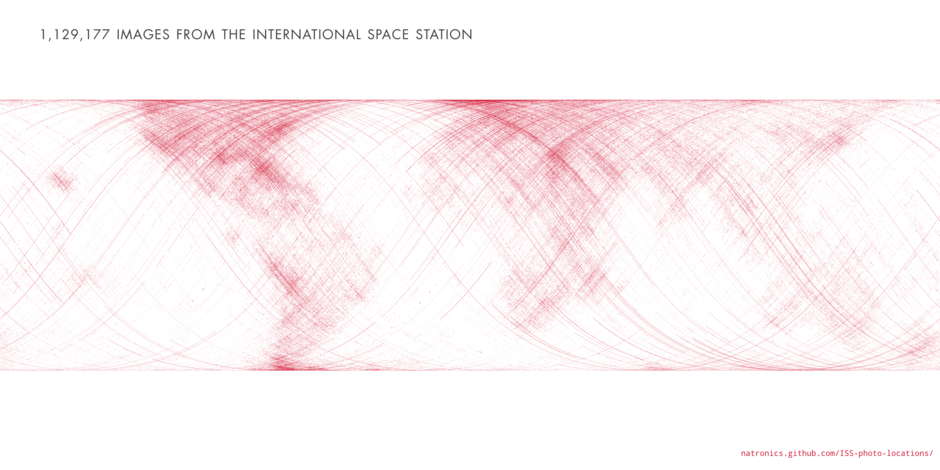
Satellites can now fit in the palm of your hand.
Known as Cubesats, several of these tiny but cost-effective payloads use off-the-shelf technology that you may currently carry in your pocket. In fact, engineers have put out a call for app designers to write programs for these tiny micro-satellites. Four of this new breed of satellites are part of the Antares A-One mission and another four are slated to launch tomorrow atop a Soyuz rocket from Plesetsk along with the Bion M-1 payload.
Yesterday’s launch of Orbital Sciences’ Antares rocket was scrubbed with minutes to go due to the premature retraction of an umbilical. Current plans call for a 48 hour turnaround with a new launch window opening Friday night on April 19th at 5:00 PM EDT/ 21:00 UT.
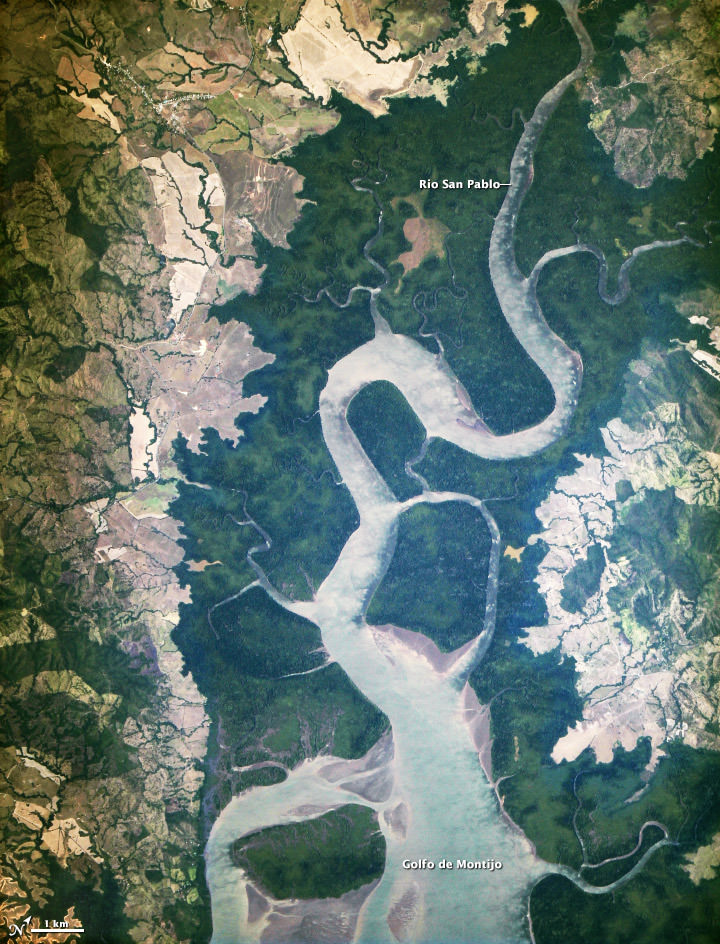
Cubesats are nothing new. As technology becomes miniaturized, so have the satellites that they’re contained in. Cubesats have even been deployed from the International Space Station.
