As the COVID-19 disease continues to wreak its viral havoc on the human population of Earth, governments around the world have closed their schools, shut down non-essential businesses, and told their citizens to stay at home as much as possible. In other words, there’s a lot less human activity on our planet, and it’s led to a detectable drop in seismic activity.
Continue reading “Thanks to COVID-19, nothing’s moving, and seismologists can tell”During Mass Extinction Events, Volcanoes Were Releasing About the Same Amount of CO2 as We Are Today
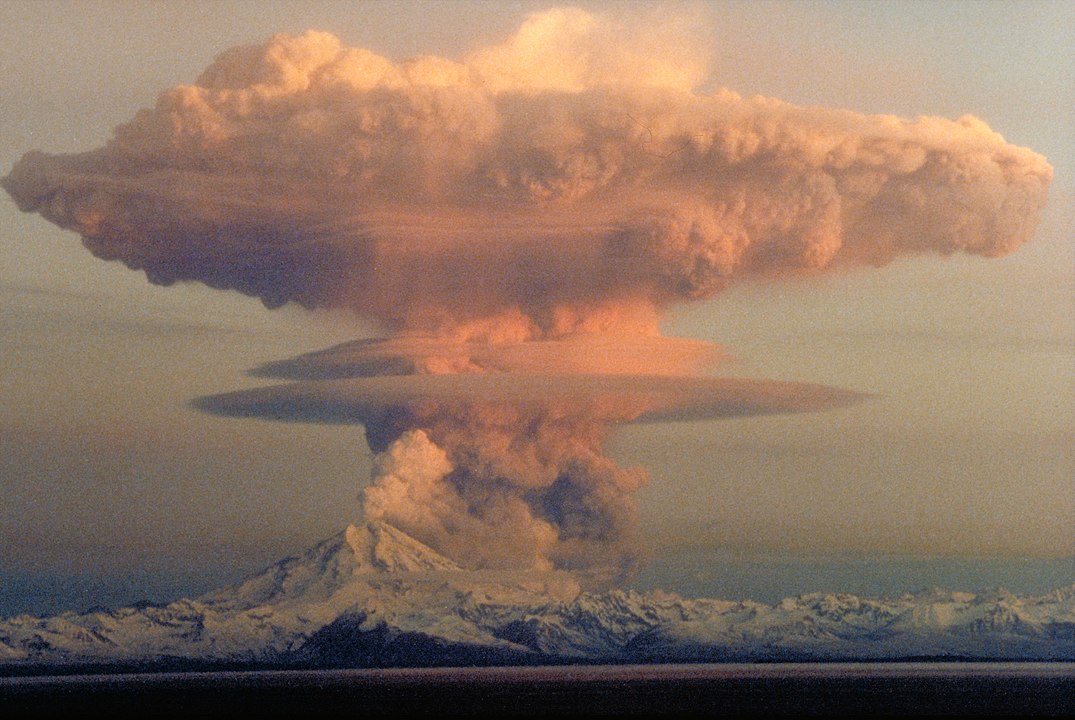

200 million years ago, a mass extinction event wiped out about 76% of all species on Earth—both terrestrial and marine. That event was called the end-Triassic extinction, or the Jurassic-Triassic (J-T) extinction event. At that time, the world experienced many of the same things as Earth is facing now, including a warming climate and the acidification of the oceans.
A new paper shows that pulses of volcanic eruptions were responsible, and that those pulses released the same amount of CO2 as humans are releasing today.
Continue reading “During Mass Extinction Events, Volcanoes Were Releasing About the Same Amount of CO2 as We Are Today”When Comets Break Up, the Fragments Can Be Devastating If They Hit the Earth

Comet breakups are a timely topic right now. The interstellar comet 2I/Borisov just broke into at least two pieces. And though that comet is speeding out of the Solar System, never to be seen again, most of them don’t leave the Solar System. Most of them orbit the Sun, and return to the inner Solar System again and again.
