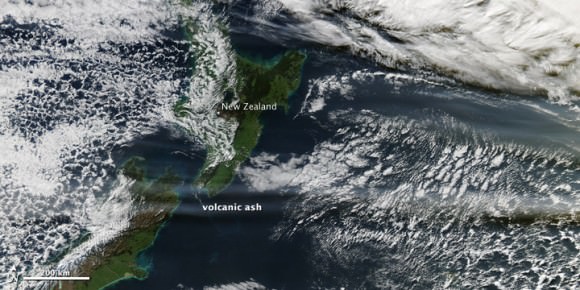
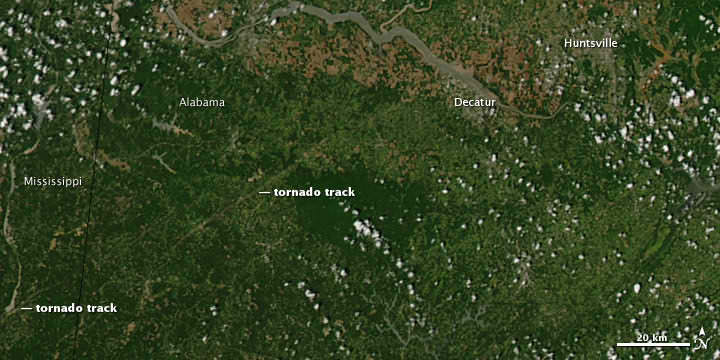
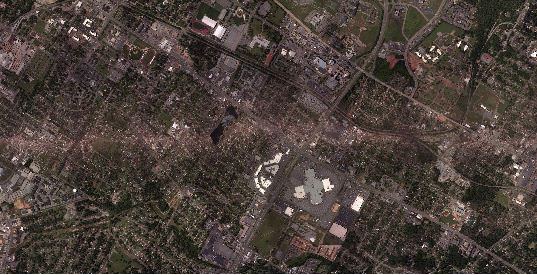
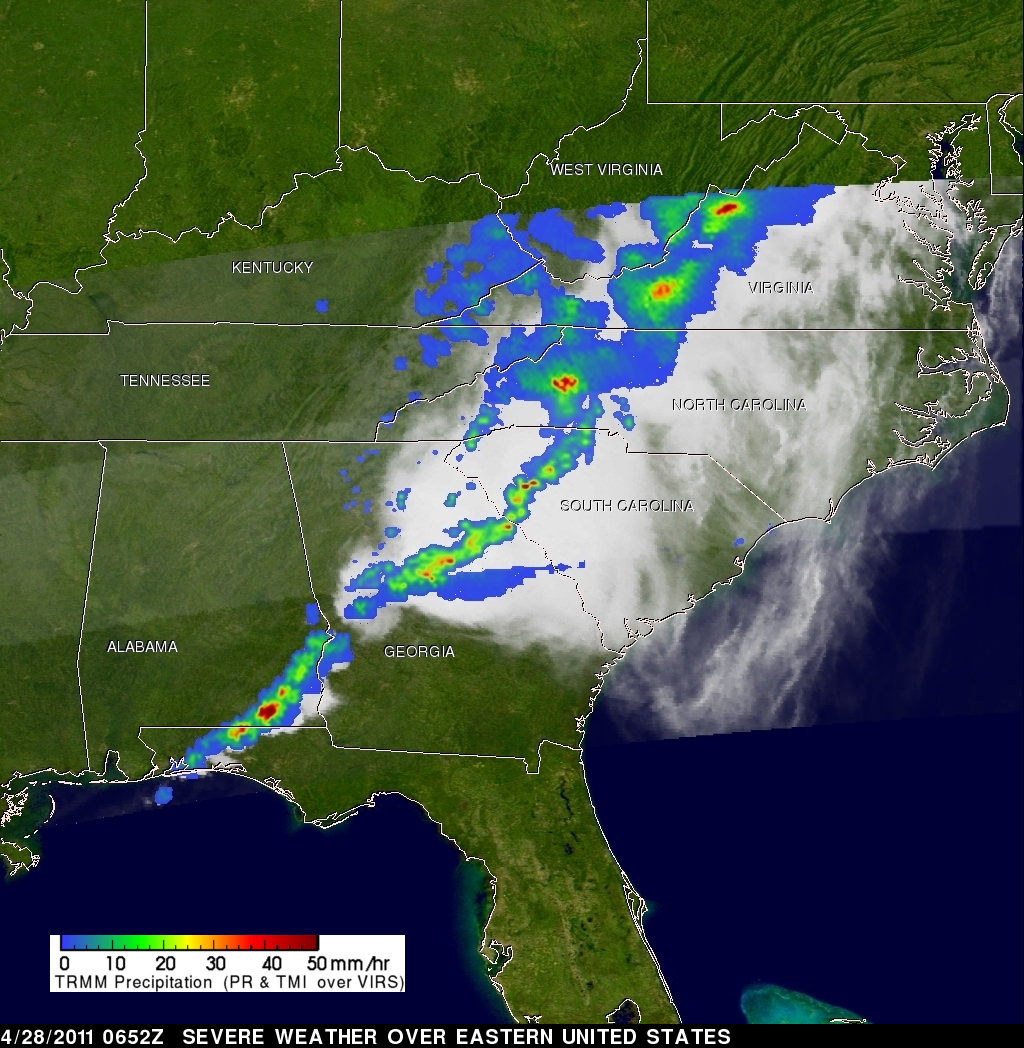
[/caption]
From a JPL press release:
Final preparations are under way for the June 9 launch of the international Aquarius/SAC-D observatory. The mission’s primary instrument, Aquarius, will study interactions between ocean circulation, the water cycle and climate by measuring ocean surface salinity.
