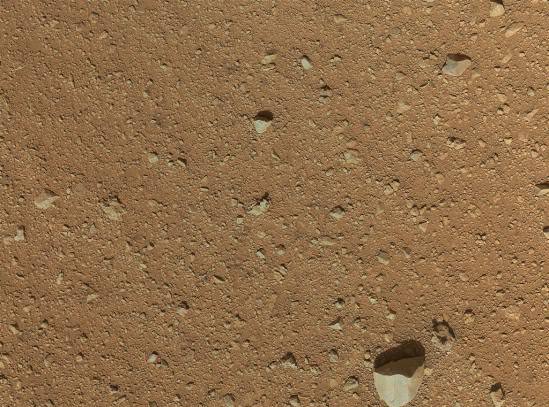
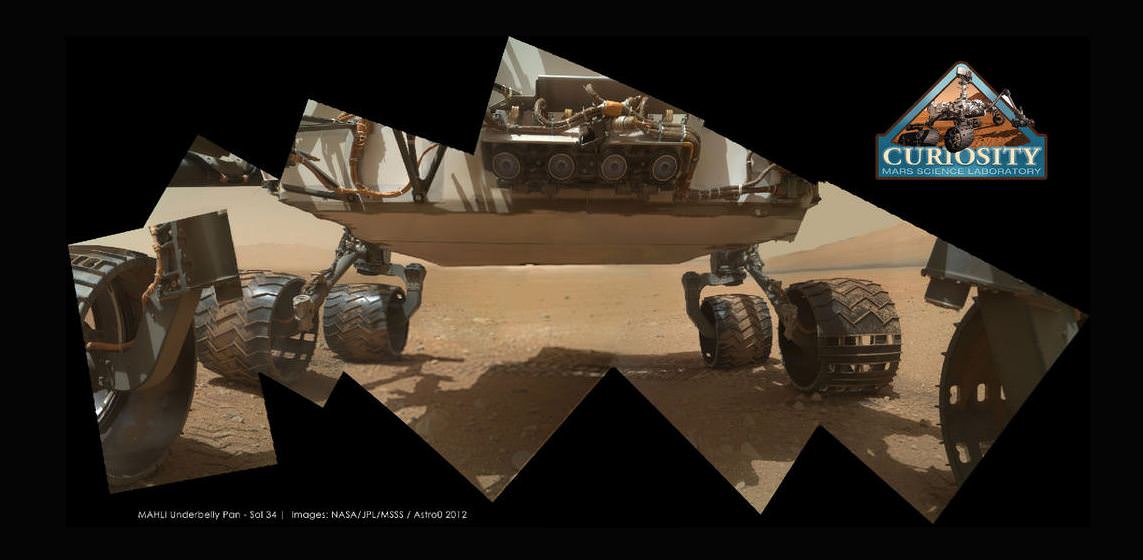
Curiosity’s underside as imaged by the MAHLI camera. Credit: NASA/JPL/MSSS; image editing by Astro0.
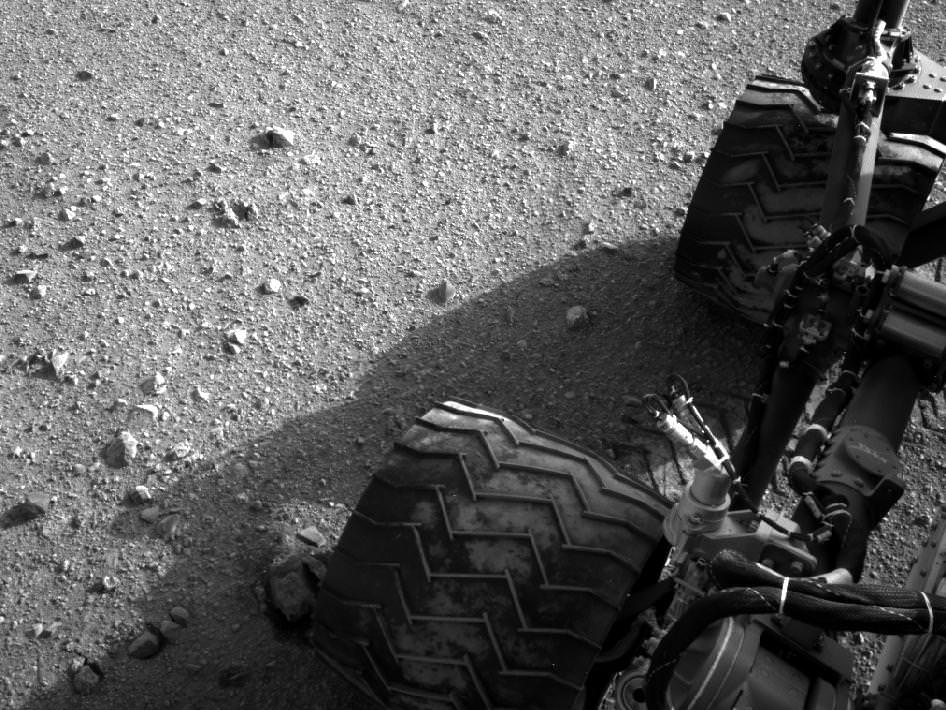
One of Curiosity’s amazing color cameras, the Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) that is mounted on the turret at the end of the MSL robotic arm, is now officially in action, with its dust cover removed over the weekend. The first picture it sent back to Earth was of the soil in its field of view (see below). That’s great, as the camera’s purpose is to acquire close-up images of materials on the Martian surface—rocks, fine particles and even frost. But then engineers commanded the camera to take a look at Curiosity’s underbelly – the rover’s ‘tummy’ so to speak. And the views are awesome, especially when some of the image wizards at UnmannedSpaceflight stitched a few of the images together to put together a mosaic of the entire view of the rover’s underside. This image was put together by Astro0 at UMSF. Click the image to see a larger version on his website.
