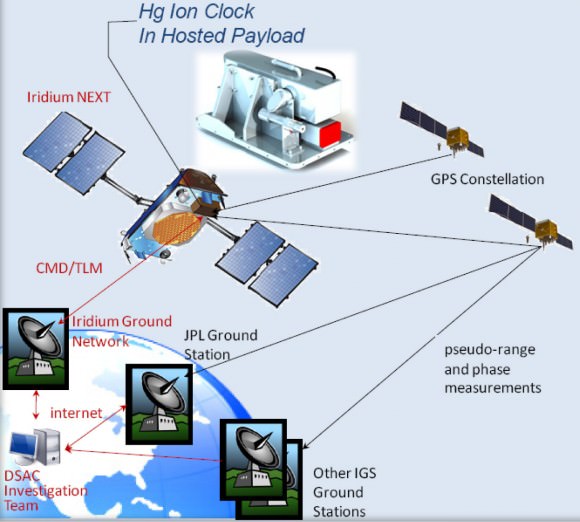
[/caption]
The United States Air Force has entered into a Memorandum of Understanding or MOU with the National Reconnaissance Office (NRO) and NASA to bring more players into the launch vehicle arena. On Oct. 14, NASA, the NRO and the U.S. Air Force announced plans to certify commercial rockets so that they could compete for future contracts involving Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle, or EELVs. This means that Space Exploration Technologies’ (SpaceX) could compete for upcoming military contracts.
“This strategy will provide us with the ability to compete in the largest launch market in the world,” said Kirstin Brost Grantham, a spokeswoman with SpaceX. “There are those who are opposed to competition for space launches, they would prefer to see the status quo protected. But SpaceX has shown it is no longer possible to ignore the benefits competition can bring.”
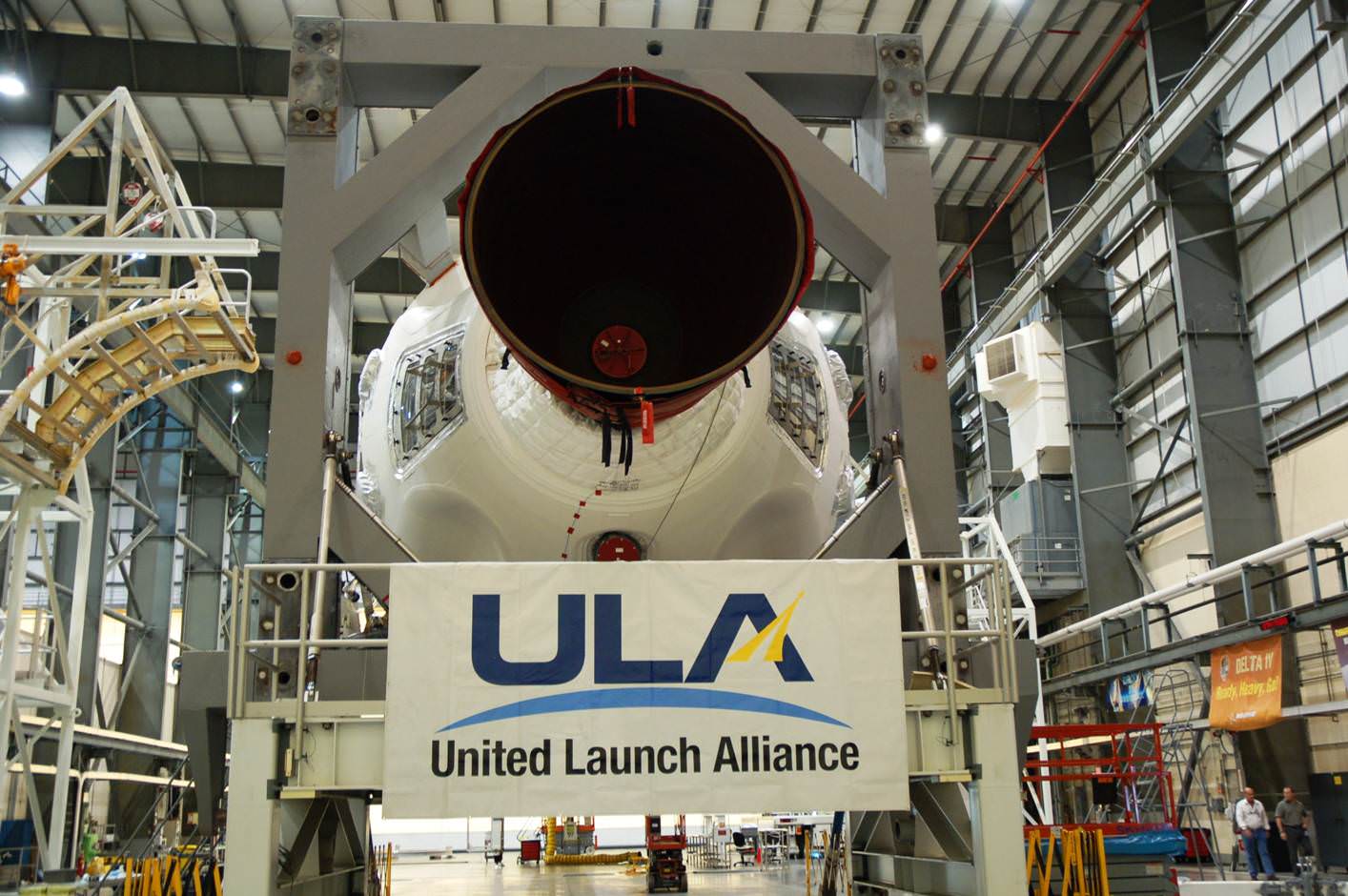
In terms of sheer numbers of launch vehicles purchased – the U.S. Air Force is the largest customer in the world – with the U.S. taxpayer picking up the tab. Therefore it was considered to be in the Air Force’s best interest to find means to reduce this cost. The U.S. Air Force’s requirements are currently handled by United Launch Alliance (ULA) in what is essentially a monopoly (or duopoly considering that ULA is a collective organization – comprised of both Boeing and Lockheed Martin).

“SpaceX welcomes the opportunity to compete for Air Force launches. We are reviewing the MOU, and we expect to have a far better sense of our task after the detailed requirements are released in the coming weeks,” said Adam Harris, SpaceX vice president of government affairs.
The U.S. Department of Defense (DoD) has decided to go ahead with a five-year, 40-booster “block-buy” plan with ULA – despite the fact that the U.S. General Accounting Office’s (GAO) has requested that the DoD rethink that strategy. The GAO stated on Oct. 17, that they are concerned that the DoD is buying too many rockets and at too high of a price.
Under the Evolved Expendable Launch Vehicle Plan, the DoD is set to spend some $15 billion between 2013 and 2017 to acquire some 40 boosters from ULA to send satellites into orbit. For its part, the DoD conceded that it might need to reassess the manner in which it obtained launch vehicles.

The new strategy which is set to allow new participants in to bid on DoD and NRO contracts is an attempt to allow the free-market system drive down the cost of rockets. Recently, the price of these rockets has actually increased. The cause for this price increase has been somewhat attributed to the vacuum created by the end of the space shuttle program.
Firms like SpaceX, which seek to compete for military contracts, will have to meet requirements that are laid out in “new entrant certification guides.”
“Fair and open competition for commercial launch providers is an essential element of protecting taxpayer dollars,” said Elon Musk, SpaceX CEO. “Our American-made Falcon vehicles can deliver assured, responsive access to space that will meet warfighter needs while reducing costs for our military customers.”