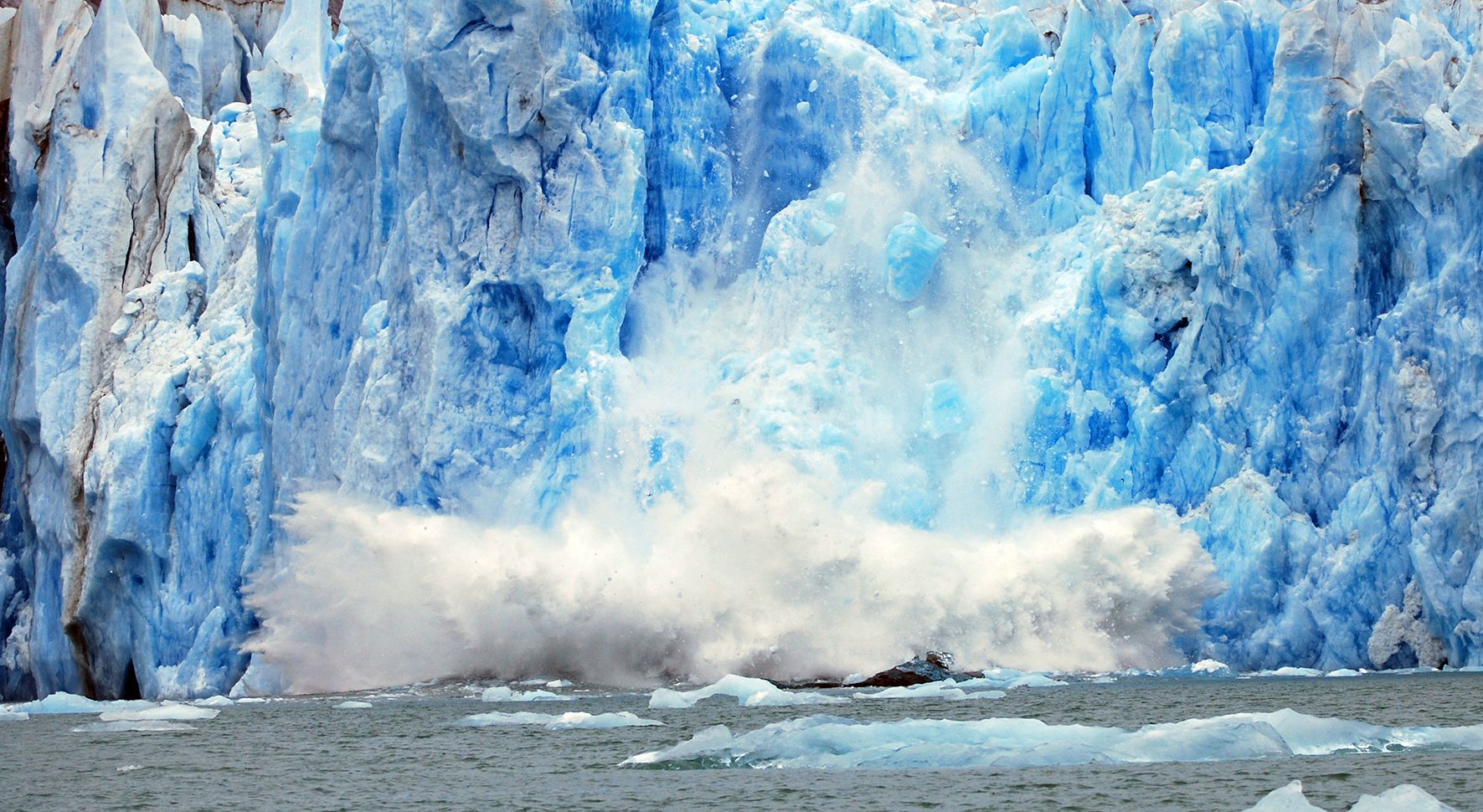
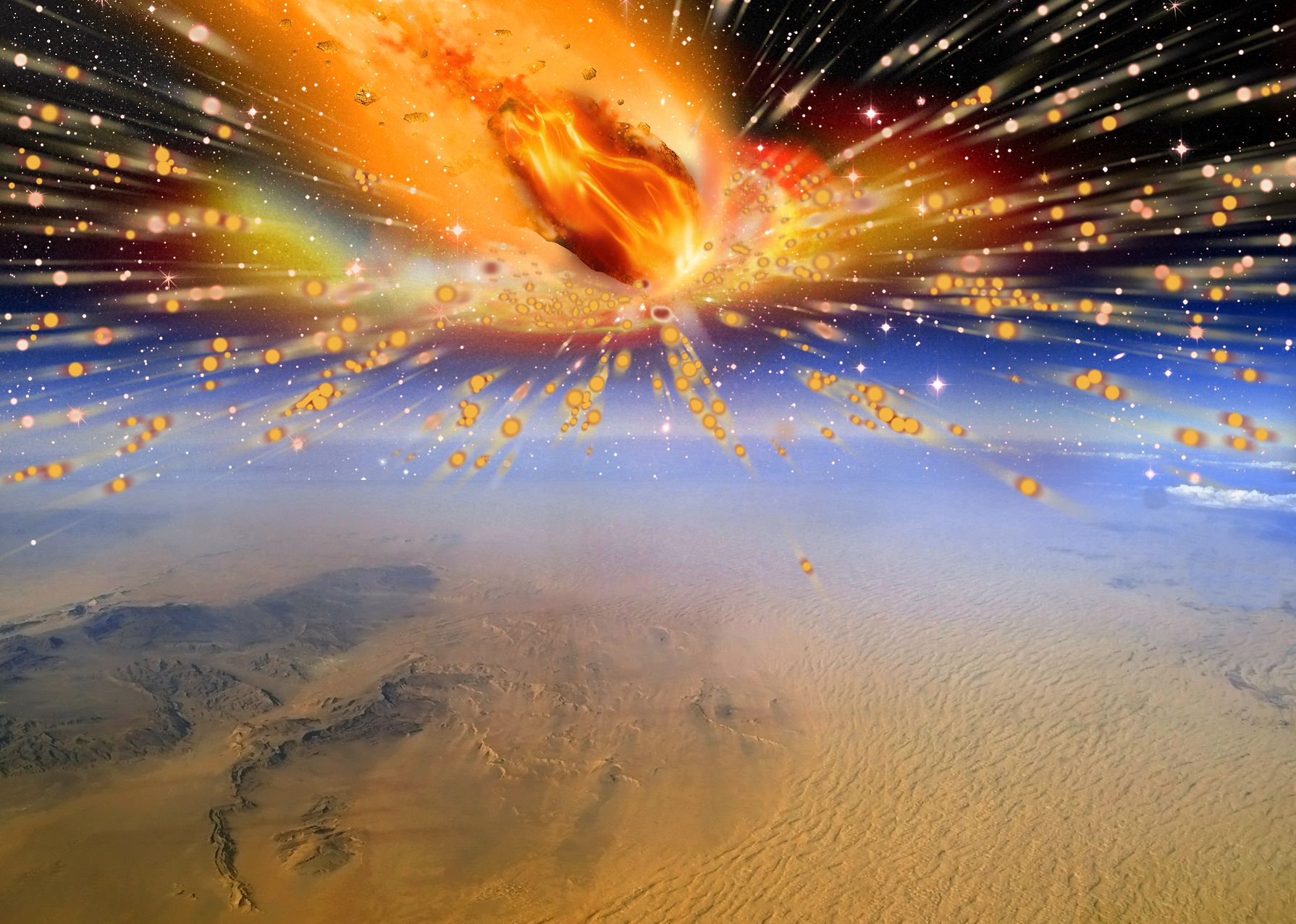
The Earth wasn’t formed containing the necessary chemicals for life to begin. One well-supported theory, called the “late veneer theory”, suggests that the volatile chemicals needed for life arrived long after the Earth formed, brought here by meteorites. But a new study challenges the late veneer theory.
Evidence shows that the Moon was created when a Mars-sized planet named Theia collided with the Earth. The impact created a debris ring out of which the Moon formed. Now, this new study says that same impact may have delivered the necessary chemicals for life to the young Earth.





![This illustration shows the percentage of marine animals that went extinct during Earth's worst extinction at the end of the Permian era by latitude, from the model (black line) and from the fossil record (blue dots).A greater percentage of marine animals survived in the tropics than at the poles. The color of the water shows the temperature change, with red being most severe warming and yellow less warming. At the top is the supercontinent Pangaea, with massive volcanic eruptions emitting carbon dioxide. The images below the line represent some of the 96 percent of marine species that died during the event. [Includes fossil drawings by Ernst Haeckel/Wikimedia; Blue crab photo by Wendy Kaveney/Flickr; Atlantic cod photo by Hans-Petter Fjeld/Wikimedia; Chambered nautilus photo by John White/CalPhotos.]Justin Penn and Curtis Deutsch/University of Washington](https://www.universetoday.com/wp-content/uploads/2018/12/Penn_sumfig_final.jpg)



