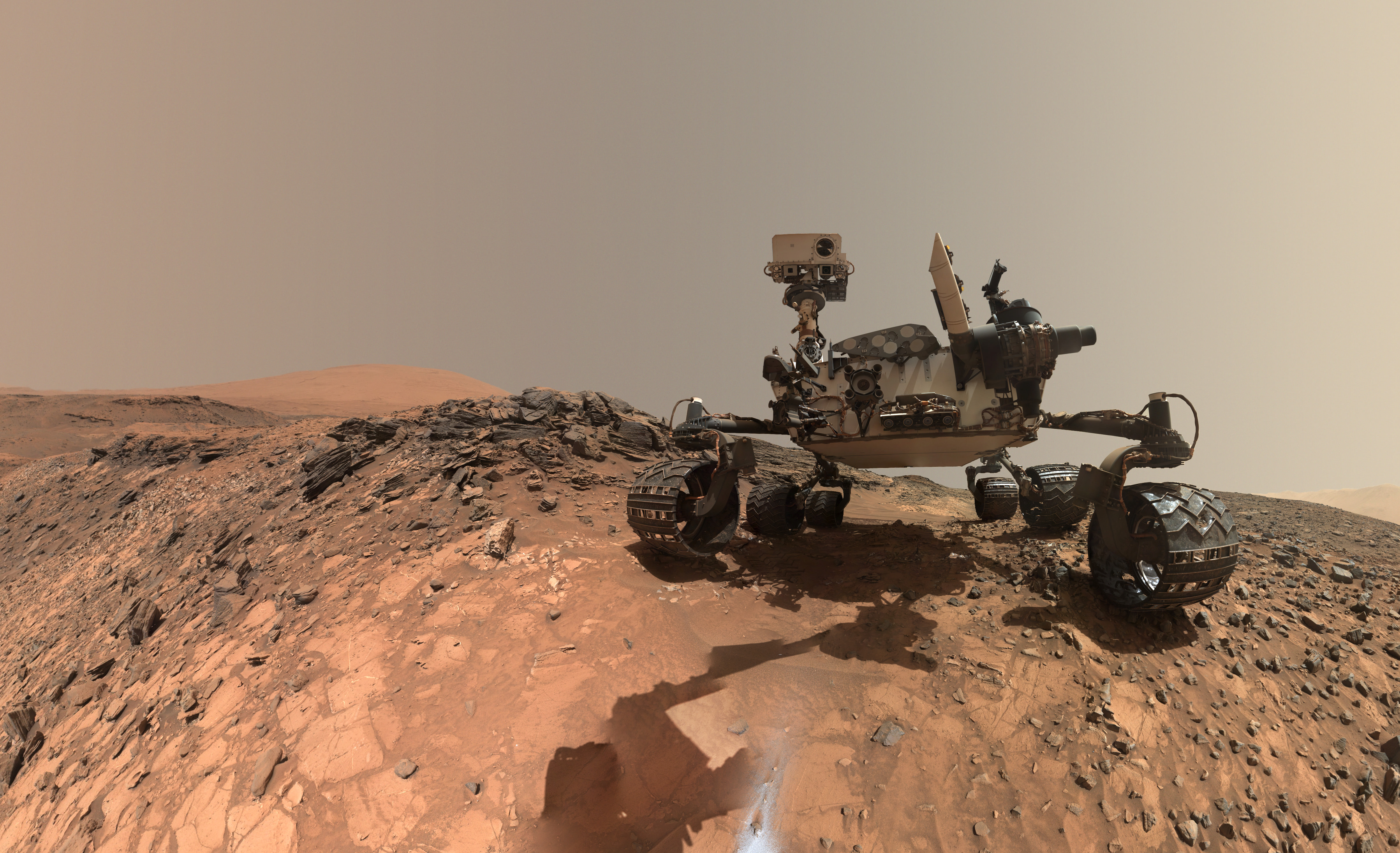
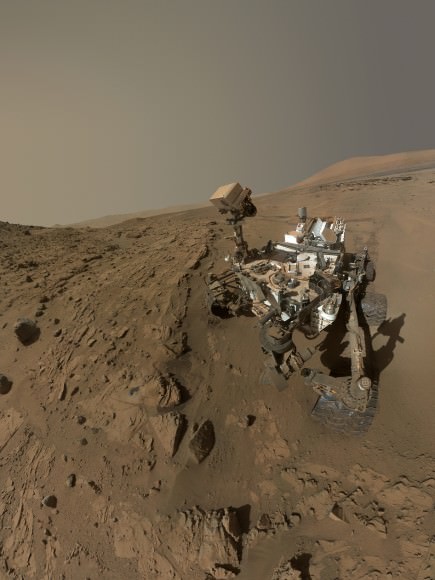
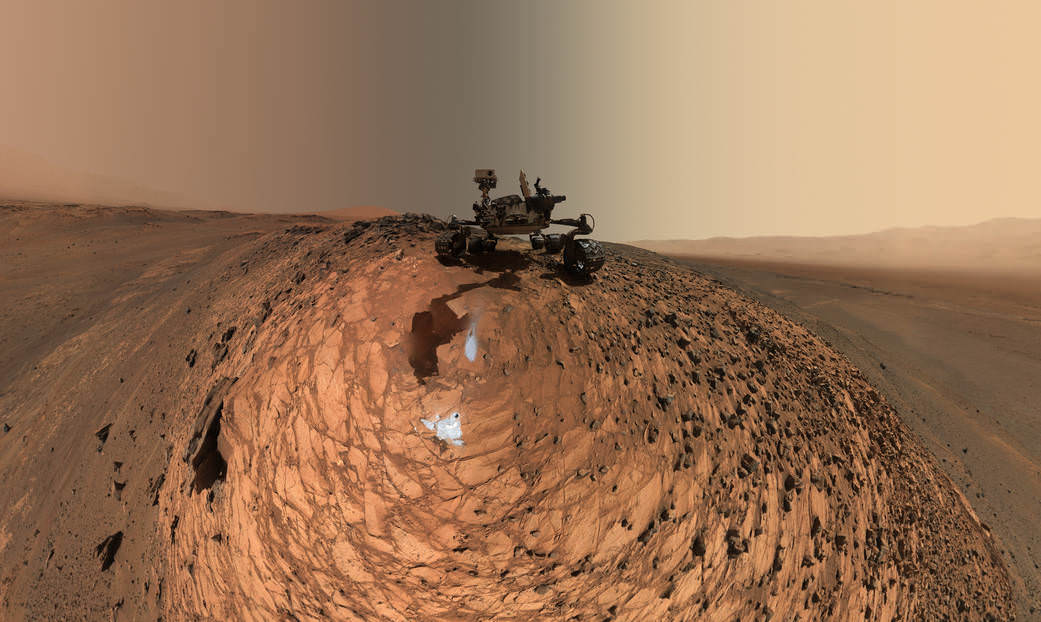
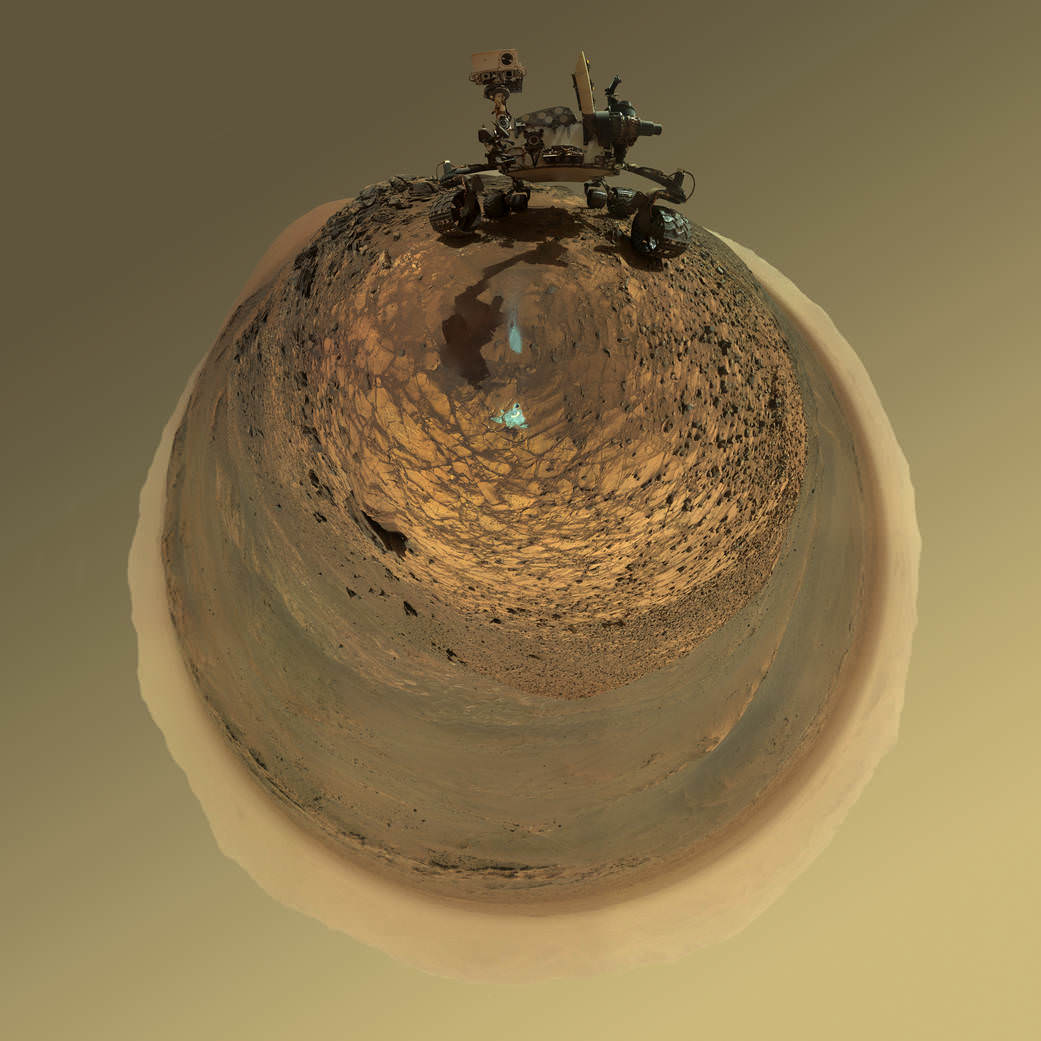
This low-angle self-portrait of NASA’s Curiosity Mars rover shows the vehicle at the site from which it reached down to drill into a rock target called “Buckskin.” The MAHLI camera on Curiosity’s robotic arm took multiple images on Aug. 5, 2015, that were stitched together into this selfie. Credits: NASA/JPL-Caltech/MSSS
More selfie and drilling mosaics below[/caption]
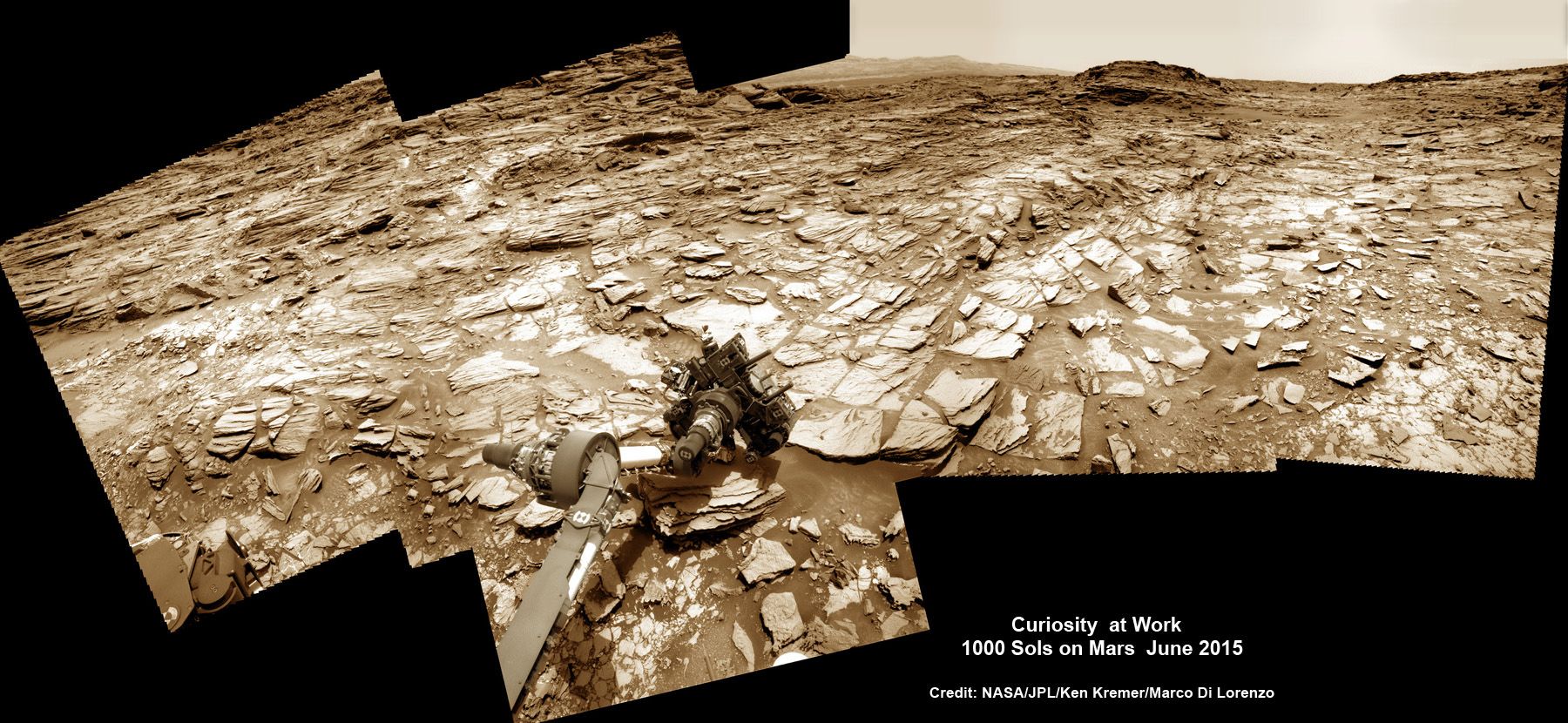
NASA’s Curiosity rover has snapped a stunningly beautiful, one of a kind ‘belly selfie’ amidst the painstaking ‘Buckskin’ drill campaign at the Martian mountain base marking the third anniversary since her touchdown on the Red Planet.
The unique self portrait was taken from a low-angle for the first time and shows the six wheeled rover at work collecting her seventh drilled sample at the ‘Buckskin’ rock target earlier this month in the “Marias Pass” area of lower Mount Sharp.
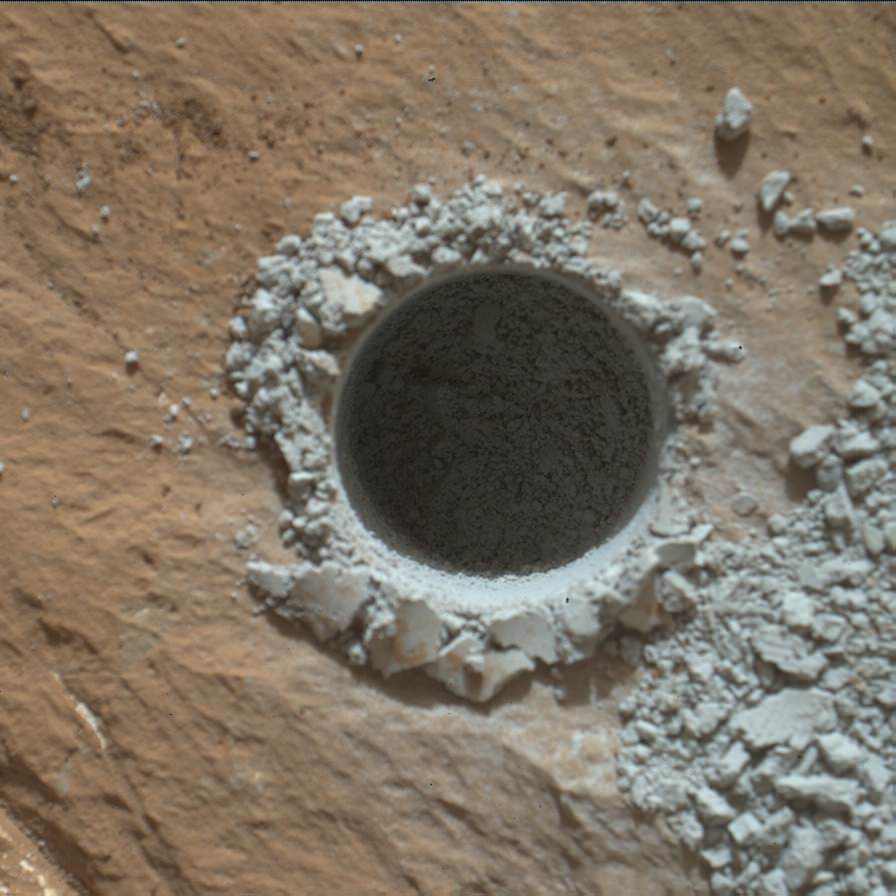
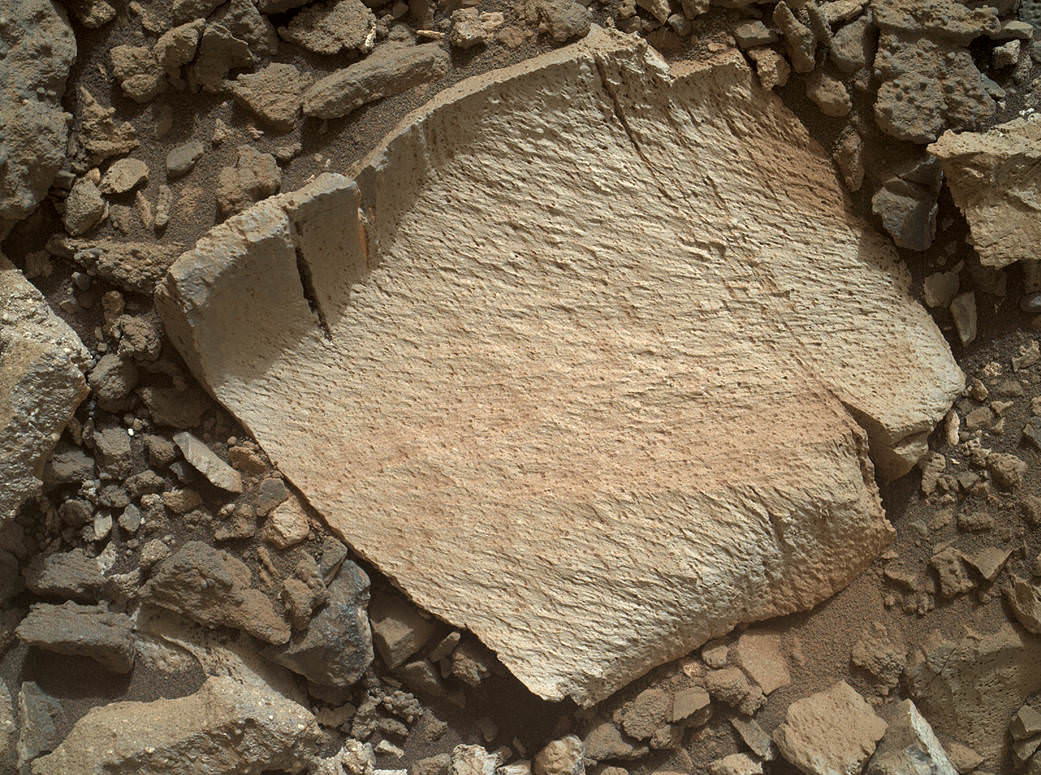
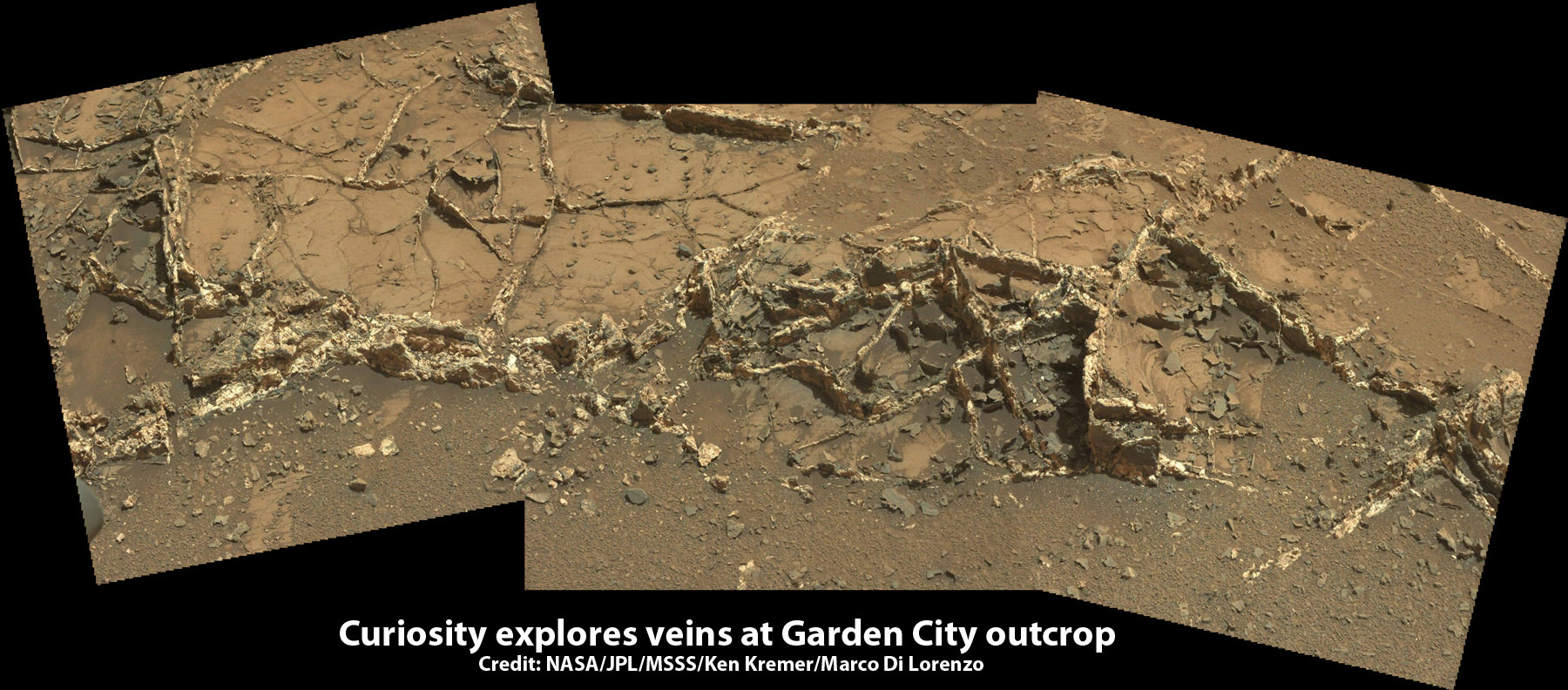
‘Buckskin’ is also unique in a fabulously scientifically way because the rover discovered a new type of Martian rock that’s surprisingly rich in silica – and unlike any other targets found before.
