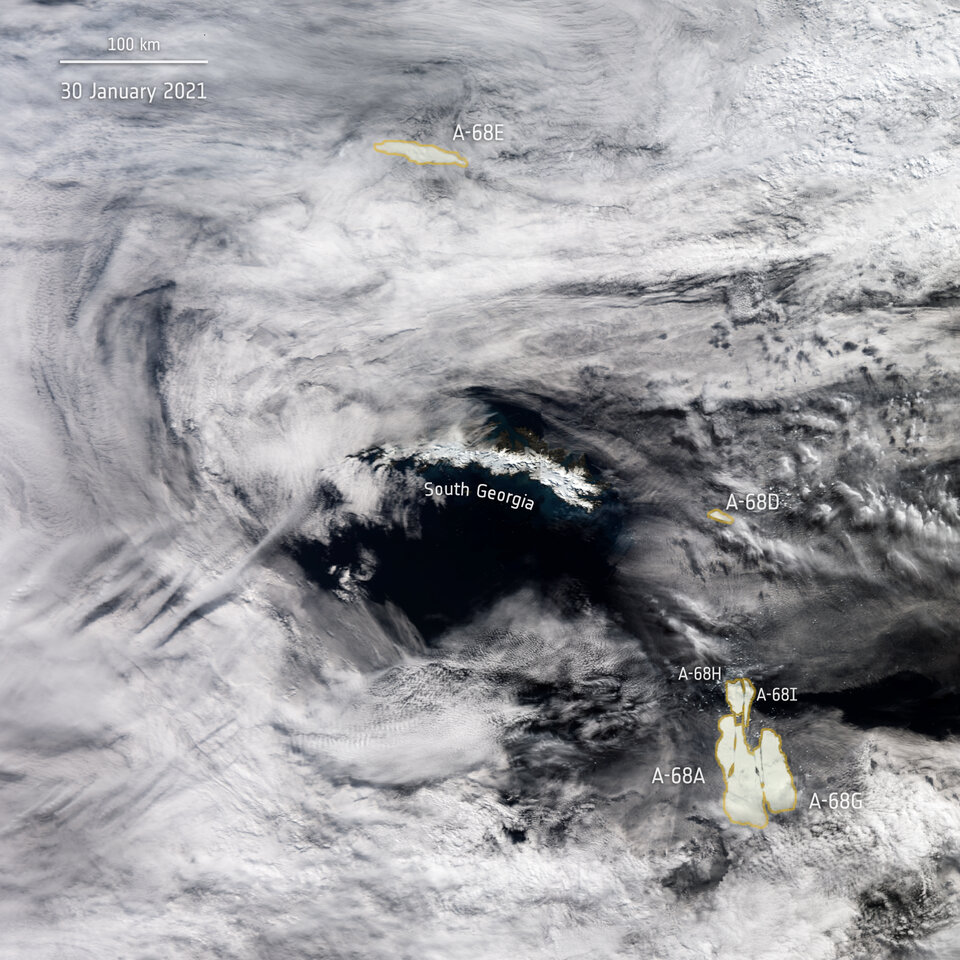
In addition to investigating the big questions about life in our Universe (origins, evolution, distribution, etc.), one of the chief aims of astrobiologists is to characterize extraterrestrial environments to determine if life could exist there. However, there are still unresolved questions about the range of conditions under which life can survive and thrive. Placing better constraints on this will help astrobiologists search for life beyond Earth.
To get a better understanding of how ecosystems can exist beneath the ocean floor (so far from the Sun) a team of researchers led by the University of Rhode Island’s Graduate School of Oceanography (GSO) conducted a study on microbes in ancient seafloor sediment. What they found, to their surprise, was that these lifeforms are sustained primarily by chemicals created by the natural irradiation of water molecules.
Continue reading “Microbes Found That Survive on the by-Products of Radioactive Decay”