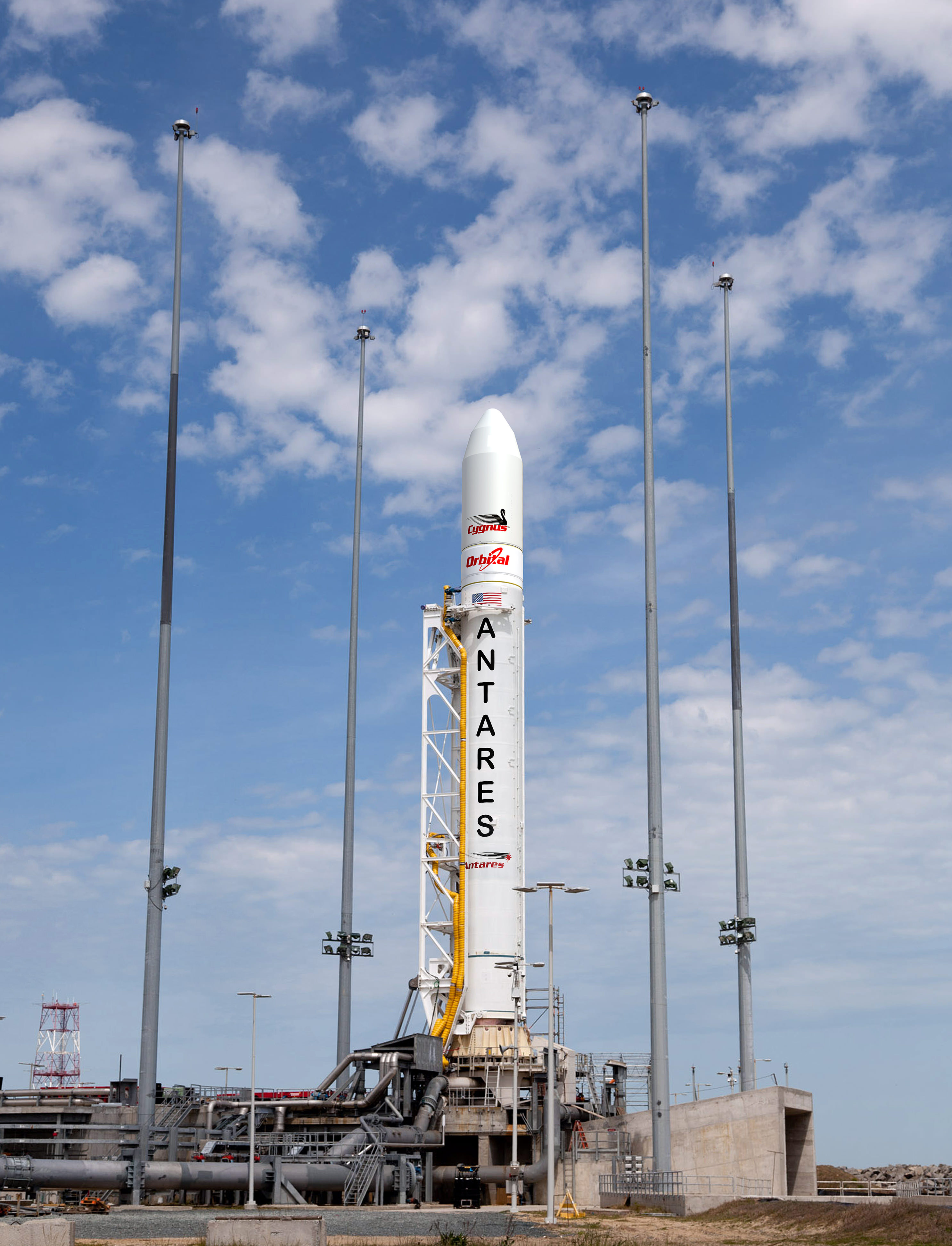
Caption: Blastoff of SpaceX Cargo Dragon atop Falcon 9 from Cape Canaveral, Florida on May, 22, 2012, bound for the ISS. Credit: Ken Kremer
“We are the emotional successors to the shuttle,” said Mark Sirangelo, Sierra Nevada Corp. vice president and SNC Space Systems chairman. “Our target was to repatriate that industry back to the United States, and that’s what we’re doing.”
Sierra Nevada is developing the winged Dream Chaser, a mini-shuttle that launches atop an Atlas V rocket and lands on a runway like the shuttle. Boeing and SpaceX are building capsules that will launch atop Atlas V and Falcon 9 rockets, respectively, and then land by parachute like the Russian Soyuz capsule.
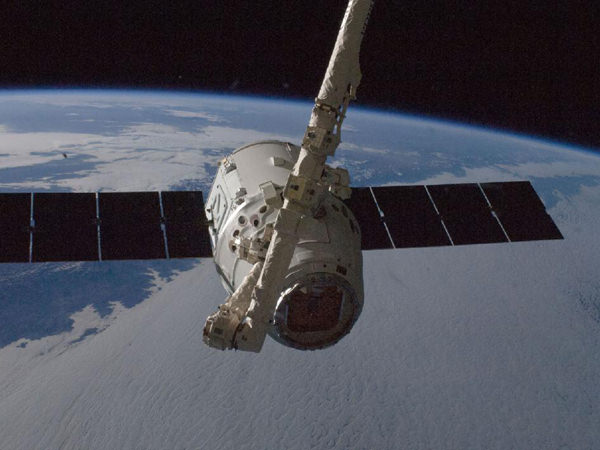
SpaceX appears to be leading the pack using a man-rated version of their Dragon capsule which has already docked twice to the ISS on critical cargo delivery missions during 2012. From the start, the SpaceX Dragon was built to meet the specification ratings requirements for a human crew.