The low camera angle is what enables the awesome Buckskin belly selfie. It’s a distinctively dramatic view and actually stitched from 92 images captured by the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) on Aug. 5, 2015, or Sol 1065 of the mission.
The high resolution MAHLI color camera is located on the end of the 7 foot-long (2.1 meter-long) robotic arm.

Indeed the car-sized rover has taken spectacular selfies several times before during her three year long trek across the Martian surface, since the August 2012 landing inside Mars’ Gale Crater. But for those past selfies the MAHLI camera was hoisted higher to give the perspective of looking somewhat downward and showing the rovers top deck and trio of sample inlet ports.
In this case, the rover team specifically commanded Curiosity to position “the camera lower in relation to the rover body than for any previous full self-portrait of Curiosity,” said NASA officials.
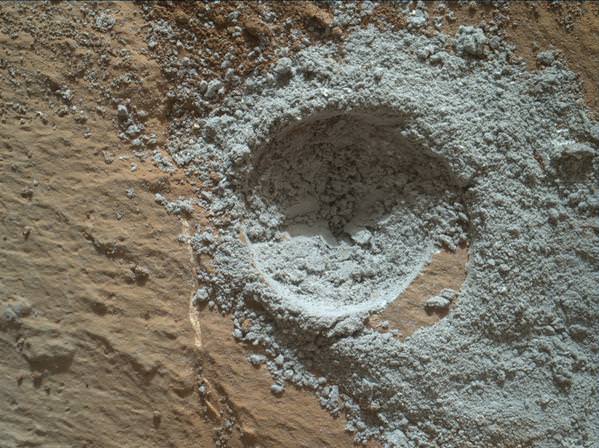
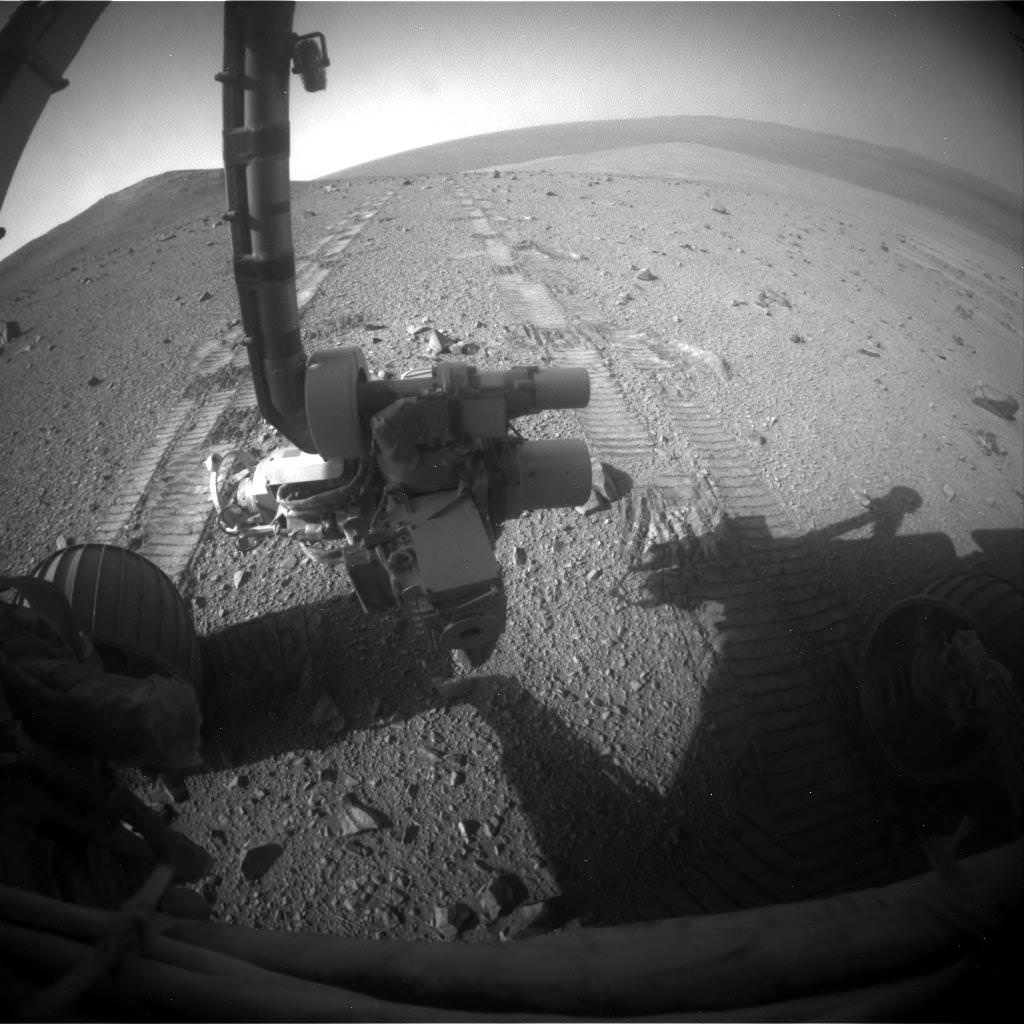
Two patches of gray colored powdered rock material drilled from Buckskin are visible in the selfie scene, in front of the rover.