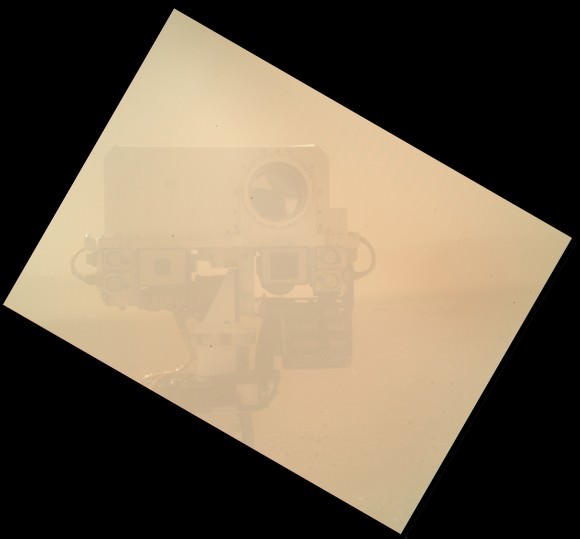
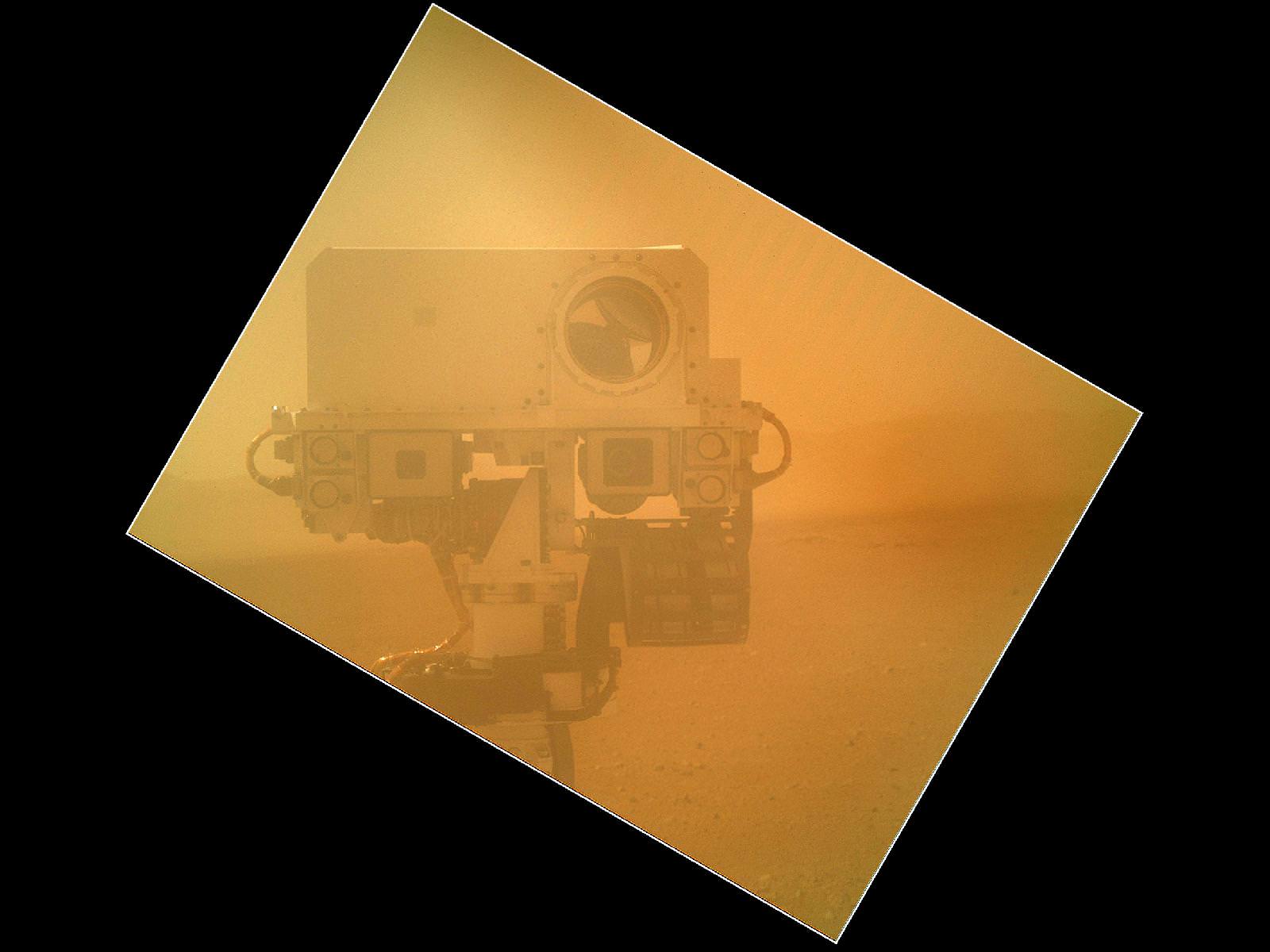
The first image to come from Curiosity’s Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) with the dust cap off. Credit: NASA/MSL-Caltech
MAHLI, built by Malin Space Science Systems (MSSS) will be used to help characterize the geology of the site investigated by MSL, and it will be used to document the materials being examined by MSL’s geochemical and mineralogical experiments.
You can see the “raw images” at the MSL website, the images that are just being beamed back from the rover, and see more at UnmannedSpaceflight; Emily Lakdawalla at the Planetary Blog also has some images she has put together from MAHLI’s views of Curiosity’s underside.
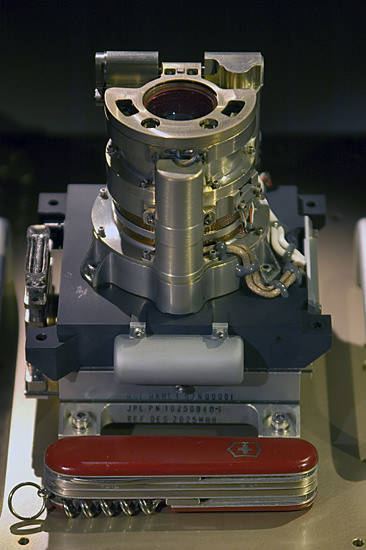
Here’s a picture of the camera itself:
The Mars Hand Lens Imager (MAHLI) camera head. The knife is 88.9 mm (3.5 inches) long. Image credit: Malin Space Science Systems
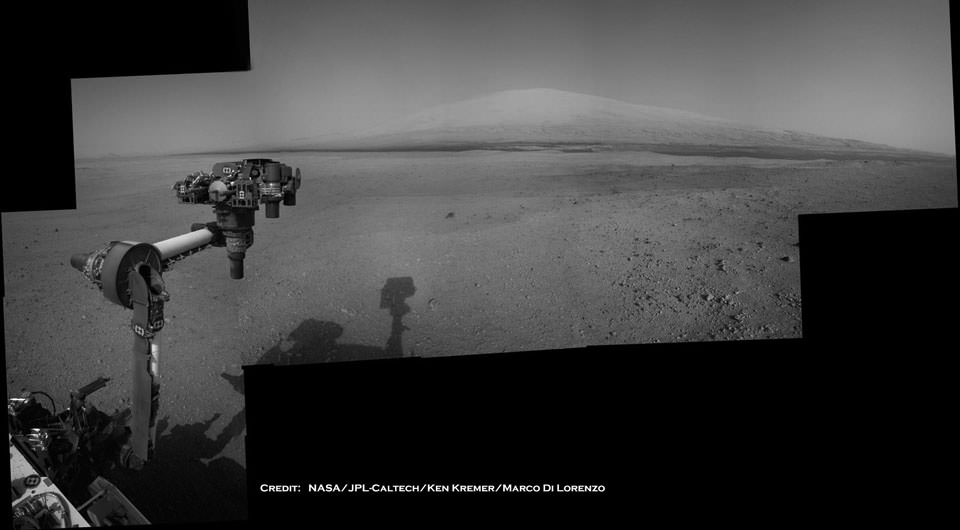
MAHLI is the equivalent of a 2 Megapixel camera. Because MAHLI can focus at infinity, in addition to being able to get microscopic views of surface materials MAHLI can also be used for other purposes, including inspection of areas on the rover or imaging the local landscape — as the images here attest.
MAHLI can also acquire multiple images of the same feature at different focus positions; additionally look upcoming for 3-D views of selected targets from this camera, since it is located on the robotic arm, it will be relatively easy to move the camera to take two images of the same object from different positions.
Learn more about MAHLI at the Malin Space Science Systems website.