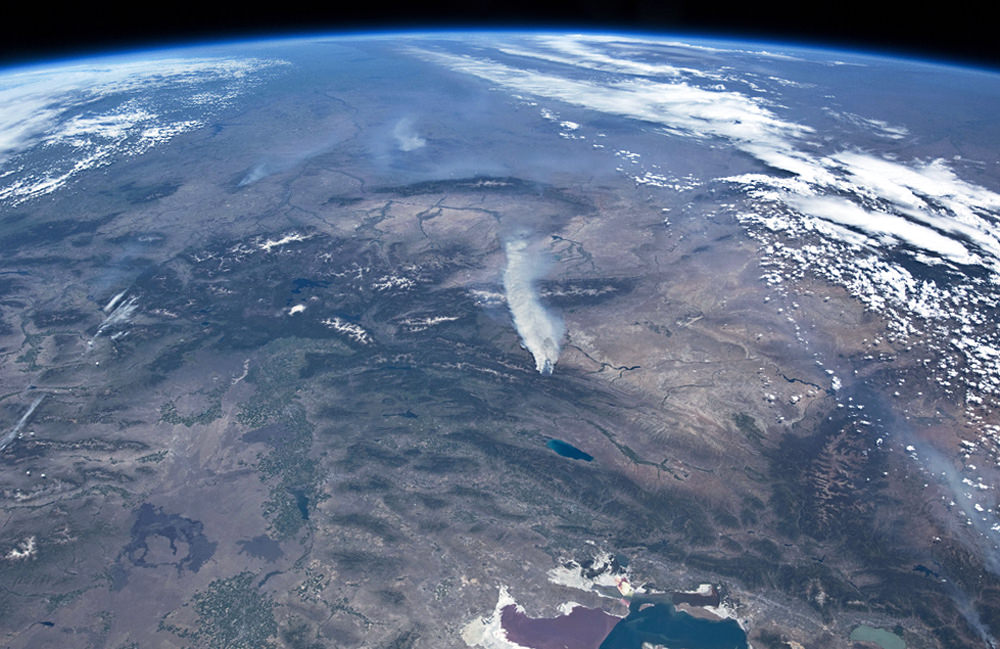
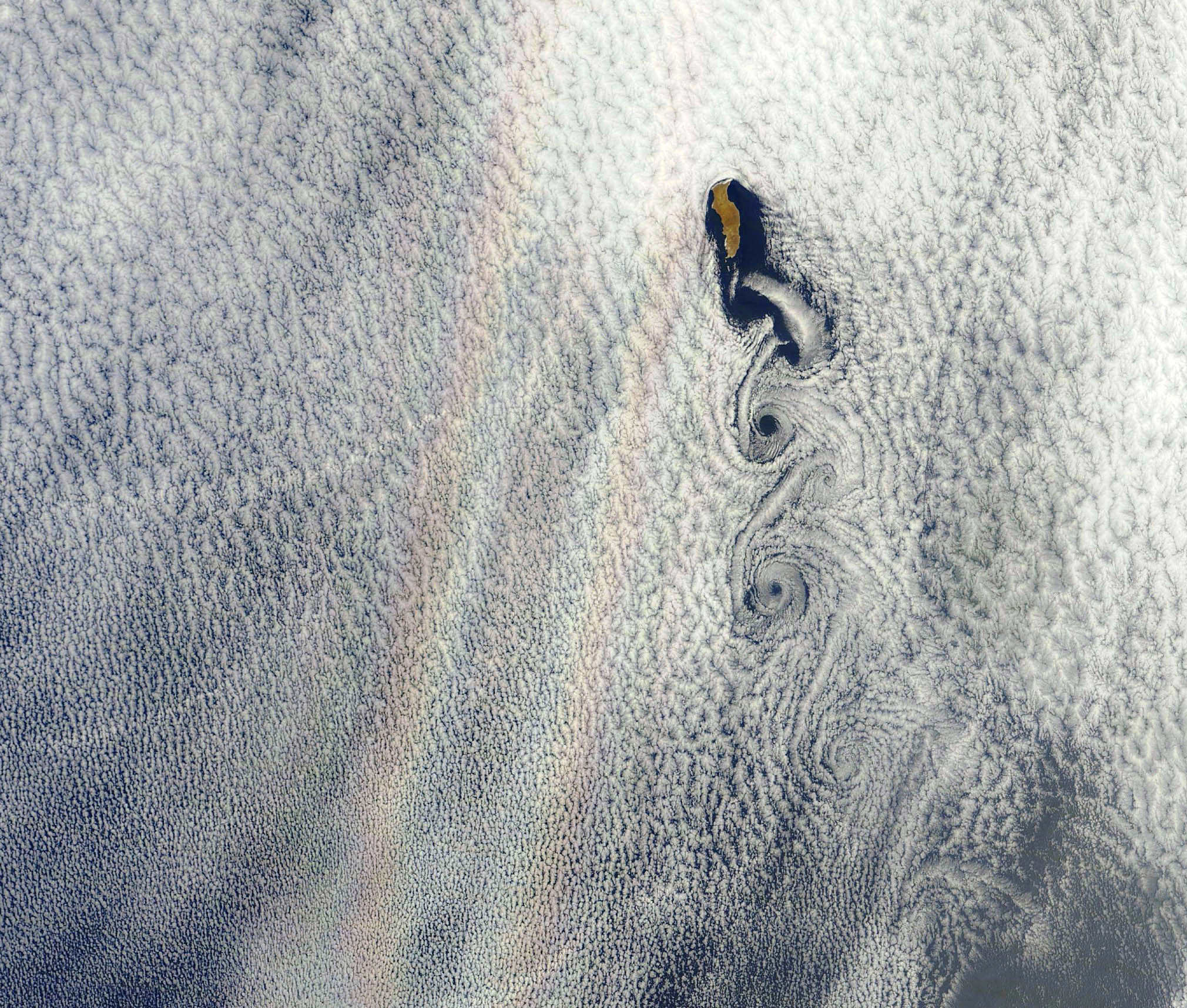
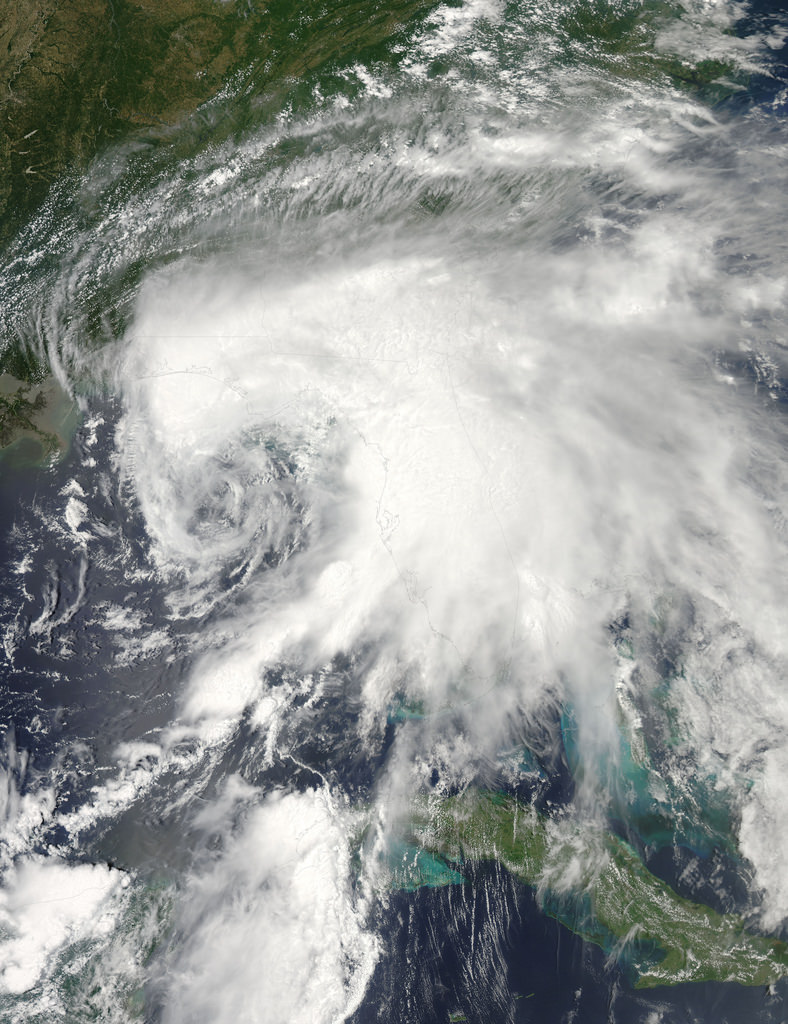
NASA’s first Earth-observing Landsat satellite launched from Vandenberg Air Force Base on July 23, 1972, and to celebrate the 40th anniversary of the program they asked the public to vote on their favorite images of the planet from the Landsat Earth as Art gallery. After over 14,000 votes, these were chosen as the top 5 favorites. Happy 40th anniversary, Landsat!
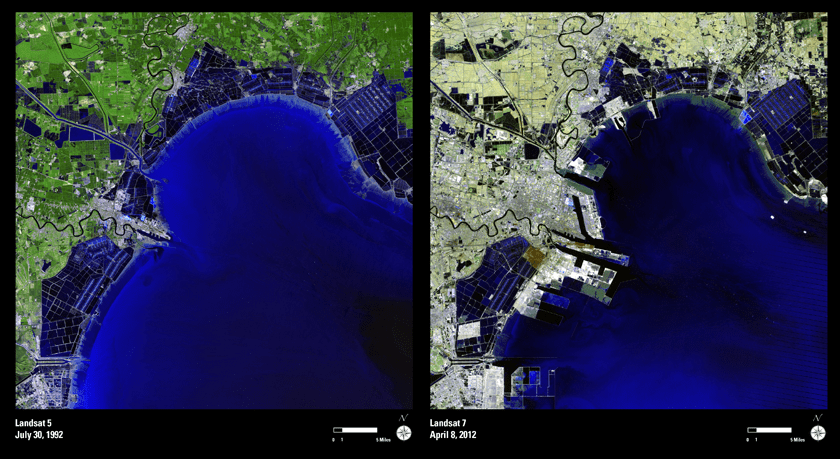
Landsat images from space are not merely pictures. They contain many layers of data collected at different points along the visible and invisible light spectrum. A single Landsat scene taken from 400 miles above Earth can accurately detail the condition of hundreds of thousands of acres of grassland, agricultural crops or forests.
“Landsat has given us a critical perspective on our planet over the long term and will continue to help us understand the big picture of Earth and its changes from space,” said NASA Administrator Charles Bolden. “With this view we are better prepared to take action on the ground and be better stewards of our home.”
In cooperation with the U.S. Geological Survey (USGS), a science agency of the Interior Department, NASA launched six of the seven Landsat satellites. The resulting archive of Earth observations forms a comprehensive record of human and natural land changes.

“The first 40 years of the Landsat program have delivered the most consistent and reliable record of Earth’s changing landscape.”
– Michael Freilich, director of NASA’s Earth Science Division
“Over four decades, data from the Landsat series of satellites have become a vital reference worldwide for advancing our understanding of the science of the land,” said Interior Department Secretary Ken Salazar. “The 40-year Landsat archive forms an indelible and objective register of America’s natural heritage and thus it has become part of this department’s legacy to the American people.”
The next satellite in the series, the Landsat Data Continuity Mission (LDCM) is scheduled to launch on February 11, 2013.
(Source: NASA/GSFC)
Find out more about the ongoing Landsat mission here, and see recent visualizations from Landsat on the USGS site here.
Video: NASA/GSFC. Inset image: Industrial growth in Binhai New Area, China. Sub-feature: Erg Iguidi, an area of ever-shifting sand dunes extending from Algeria into Mauritania in northwestern Africa, one of the chosen top 5 Earth as Art images. NASA/GSFC/USGS.