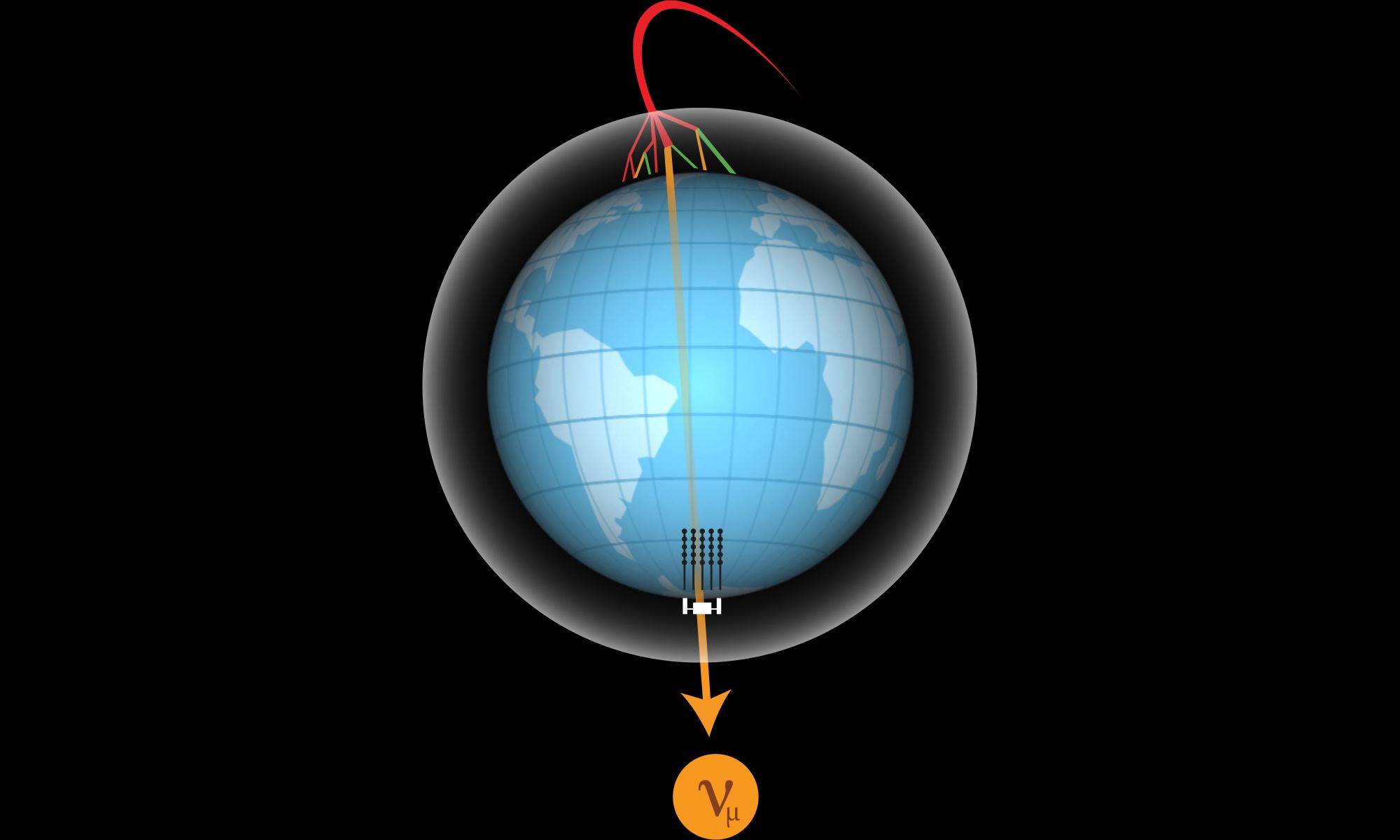
Dark matter is one of the thorniest mysteries of modern cosmology. On the one hand, astronomers have gathered a wealth of supporting evidence through galaxy clustering statistics, gravitational lensing, and cosmic microwave background fluctuations, on the other hand, there are no particles in the standard model of particle physics that could account for dark matter, and we haven’t been able to detect its effect locally. It’s a solid theory where we just can’t seem to fully pin it down. That usually means we’re just a breakthrough away from confirming or overthrowing dark matter. The good news is that there are several projects searching for dark matter, and one of them, the IceCube Neutrino Observatory, has just released a new result.
Continue reading “Astronomers Search for Dark Matter Annihilation at the Center of the Earth”