A new paper examines the potential hazard to Earth from comets that break into pieces. The author makes the case that comet breakups could have had a hand in shaping the ebb and flow of life on Earth. It could happen again.
Continue reading “When Comets Break Up, the Fragments Can Be Devastating If They Hit the Earth”Seriously, Life Really Does Get Around. It was Found in Rocks Deep Beneath the Seafloor
After a lot of hard work spanning many years, a team of scientists have discovered something surprising. They’ve found abundant bacterial life in tiny cracks in undersea volcanic rock in the Earth’s crust. The bacteria are thriving in clay deposits inside these tiny cracks.
This discovery is generating new excitement around the hope of finding life on Mars.
Continue reading “Seriously, Life Really Does Get Around. It was Found in Rocks Deep Beneath the Seafloor”New Study Shows the Earth and Moon are not so Similar After All
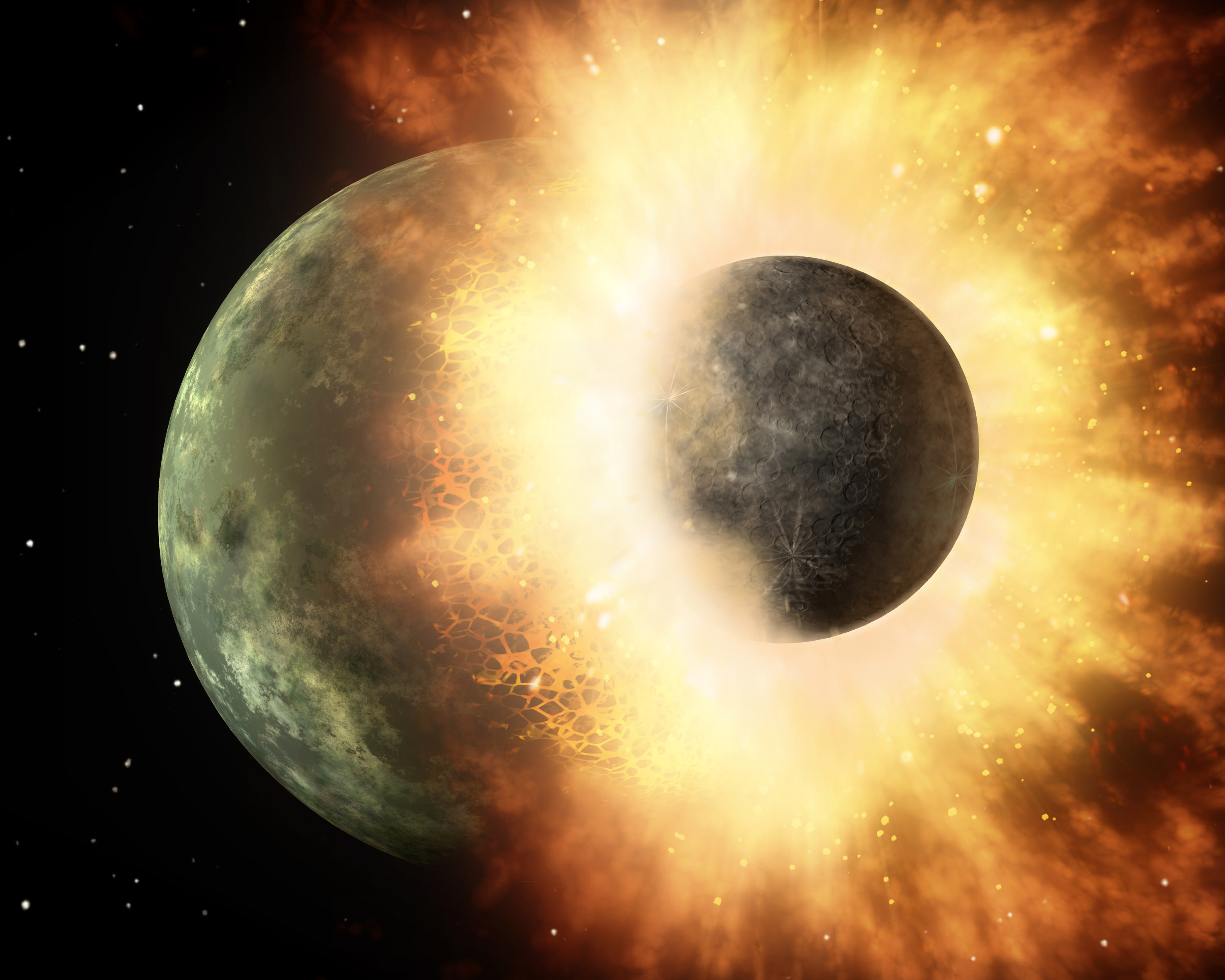

According to the most widely-accepted theory, the Moon formed roughly 4.5 billion years ago when a Mars-sized object named Theia collided with Earth (aka. the Giant Impact Hypothesis). This impact threw up considerable amounts of debris which gradually coalesced to form Earth’s only natural satellite. One of the most compelling proofs for this theory is the fact that the Earth and the Moon are remarkably similar in terms of composition.