Engineers at Vandenberg Air Force Base in California are performing final tests before mating Aquarius/SAC-D to its Delta II rocket. The mission is a collaboration between NASA and Argentina’s space agency, Comision Nacional de Actividades Espaciales (CONAE), with participation from Brazil, Canada, France and Italy. SAC stands for Satelite de Applicaciones Cientificas. Aquarius was built by NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Pasadena, Calif., and the agency’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
In addition to Aquarius, the observatory carries seven other instruments that will collect environmental data for a wide range of applications, including studies of natural hazards, air quality, land processes and epidemiology.
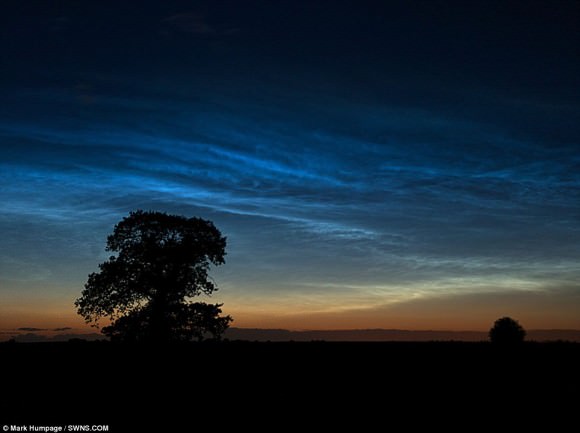
The mission will make NASA’s first space observations of the concentration of dissolved salt at the ocean surface. Aquarius’ observations will reveal how salinity variations influence ocean circulation, trace the path of freshwater around our planet, and help drive Earth’s climate. The ocean surface constantly exchanges water and heat with Earth’s atmosphere. Approximately 80 percent of the global water cycle that moves freshwater from the ocean to the atmosphere to the land and back to the ocean happens over the ocean.
Salinity plays a key role in these exchanges. By tracking changes in ocean surface salinity, Aquarius will monitor variations in the water cycle caused by evaporation and precipitation over the ocean, river runoff, and the freezing and melting of sea ice.
Salinity also makes seawater denser, causing it to sink, where it becomes part of deep, interconnected ocean currents. This deep ocean “conveyor belt” moves water masses and heat from the tropics to the polar regions, helping to regulate Earth’s climate.
“Salinity is the glue that bonds two major components of Earth’s complex climate system: ocean circulation and the global water cycle,” said Aquarius Principal Investigator Gary Lagerloef of Earth & Space Research in Seattle. “Aquarius will map global variations in salinity in unprecedented detail, leading to new discoveries that will improve our ability to predict future climate.”
Aquarius will measure salinity by sensing microwave emissions from the water’s surface with a radiometer instrument. These emissions can be used to indicate the saltiness of the surface water, after accounting for other environmental factors. Salinity levels in the open ocean vary by only about five parts per thousand, and small changes are important. Aquarius uses advanced technologies to detect changes in salinity as small as about two parts per 10,000, equivalent to a pinch (about one-eighth of a teaspoon) of salt in a gallon of water.
Aquarius will map the entire open ocean every seven days for at least three years from 408 miles (657 kilometers) above Earth. Its measurements will produce monthly estimates of ocean surface salinity with a spatial resolution of 93 miles (150 kilometers). The data will reveal how salinity changes over time and from one part of the ocean to another.
The Aquarius/SAC-D mission continues NASA and CONAE’s 17-year partnership. NASA provided launch vehicles and operations for three SAC satellite missions and science instruments for two.
JPL will manage Aquarius through its commissioning phase and archive mission data. Goddard will manage Aquarius mission operations and process science data. NASA’s Launch Services Program at the agency’s Kennedy Space Center in Florida is managing the launch.
CONAE is providing the SAC-D spacecraft, an optical camera, a thermal camera in collaboration with Canada, a microwave radiometer,; sensors from various Argentine institutions and the mission operations center there. France and Italy are contributing instruments.
See the Aquarius/SAC-D website for more information. , visit: