How do you study something invisible? This is a challenge that faces astronomers who study dark matter. Although dark matter comprises 85% of all matter in the universe, it doesn’t interact with light. It can only be seen through the gravitational influence it has on light and other matter. To make matters worse, efforts to directly detect dark matter on Earth have been unsuccessful so far.
Continue reading “New Simulation Shows Exactly What Dark Matter Would Look Like If We Could See It”Gamma Rays Detected Coming From the Crab Nebula
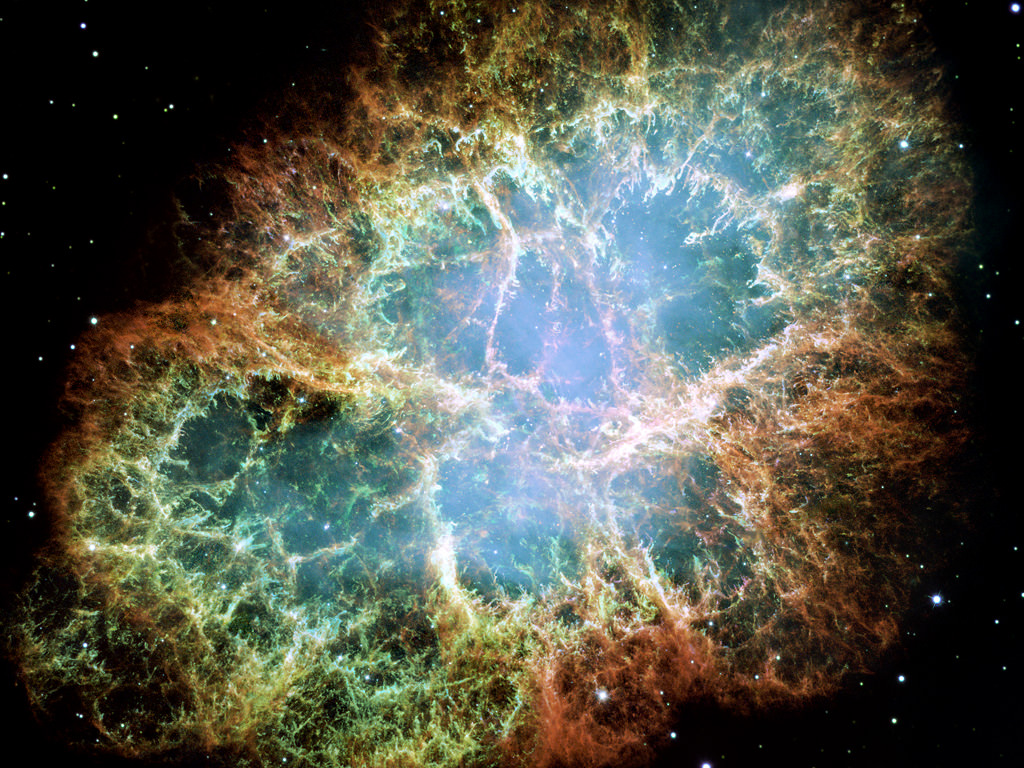
Most people with any interest in astronomy know about the Crab Nebula. It’s a supernova remnant in the constellation Taurus, and its image is all over the place. Google “Hubble images” and it’s right there with other crowd favorites, like the Pillars of Creation.
The Crab Nebula is one of the most-studied objects in astronomy. It’s the brightest source of gamma rays in the sky, and that fact is being used to establish the function of a new telescope called the Schwarschild-Couder Telescope.
Continue reading “Gamma Rays Detected Coming From the Crab Nebula”A Massive Rotating Disc Discovered in the Early Universe
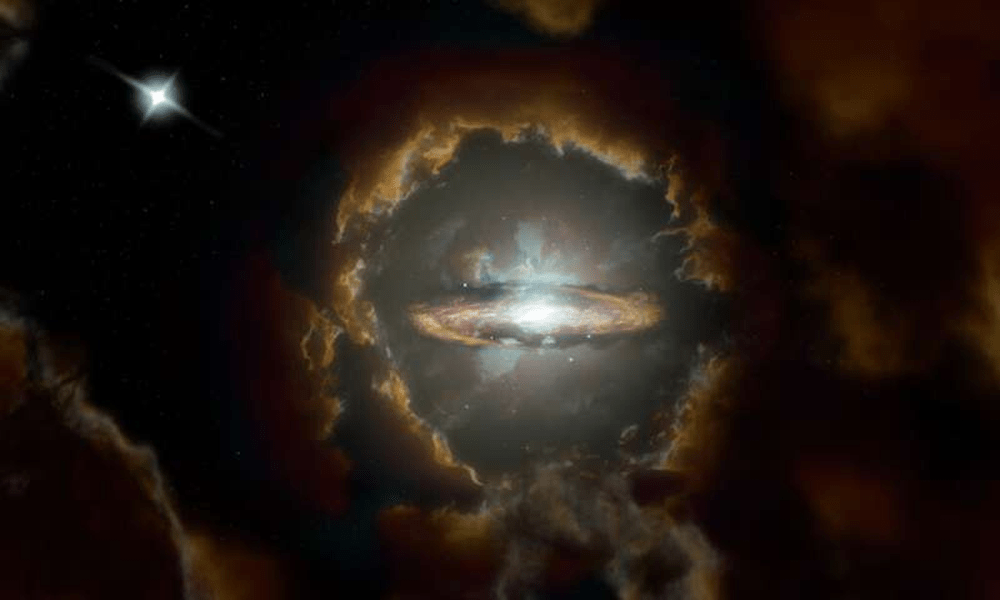

If we want to understand how the Universe evolves, we have to understand how its large structures form and evolve. That’s why astronomers study galaxy formation. Galaxies are enormous structures of stars, planets, gas, dust, and dark matter, and understanding how they form is critical to understanding the Universe itself.
In 2017, astronomers working with ALMA (Atacama Large Millimeter/sub-millimeter Array) discovered an ancient galaxy. This massive rotating disk galaxy was born when the Universe was only about 1.5 billion years old. According to the most accepted understanding of how galaxies form and evolve, it shouldn’t exist.
But there it is.
Continue reading “A Massive Rotating Disc Discovered in the Early Universe”Decaying Dark Matter Should be Visible Here in the Milky Way as a Halo Around the Galaxy

Astronomers are very sure that dark matter exists, but they’re not sure at all what it’s made of.
The problem is that it isn’t just dark, it’s invisible. As far as we know, dark matter doesn’t emit light, absorb light, reflect light, refract light, scatter light, diffract light, or really have anything to do with light at all. This makes it hard to study. We know that dark matter exists, however, through its gravitational effects. Even though it’s invisible, it still has mass, and so the dark matter in our universe (which, by the way, makes up 85% of all the mass in the cosmos) can affect the motions of normal (or light-interacting) matter, like stars and galaxies.
Continue reading “Decaying Dark Matter Should be Visible Here in the Milky Way as a Halo Around the Galaxy”Slime Mold Grows the Same as the Large Scale Structure of the Universe

Matter in the Universe is not distributed equally. It’s dominated by super-clusters and the filaments of matter that string them together, surrounded by huge voids. Galaxy super-clusters are at the top of the hierarchy. Inside those is everything else: galaxy groups and clusters, individual galaxies, and solar systems. This hierarchical structure is called the “Cosmic Web.”
But how and why did the Universe take this form?
Continue reading “Slime Mold Grows the Same as the Large Scale Structure of the Universe”Is the “D-star Hexaquark” the Dark Matter Particle?
Since the 1960s, astronomers have theorized that all the visible matter in the Universe (aka. baryonic or “luminous matter) constitutes just a small fraction of what’s actually there. In order for the predominant and time-tested theory of gravity to work (as defined by General Relativity), scientists have had to postulate that roughly 85% of the mass in the Universe consists of “Dark Matter”.
Despite many decades of study, scientists have yet to find any direct evidence of Dark Matter and the constituent particle and its origins remain a mystery. However, a team of physicists from the University of York in the UK has proposed a new candidate particle that was just recently discovered. Known as the d-star hexaquark, this particle could have formed the “Dark Matter” in the Universe during the Big Bang.
Continue reading “Is the “D-star Hexaquark” the Dark Matter Particle?”Astronomers Simulated How the Universe Would Look Without Dark Matter
Since the 1960s, there has been a general consensus among astronomers and cosmologists that the majority of the Universe is made up of an invisible, mysterious mass (known as Dark Matter). While scientists still haven’t identified the candidate particle that makes up this mass, indirect tests and simulations have shown that Dark Matter must exist in order for the Universe to be the way it is.
In a fascinating twist, a team of European researchers conducted a simulation that looked at a Universe without Dark Matter. Using an alternative theory known as MOdified Newtonian Dynamics (MOND), the team created a computer simulation in which the galaxies were actually very similar to what we see in the Universe today. These findings could help to resolve one of the most enduring mysteries of modern cosmology.
