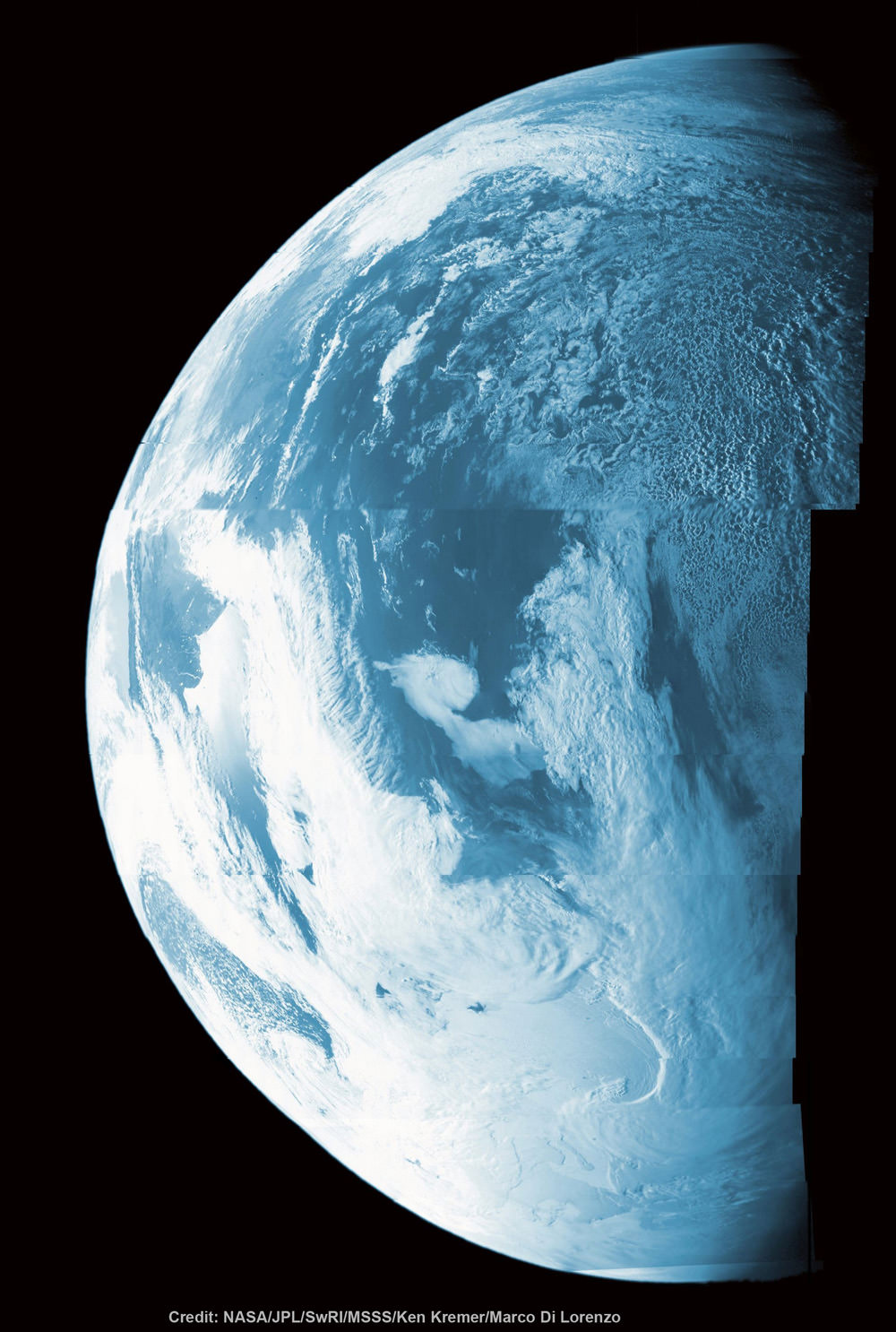
When NASA’s Juno spacecraft flew past Earth in October of this year, it focused some of its cameras on the Earth-Moon system. Immediately after the flyby, images taken by the Junocam were released, but today, NASA released an amazing video taken by the Advanced Stellar Compass (ASC) camera, a low-light camera that is primarily used as a star tracking a navigation tool. Over the course of three days, it captured the orbital ballet-like dance between the Earth and Moon.
“This is profound, and I think our movie does the same thing as “Pale Blue Dot” image from Voyager, except it’s a movie instead of an image,” said Scott Bolton, Juno principal investigator, speaking during a press briefing from the American Geophysical Union conference today in San Fransisco. “Like Carl Sagan said, everything we know is on this dot. To me this says, ‘we’re all in this together.’”
The Oct. 9 flyby was a gravity assist, accelerating Juno out of the inner solar system and toward Jupiter’s orbit. The probe is expected to arrive at Jupiter on July 4, 2016.