“The patch closer to the rover is where the sample-handling mechanism on Curiosity’s robotic arm dumped collected material that did not pass through a sieve in the mechanism. Sieved sample material was delivered to laboratory instruments inside the rover. The patch farther in front of the rover, roughly triangular in shape, shows where fresh tailings spread downhill from the drilling process.”
Prior selfies were taken at the “Rocknest” (http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA16468), “John Klein” (http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA16937), “Windjana” (http://photojournal.jpl.nasa.gov/catalog/PIA18390) and “Mojave” drill sites.
Basically in the Sol 1065 belly selfie at “Buckskin” we see the underbelly of the rover and all six wheels along with a complete self portrait.
On several prior occasions, MAHLI was used to image just the underbelly and wheels to aid in inspecting the wheels to look for signs of damage inflicted by sharp-edged Martian rocks poking holes in the aluminum wheels.
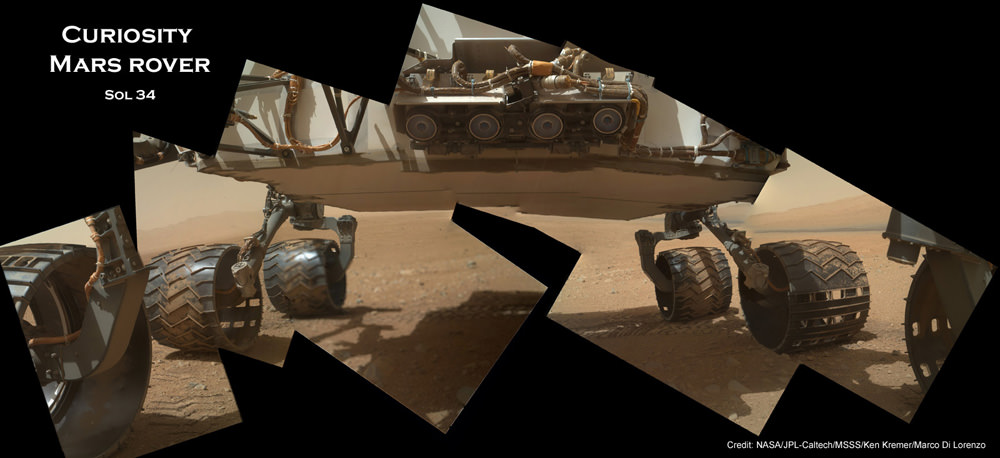