The primary goal of the Antares A-One mission is to deploy a test mass into low Earth Orbit that simulates the Cygnus spacecraft. If all goes well, Cygnus is set to make its first flight to the ISS this summer.
But also onboard are the three unique payloads; the PhoneSat-1a, 1b & 1c cubesats and the Dove 1 cubesat.
As the name implies, the PhoneSat series of satellites are each constructed around a Nexus Smartphone and operate using Google’s very own Android operating system. The mission serves as NASA’s test bed for the concept. The phone system will monitor the orientation of the satellites. The PhoneSats will also use their off-the-shelf built-in cameras to take pictures of the Earth from orbit.
A separate watchdog circuit will reboot the phones if necessary. The PhoneSats are expected to last about a week in orbit until their batteries die. One of the PhoneSats is equipped with solar panels to test rechargeable technology for the platform.
Two of the nano satellites are built around a Samsung Nexus S and the other around a HTC Nexus Smartphone. The satellites will also use the SD card for info storage plus the 3-axis magnetometer and accelerometer incorporated into the phones for measurements and orientation.

Dove-1 will test a similar technology. It is built around a low-cost bus using off-the-shelf components. Each of the three PhoneSats cost less than $3,500 dollars U.S. to build.
Amateur radio operators will also be able to monitor the satellites as well. The PhoneSats will transmit at 437.425 MHz. Information will also available to track them in real time on the web once they’re deployed.
The two PhoneSat 1.0 satellites are dubbed Graham and Bell and will transmit every 28 and 30 seconds, and the one PhoneSat 2.0 satellite is named Alexandre and will transmit every 25 seconds.
The PhoneSat 2.0 series will also employ magnets that interact with the Earth’s magnetic field. A future application of this could include use of a PhoneSat for a possible heliophysics mission.
Although the Antares A-One mission is aiming to place the Cygnus test mass and the Cubesats in an inclination of 51.6° degrees similar to the ISS, it will not be following the ISS in its orbit and won’t present a hazard to the station.
The goal of NASA’s PhoneSat team based out of the Ames Research Center at Moffett Field California is to “release early and often.” Missions like Antares A-One present a unique opportunity for the teams to get “piggyback payloads” into orbit. To this end, NASA’s Cubesat Launch Initiative (CSLI) issues periodic calls for teams across the nation to make proposals and build tiny satellites.
Basic dimensions of a cubesat are 10x10x14 centimetres (for comparison, a CD jewel case is about 14×12 cm) and must weigh less than 1.33 kilograms for 1U, 2U & 3U variants. Up to 14kg is allowed for 6U models. Cubesats are deployed from a Poly-Picosatellite Deployer, or P-Pod.
Another set of cubesats is also slated to launch tomorrow from Plesetsk. The primary payload of the mission is deployment of the Bion M-1 biological research satellite. Bion M-1 will carry an assortment of organisms including lizards, mice and snails for a one month mission to study the effects of a long duration spaceflight on micro-organisms.
The Bion M-1 mission will also deploy the AIST microsatellite built by students of Samara Aerospace University, & BeeSats 2 & 3 provided by the Technical University of Berlin. A twin of the Dove-1 satellite launching on Antares named Dove-2 is also onboard.
One of the micro-satellites named OSSI-1 is of particular interest to backyard satellite trackers. Part of the Open Source Satellite Initiative, OSSI-1 was developed by radio amateur and artist Hojun Song. In addition to a Morse Code beacon, OSSI-1 will also contain a 44 watt optical LED beacon that will periodically be visible to observers on Earth.
Another similar project, FITSAT-1, has been tracked and imaged by observers in recent months. Follow the AmSat-UK website for predictions and visibility prospects of OSSI-1 after launch and deployment. FITSAT-1 has been visible with binoculars only, but OSSI-1 may just be visible to the unaided eye during shadow passes while it’s operational.
It will be interesting to watch these “home-brewed” projects take to orbit. The price tag and the technology is definitely within reach of a sufficiently motivated basement tinker or student team with an idea. Hey, how about the world’s first free-flying “Amateur Space Telescope?” Just throwing that out there!