However, previous studies involving computer simulations have shown that if the Moon were created by a giant impact, it should have retained more material from the impactor itself. But according to a new study conducted by a team from the University of New Mexico, it is possible that the Earth and the Moon are not as similar as previously thought.
Continue reading “New Study Shows the Earth and Moon are not so Similar After All”Greenland and Antarctica are Losing Their Ice 6 Times Faster than in the 1990s
70 Million Years Ago, Days Were 30 Minutes Shorter, According to this Ancient Clam
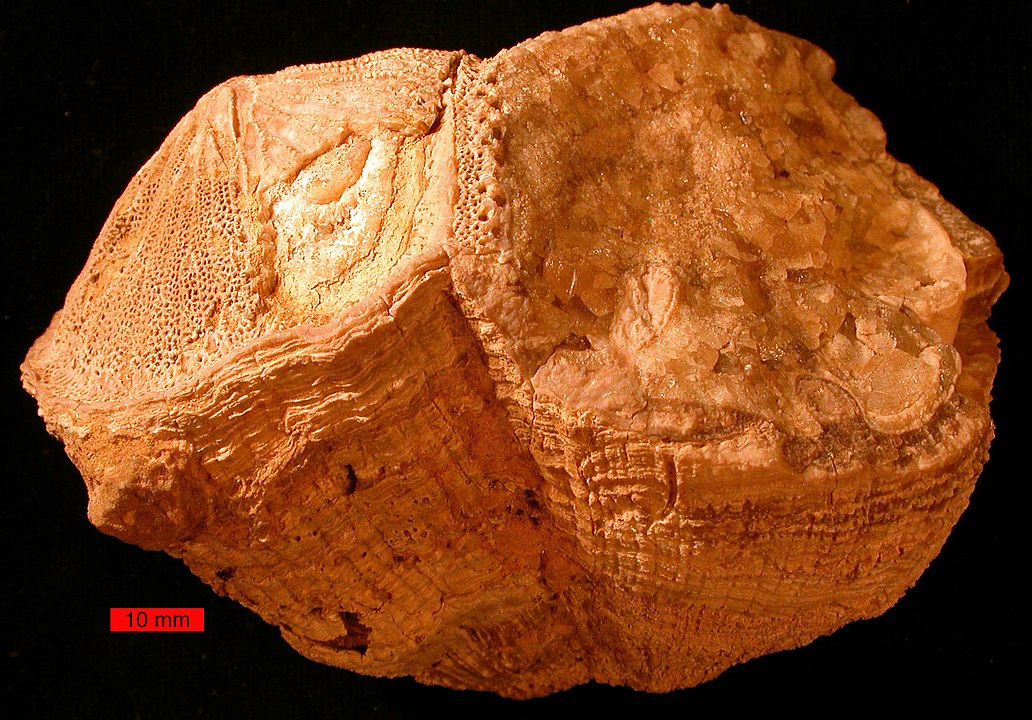

Has humanity been doing it all wrong? We’re busy staring off into space with our futuristic, ultra-powerful telescopes, mesmerized by ethereal nebulae and other wondrous objects, and trying to tease out the Universe’s well-kept secrets. Turns out, humble, ancient clams have something to tell us, too.