Caption: Dragon spacecraft approaches the International Space Station on May 25, 2012 for grapple and berthing . Photo: NASA
Reisman said the first manned Dragon test flight with SpaceX test pilots could be launched in mid 2015. A flight to the ISS could take place by late 2015. Leading up to that in April 2014, SpaceX is planning to carry out an unmanned in-flight abort test to simulate and test a worst case scenario “at the worst possible moment.”
Boeing is aiming for an initial three day orbital test flight of their CST-100 capsule during 2016, said John Mulholland, the Boeing Commercial Programs Space Exploration vice president and program manager. Mulholland added that Chris Ferguson, the commander of the final shuttle flight by Atlantis, is leading the flight test effort.
Boeing has leased one of NASA’s Orbiter Processing Facility hangers (OPF-3) at KSC. Mulholland told me that Boeing will ‘cut metal’ soon. “Our first piece of flight design hardware will be delivered to KSC and OPF-3 within 5 months.”
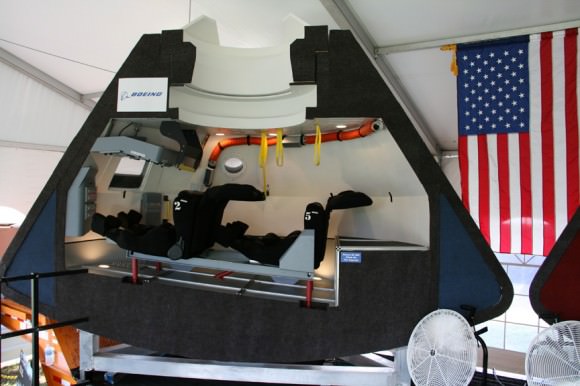
Caption: Boeing CST-100 capsule mock-up, interior view. Credit: Ken Kremer
Sierra Nevada plans to start atmospheric drop tests of an engineering test article of the Dream Chaser from a carrier aircraft in the next few months in an autonomous mode. The test article is a full sized vehicle.
“It’s not outfitted for orbital flight; it is outfitted for atmospheric flight tests,” Sirangelo told me. “The best analogy is it’s very similar to what NASA did in the shuttle program with the Enterprise, creating a vehicle that would allow it to do significant flights whose design then would filter into the final vehicle for orbital flight.”
Now to the issue of using commercial space test pilots in place of NASA astronauts on the initial test flights.
At the briefing, Reisman stated, “We were told that because this would be part of the development and prior to final certification that we were not allowed, legally, to use NASA astronauts to be part of that test pilot crew.”
So I asked NASA’s Ed Mango, “Why are NASA astronauts not allowed on the initial commercial test flights?”
Mango replied that NASA wants to implement the model adopted by the military wherein the commercial company assumes the initial risk before handing the airplanes to the government.
“We would like them to get to a point where they’re ready to put their crew on their vehicle at their risk,” said Mango. “And so it changes the dynamic a little bit. Normally under a contract, the contractor comes forward and says he’s ready to go fly but it’s a NASA individual that’s going to sit on the rocket, so it becomes a NASA risk.
“What we did is we flipped it around under iCAP. It’s not what we’re going to do long term under phase two, but we flipped it around under iCAP and said we want to know when you’re ready to fly your crew and put your people at risk. And that then becomes something that we’re able to evaluate.”
“In the end all our partners want to fly safe. They’re not going to take any shortcuts on flying safe,” he elaborated. “All of us have the same initiative and it doesn’t matter who’s sitting on top of the vehicle. It’s a person, and that person needs to fly safely and get back home to their families. That’s the mission of all our folks and our partners – to go back home and see their family.”
Given the nations fiscal difficulties and lack of bipartisan cooperation there is no guarantee that NASA will receive the budget it needs to keep the commercial crew program on track.
Indeed, the Obama Administrations budget request for commercial crew has been repeatedly slashed by the US Congress to only half the request in the past two years. These huge funding cuts have already forced a multi-year delay in the inaugural test flights and increased the time span that the US has no choice but to pay Russia to launch US astronauts to the ISS.
“The budget is going to be an extremely challenging topic, not only for this program but for all NASA programs,” said Phil McAlister, NASA Commercial Spaceflight Development director.
NASA is pursuing a dual track approach in reviving NASA’s human spaceflight program. The much larger Orion crew capsule is simultaneously being developed to launch atop the new SLS super rocket and carry astronauts back to the Moon by 2021 and then farther into deep space to Asteroids and one day hopefully Mars.
Ken Kremer
![Dream_Chaser_Atlas_V_Integrated_Launch_Configuration[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/Dream_Chaser_Atlas_V_Integrated_Launch_Configuration1-315x580.jpg)
Caption: Dream Chaser awaits launch atop Atlas V rocket
























![Dream_Chaser_Atlas_V_Integrated_Launch_Configuration[1]](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2013/01/Dream_Chaser_Atlas_V_Integrated_Launch_Configuration1-315x580.jpg)