Continue reading “Astronomers Simulated How the Universe Would Look Without Dark Matter”Hubble Finds Teeny Tiny Clumps of Dark Matter

To put it simply, Dark Matter is not only believed to make up the bulk of the Universe’s mass but also acts as the scaffolding on which galaxies are built. But to find evidence of this mysterious, invisible mass, scientists are forced to rely on indirect methods similar to the ones used to study black holes. Essentially, they measure how the presence of Dark Matter affects stars and galaxies in its vicinity.
To date, astronomers have managed to find evidence of dark matter clumps around medium and large galaxies. Using data from the Hubble Space Telescope and a new observing technique, a team of astronomers from UCLA and NASA JPL found that dark matter can form much smaller clumps than previously thought. These findings were presented this week at the 235th meeting of the American Astronomical Society (AAS).
Continue reading “Hubble Finds Teeny Tiny Clumps of Dark Matter”Dark Matter Could Be A Source of Gamma Rays Coming from the Center of the Milky Way
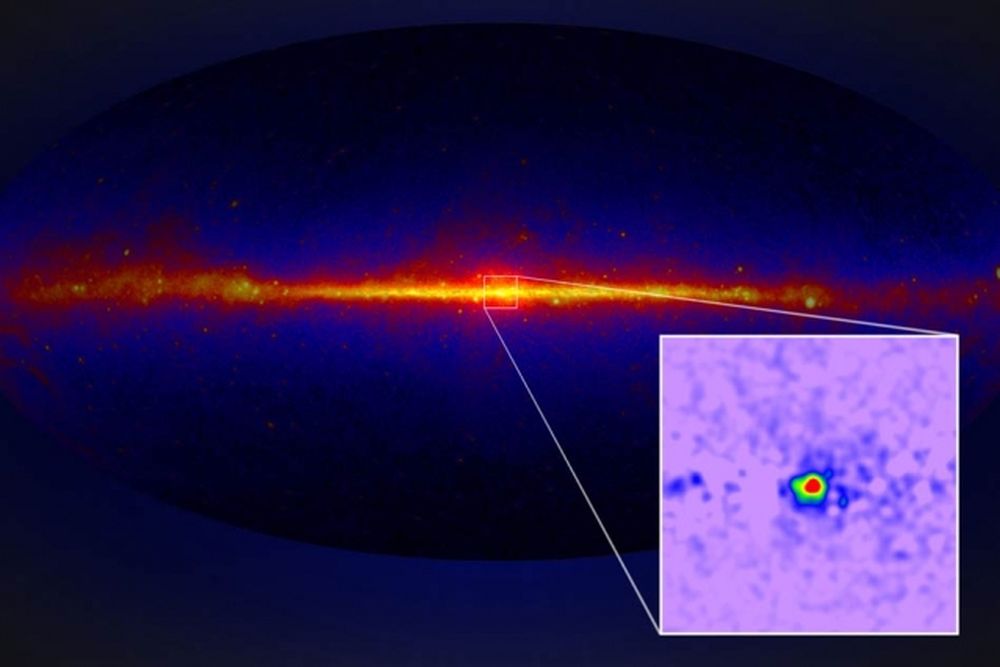
There’s a lot of mysterious goings-on at the center of the Milky Way. The supermassive black hole that resides there is chief among them. But there’s another intriguing puzzle there: an unexpected spherical region of intense gamma ray emissions.
A new study suggests that dark matter could be behind those emissions.
Continue reading “Dark Matter Could Be A Source of Gamma Rays Coming from the Center of the Milky Way”Gravitational Wave Detectors Might be Able to Detect Dark Matter Particles Colliding With Their Mirrors
The field of astronomy has been revolutionized thanks to the first-ever detection of gravitational waves (GWs). Since the initial detection was made in February of 2016 by scientists at the Laser Interferometer Gravitational-wave Observatory (LIGO), multiple events have been detected. These have provided insight into a phenomenon that was predicted over a century ago by Albert Einstein.
As it turns out, the infrastructure that is used to detect GWs could also help crack another astronomical mystery: Dark Matter! According to a new study by a team of Japanese researchers, laser interferometers could be used to look for Weakly-Interacting Massive Particles (WIMPs), a major candidate particle in the hunt for Dark Matter.
Continue reading “Gravitational Wave Detectors Might be Able to Detect Dark Matter Particles Colliding With Their Mirrors”


