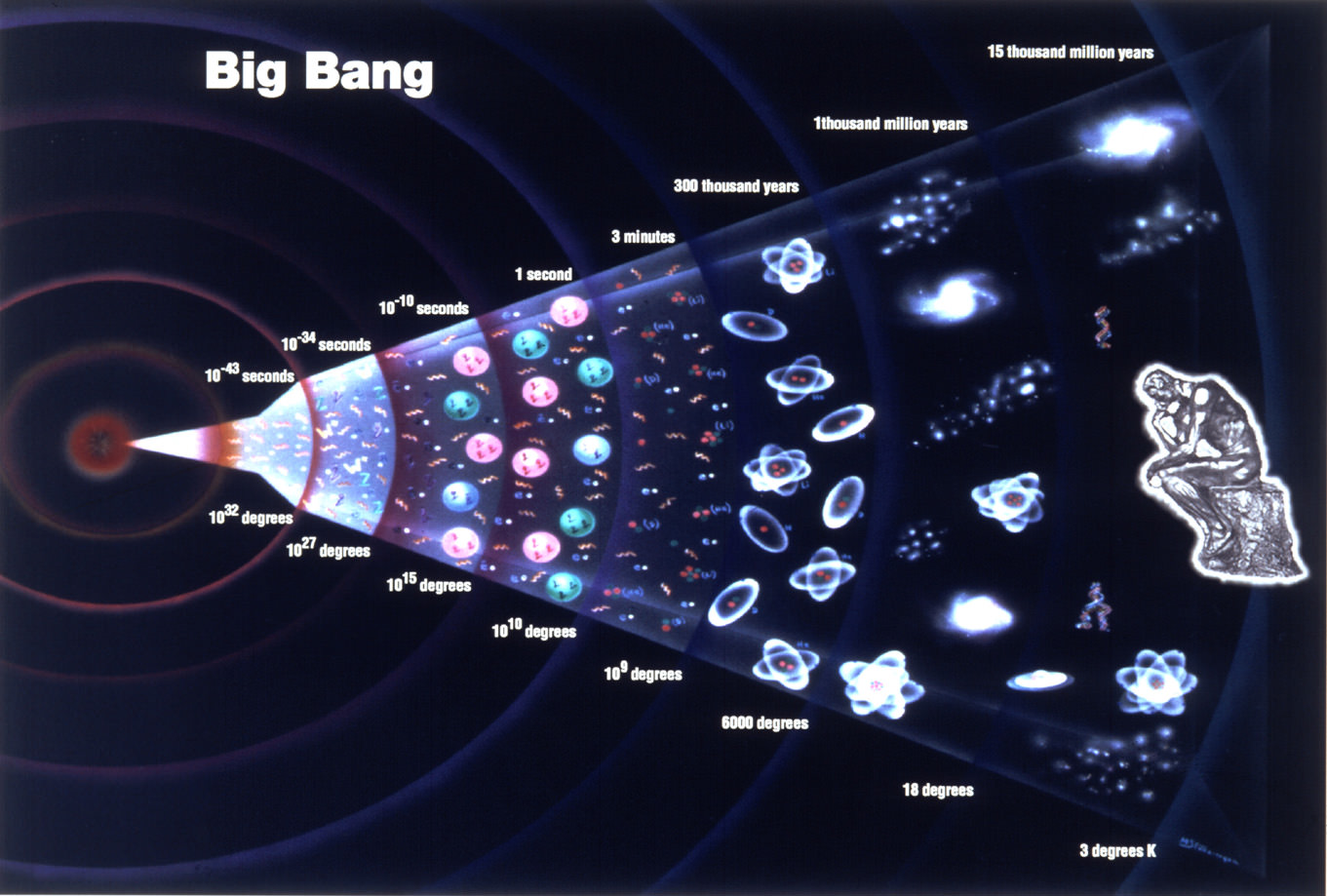
When it comes to our cosmic origins, a number of theories have been advanced throughout the course of history. Literally every culture that’s ever existed has had its own mythological tradition, which naturally included a creation story. With the birth of the scientific tradition, scientists began to understand the Universe in terms of physical laws that could be tested and proven.
With the dawn of the Space Age, scientists began testing cosmological theories in terms of observable phenomena. From all of this, a number of theories emerged by the latter half of the 20th century that attempted to explain how all matter and the physical laws governing it came to be. Of these, the Big Bang Theory remains the most widely accepted while the Steady-State Hypothesis has historically been its greatest challenger.
Continue reading “What is the Steady State Hypothesis?”