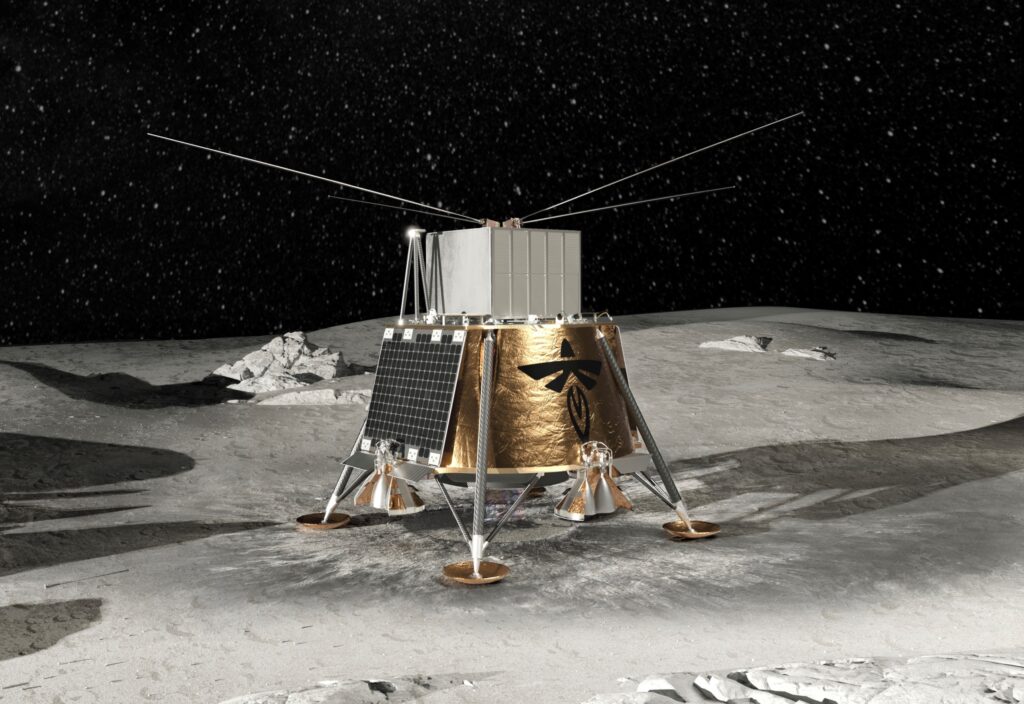
The Moon will be a popular destination for space programs worldwide in the coming years. By 2025, NASA’s Artemis III mission will land the first astronauts (“the first woman and first person of color”) onto the lunar surface for the first time since the end of the Apollo Era, over fifty years ago. They will be joined by multiple space agencies, as per the Artemis Accords, that will send European, Canadian, Japanese, and astronauts of other nationalities to the lunar surface. These will be followed in short order by taikonauts (China), cosmonauts (Russia), and vyomanauts (India), who will conduct similarly lucrative research and exploration.
Having facilities in orbit of the Moon, like the Artemis Base Camp, the International Lunar Research Station, and others, will enable all manner of scientific research that is not possible on Earth or in Earth orbit. This includes radio astronomy, which would be free of terrestrial interference on the far side of the Moon and sensitive enough to detect light from previously unexplored cosmological periods. This is the purpose of a pathfinder project known as the Lunar Surface Electromagnetics Experiment-Night (LuSEE-Night) that will leave for the Moon next year and spend the next 18 months listening to the cosmos!
Continue reading “Astronomers are Working to Put a Radio Telescope on the Far Side of the Moon by 2025”