Each wheel measures 20 inches (50 centimeters) in diameter and about 16 inches (40 centimeters) wide. And the MAHLI monitoring images have shown the effects of increasing wear and tear that ultimately forced the rover drivers to alter Curiosity’s driving route on the crater floor in favor of smoother and less rocky terrain imparting less damage to the critical wheels.
If you take a close look at the new selfie up top, you’ll see a small rock stuck onto Curiosity’s left middle wheel (on the right in this head-on view). The rock was seen also in prior wheel monitoring images taken three weeks ago.
“The selfie at Buckskin does not include the rover’s robotic arm beyond a portion of the upper arm held nearly vertical from the shoulder joint. With the wrist motions and turret rotations used in pointing the camera for the component images, the arm was positioned out of the shot in the frames or portions of frames used in this mosaic,” according to officials.
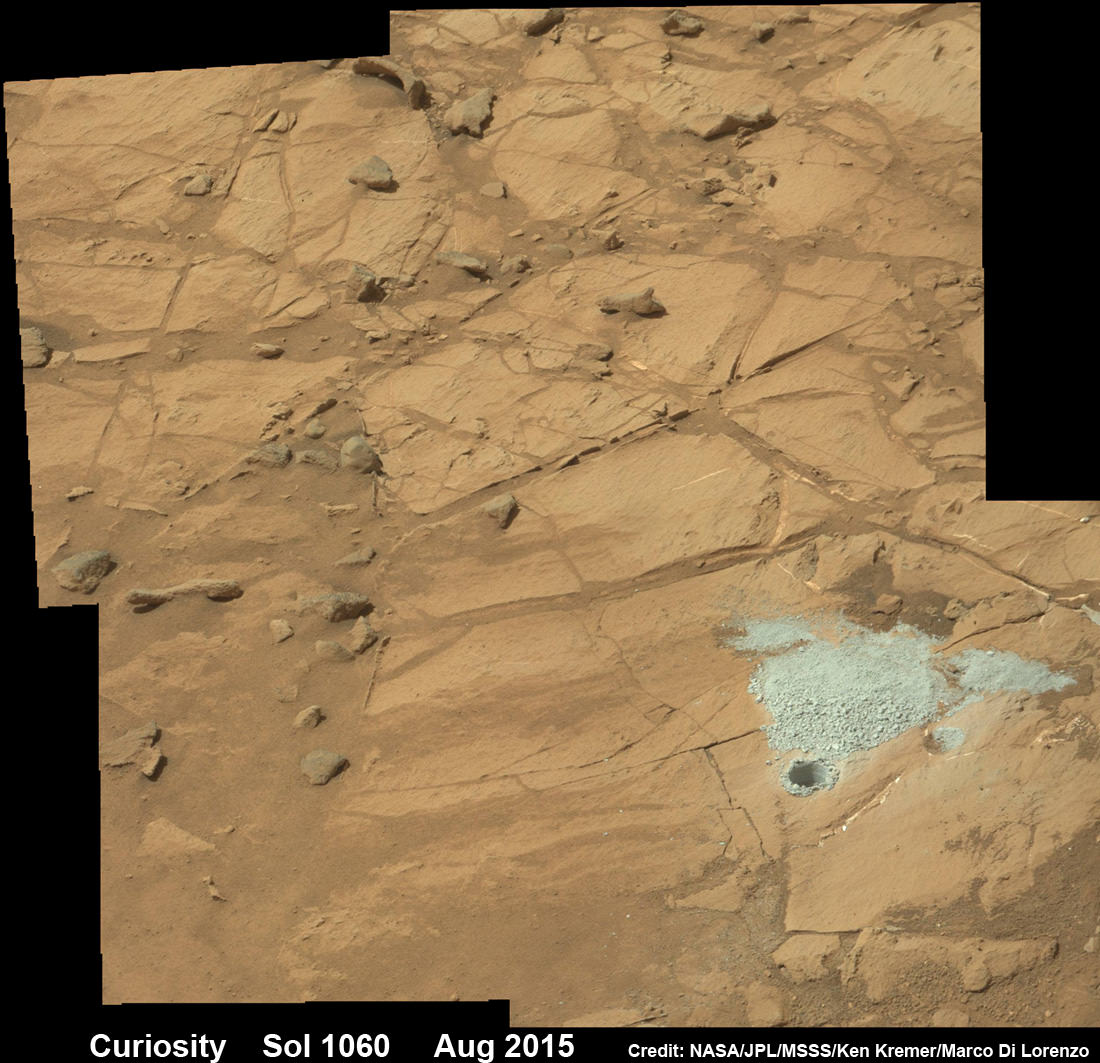
The drilling campaign into “Buckskin” was successfully conducted on Sol 1060 (July 30, 2015) at the bright toned “Lion” outcrop to a full depth of about 2.6 inches (6.5 centimeters) and approximately 1.6 cm (0.63 inch) diameter.

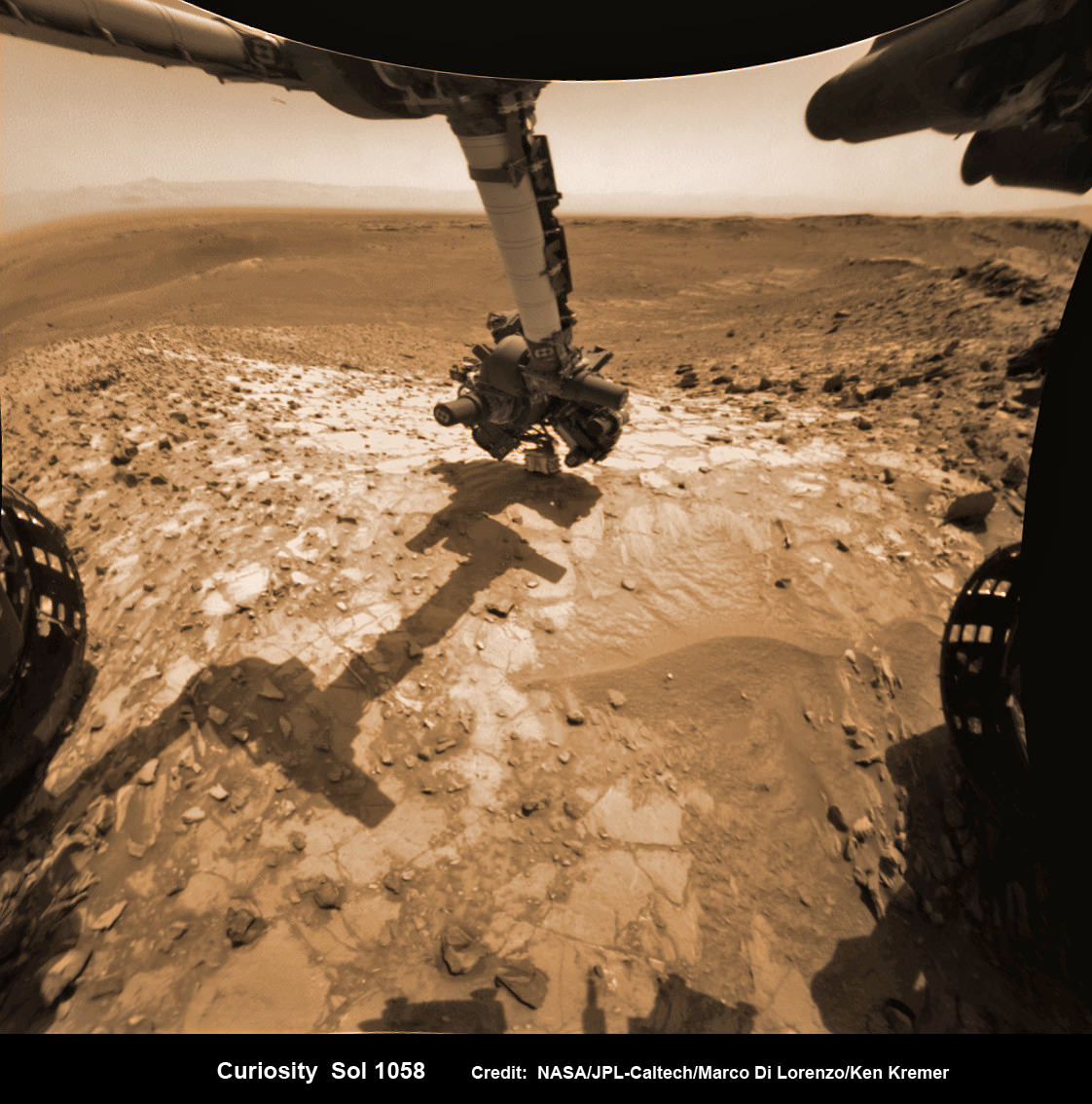
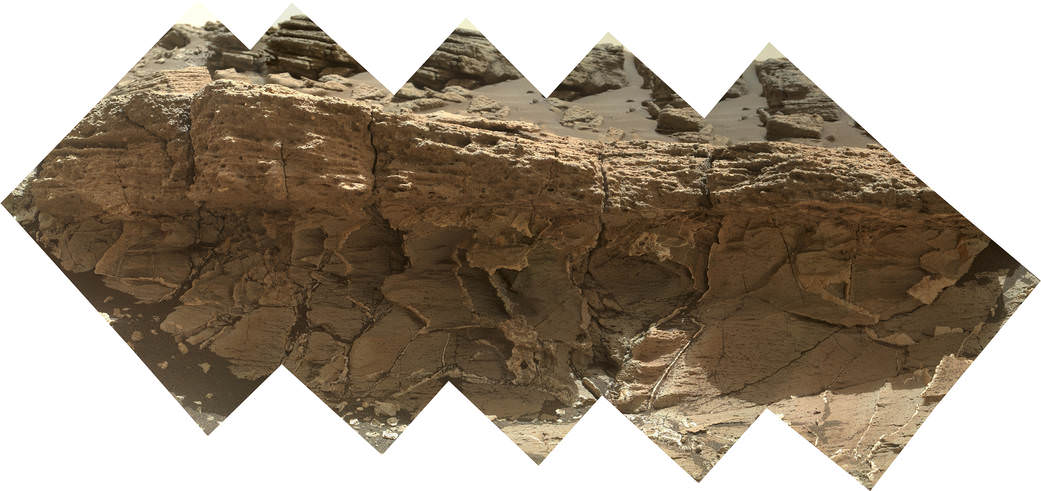