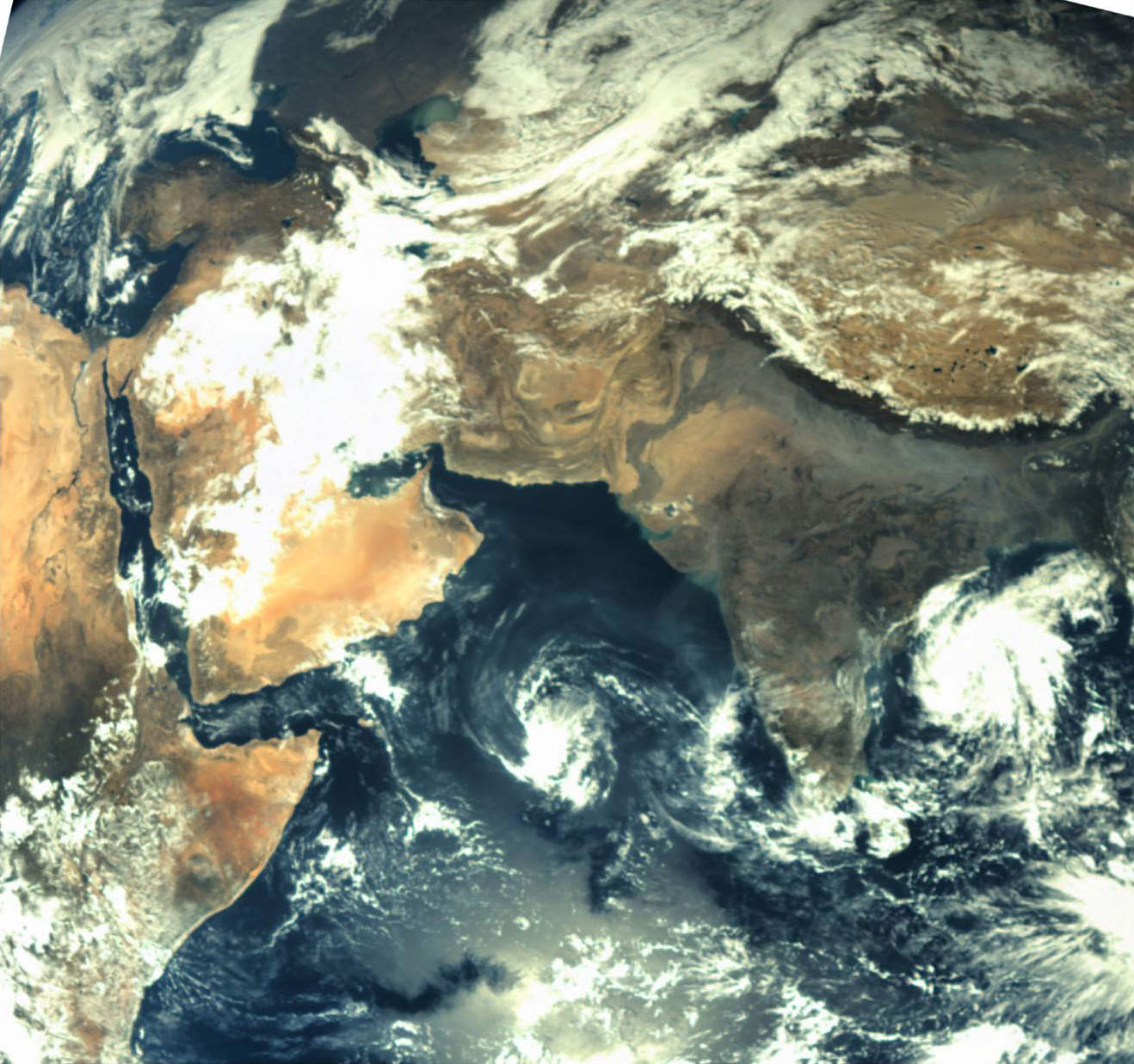
The movie begins at 2:00 UTC on Oct. 6, more than four days before Juno’s closest approach, when the spacecraft was approximately 2.1 million miles (3.3 million kilometers) from Earth. Earth’s moon is seen transiting in front of our planet, and then moves out of frame toward the right as Juno enters the space inside the orbit of our natural satellite. As Juno gets closer to Earth, hints of clouds and continents are visible before the planet’s brightness overwhelms the cameras, which were not designed to image so bright an object. The sequence ends as Earth passes out of view, which corresponds to approximately 17:35 UTC Oct. 9 when Juno was at an altitude of about 47,000 miles (76,000 kilometers) above Earth’s surface.
“From a half-million kilometers out, the Moon is dark as charcoal and but Earth way brighter, as a shiny blue dot,” said John Joergensen, who lead the team that designed the star tracking cameras. “It’s amazing to think that all of humanity being scanned in this movie, and to see how small the Moon is relative to Earth.”
The cameras that took the images for the movie are located near the pointed tip of one of the spacecraft’s three solar-array arms. They are part of Juno’s Magnetic Field Investigation (MAG) and are normally used to determine the orientation of the magnetic sensors. These cameras look away from the sunlit side of the solar array, so as the spacecraft approached, the system’s four cameras pointed toward Earth. Earth and the moon came into view when Juno was about 600,000 miles (966,000 kilometers) away — about three times the Earth-moon separation.
During the flyby, timing was everything. Juno was traveling about twice as fast as a typical satellite, and the spacecraft itself was spinning at 2 rpm. To assemble a movie that wouldn’t make viewers dizzy, the star tracker had to capture a frame each time the camera was facing Earth at exactly the right instant. The frames were sent to Earth, where they were processed into video format.
As Juno is a spinning spacecraft, the images were aligned to remove their apparent rotation. The original ASC images are monochrome; faint coloration has been added by converting the measured grayscale values into false colors matching a true color image of Earth.