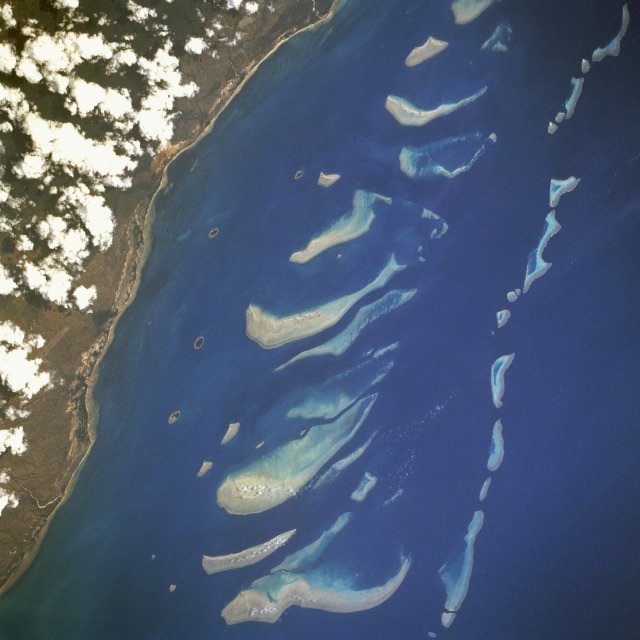
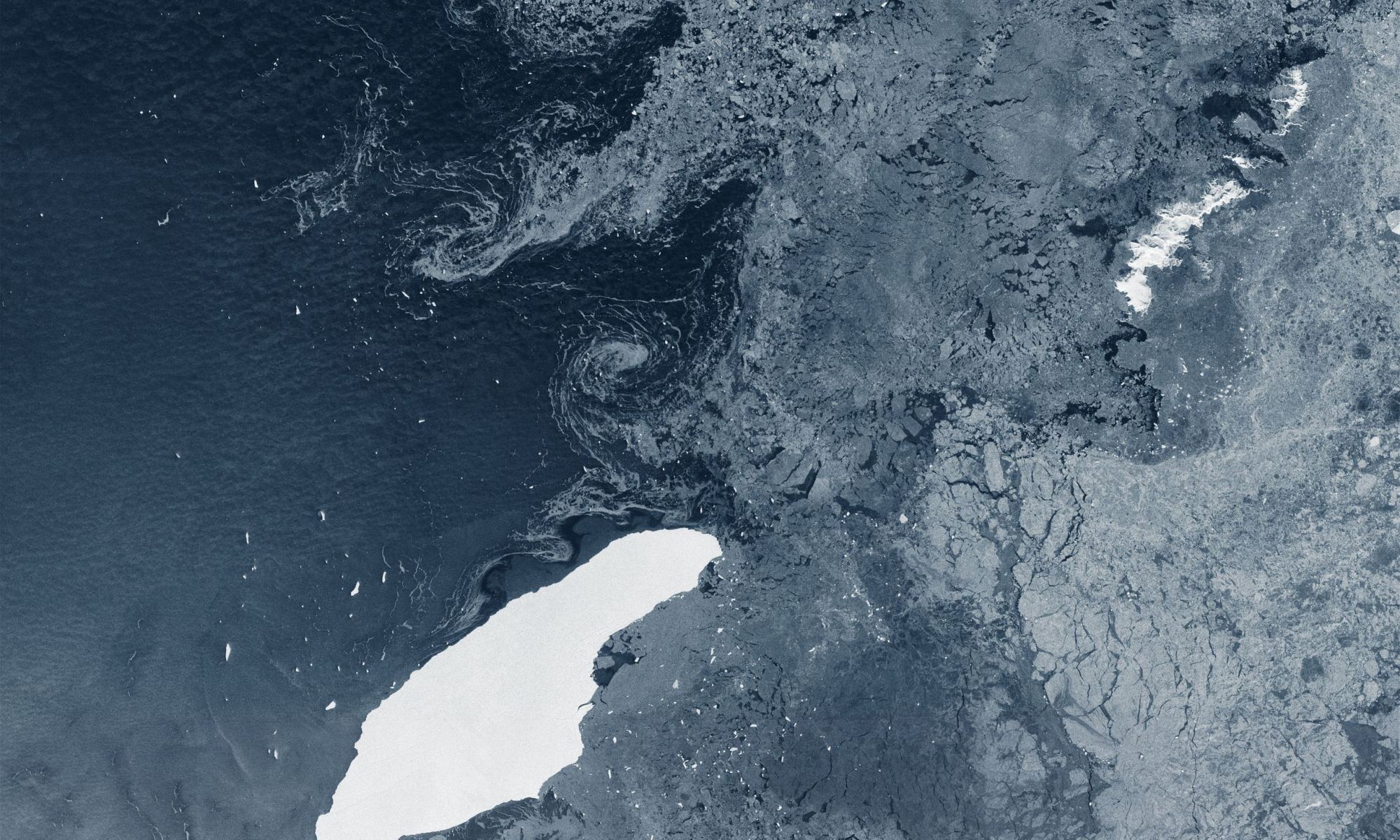
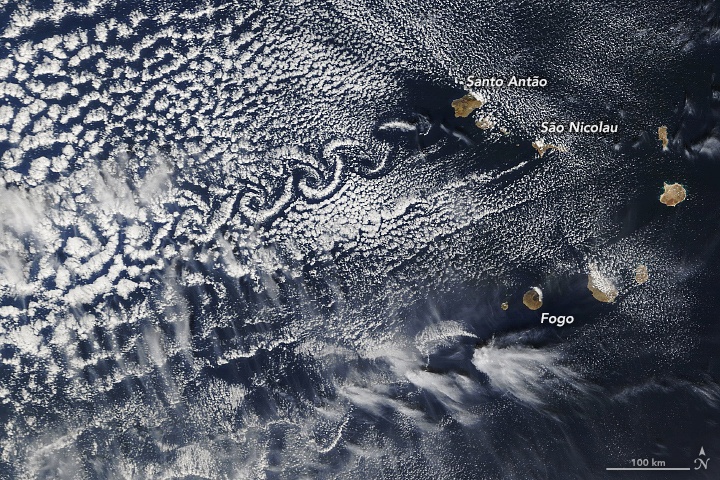
This is an image of some of the islands that make up the nation of Cape Verde. While most in that group of ten islands are flat, some are very tall: Fogo, Santa Antão, and São Nicolau. Those three stand well above their compatriots, with Fogo reaching an altitude of 2,829 metres (9,281 feet).
The three tall volcanic islands sometimes interact with the wind to create von Kármán vortices, also called von Kármán vortex streets.
Continue reading “These Bizarre Cloud Patterns are von Kármán’s Vortices, Caused by the air Wrapping Around Tall Islands”



![This illustration shows the percentage of marine animals that went extinct during Earth's worst extinction at the end of the Permian era by latitude, from the model (black line) and from the fossil record (blue dots).A greater percentage of marine animals survived in the tropics than at the poles. The color of the water shows the temperature change, with red being most severe warming and yellow less warming. At the top is the supercontinent Pangaea, with massive volcanic eruptions emitting carbon dioxide. The images below the line represent some of the 96 percent of marine species that died during the event. [Includes fossil drawings by Ernst Haeckel/Wikimedia; Blue crab photo by Wendy Kaveney/Flickr; Atlantic cod photo by Hans-Petter Fjeld/Wikimedia; Chambered nautilus photo by John White/CalPhotos.]Justin Penn and Curtis Deutsch/University of Washington](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Penn_sumfig_final.jpg)