You can also see another perspective of the rover at work while reaching out with the robotic arm and drilling into ‘Buckskin’ as illustrated in our mosaics of mastcam and navcam camera raw images created by the image processing team of Ken Kremer and Marco Di Lorenzo.
The main bore hole was drilled next to the initial mini hole test and shows the indicative residue of grey colored tailings from the Martian subsurface seen distributed around the new hole.

Curiosity has now moved on from the “Marias Pass” area.
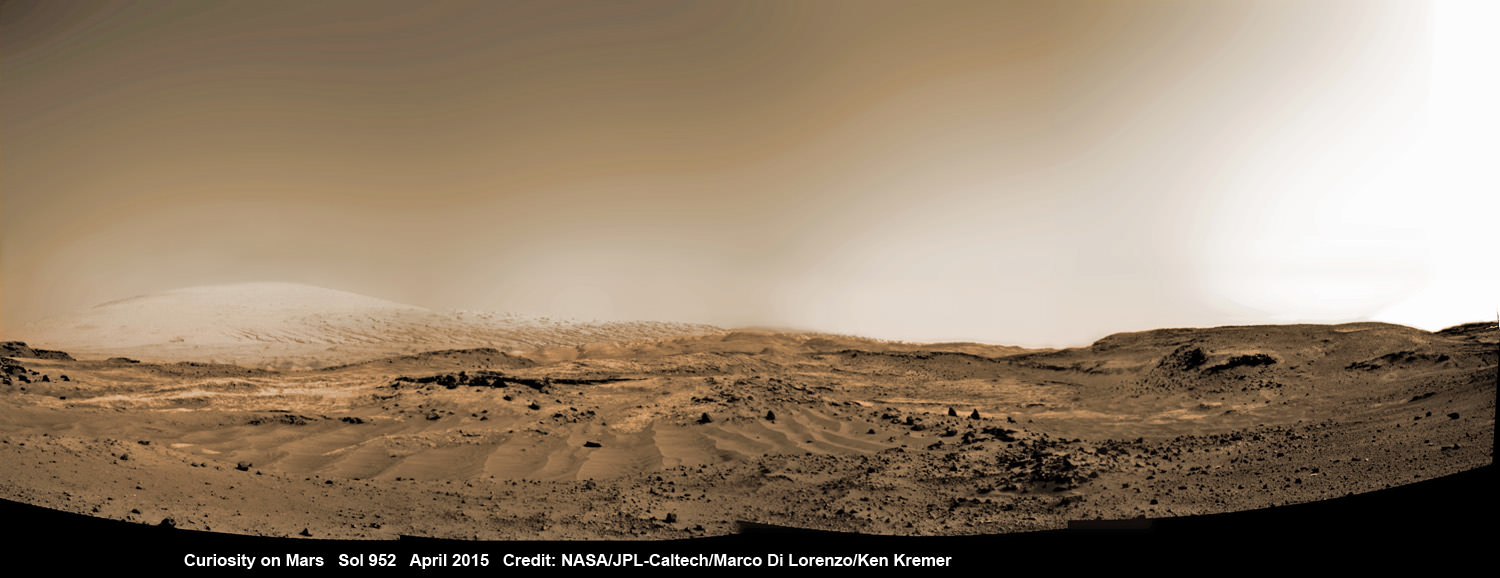
Curiosity recently celebrated 1000 Sols of exploration on Mars on May 31, 2015 – detailed here with our Sol 1000 mosaic also featured at Astronomy Picture of the Day on June 13, 2015.
As of today, Sol 1080, August 20, 2015, she has driven some 6.9 miles (11.1 kilometers) kilometers and taken over 260,000 amazing images.

Curiosity has already accomplished her primary objective of discovering a habitable zone on the Red Planet – at the Yellowknife Bay area – that contains the minerals necessary to support microbial life in the ancient past when Mars was far wetter and warmer billions of years ago.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.