Continue reading “70 Million Years Ago, Days Were 30 Minutes Shorter, According to this Ancient Clam”Phew, Earth-Watching DSCOVR is Operational Again

Rejoice! If you’ve missed your daily fix of seeing views of our rotating Earth from space, NOAA announced that its Deep Space Climate Observatory (DSCOVR) is now back in action. The deep space satellite, which produces incredible full-disk images of our Blue Marble, has been offline since June 27, 2019 because of a problem with the spacecraft’s attitude control system. But NOAA and NASA engineers developed and uploaded a software patch to restore DSCOVR’s operations.
Continue reading “Phew, Earth-Watching DSCOVR is Operational Again”3 Billion Years Ago, the World Might Have Been a Waterworld, With No Continents At All

Evidence from an ancient section of the Earth’s crust suggest that Earth was once a water-world, some three billion years ago. If true, it’ll mean scientists need to reconsider some thinking around exoplanets and habitability. They’ll also need to reconsider their understanding of how life began on our planet.
Continue reading “3 Billion Years Ago, the World Might Have Been a Waterworld, With No Continents At All”A Picture of Earth’s New Temporary Moon
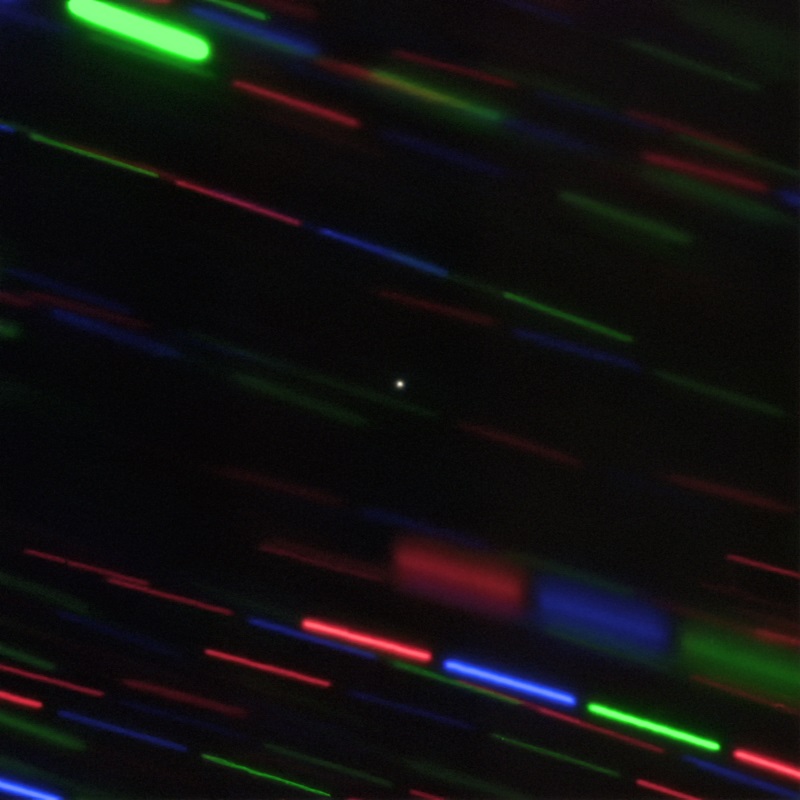
With the excitement and interest in the newly discovered ‘mini-moon’ found orbiting Earth, astronomers quickly set their sights on trying to get more details, to determine what this object actually is.
Using the Gemini Observatory in Hawaii, a group of astronomers captured a clearer view of this so-called Temporarily Captured Object (TCO), named 2020 CD3. The image, above, was obtained on February 24, 2020. It shows a tiny pinpoint of light against trailing stars.
Continue reading “A Picture of Earth’s New Temporary Moon”