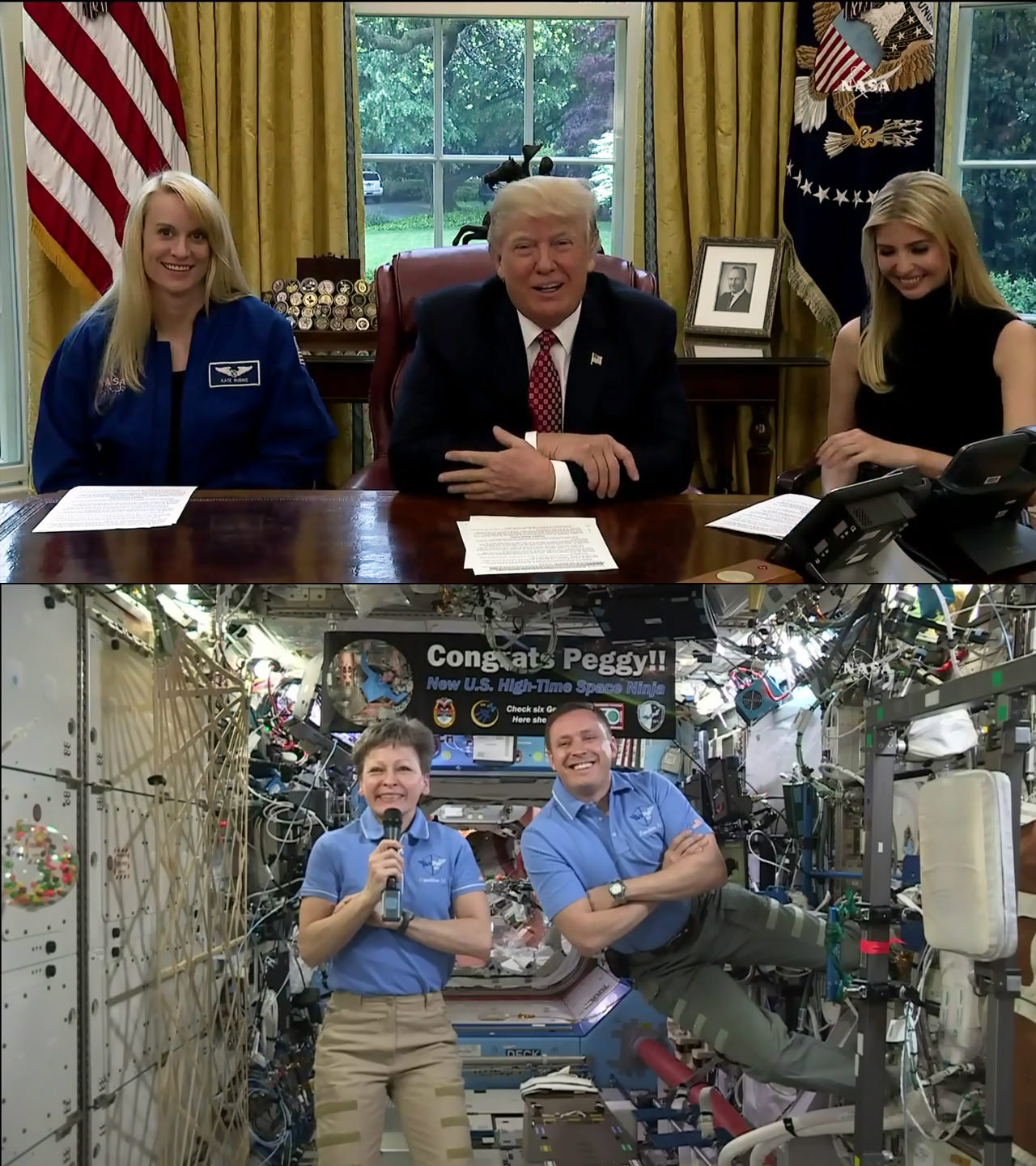
NASA Astronaut Peggy Whitson set the endurance record for time in space by a U.S, astronaut today, Monday, April 24, during her current stint of living and working aboard the International Space Station (ISS) along with her multinational crew of five astronauts and cosmonauts.
Furthermore Whitson received a long distance phone call of exuberant congratulations from President Donald Trump, First Daughter Ivanka Trump, and fellow astronaut Kate Rubins direct from the Oval Office in the White House to celebrate the momentous occasion.
“This is a very special day in the glorious history of American spaceflight!” said President Trump during the live phone call to the ISS broadcast on NASA TV.
As of today, Whitson exceeded 534 cumulative days in space by an American astronaut, breaking the record held by NASA astronaut Jeff Williams.
“Today Commander Whitson you have broken the record for the most total time spent in space by an American astronaut. 534 days and counting,” elaborated President Trump.
“That’s an incredible record to break. And on behalf of the nation and frankly the world I would like to congratulate you. That is really something!”
“You’re an incredible inspiration to us all.”
Trump noted that thousands of school students were listening in to the live broadcast which also served to promote students to study STEM subjects.
“Peggy is a phenomenal role model for young women, and all Americans, who are exploring or participating in STEM education programs and careers,” said President Trump.
“As I have said many times before, only by enlisting the full potential of women in our society will we be truly able to make America great again. When I signed the INSPIRE Women Act in February, I did so to ensure more women have access to STEM education and careers, and to ensure America continues to benefit from the contributions of trailblazers like Peggy.”
How does it feel to break the endurance record? Trump asked Whitson.
“It’s actually a huge honor to break a record like this, but it’s an honor for me basically to be representing all the folks at NASA who make this spaceflight possible and who make me setting this record feasible,” Whitson replied from orbit to Trump.
“And so it’s a very exciting time to be at NASA. We are all very much looking forward, as directed by your new NASA bill — we’re excited about the missions to Mars in the 2030s. And so we actually, physically, have hardware on the ground that’s being built for the SLS rocket that’s going to take us there.”
“It’s a very exciting time, and I’m so proud of the team.”
“We have over 200 investigations ongoing onboard the space station, and I just think that’s a phenomenal part of the day.”
NASA astronaut Jack Fischer is also serving aboard the station on his rookie flight and also took part in the phone call with President Trump.
Whitson is currently serving as Space Station Commander of Expedition 51. She most recently launched to the ISS on Nov 17, 2016 aboard a Russian Soyuz capsule from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan, as part of a three person crew.
At the time of her Soyuz launch she had accumulated 377 total days in space.
She holds several other prestigious records as well. Whitson is the first woman to serve twice as space station commander.
Indeed in 2008 Whitson became the first woman ever to command the space station during her prior stay on Expedition 16 a decade ago. Her second stint as station commander began earlier this month on April 9.
Whitson also holds the record for most spacewalks by a female astronaut. Altogether she has accumulated 53 hours and 23 minutes of EVA time over eight spacewalks.
Overall, Expedition 51 involved her third long duration stay aboard the massive orbiting laboratory complex.
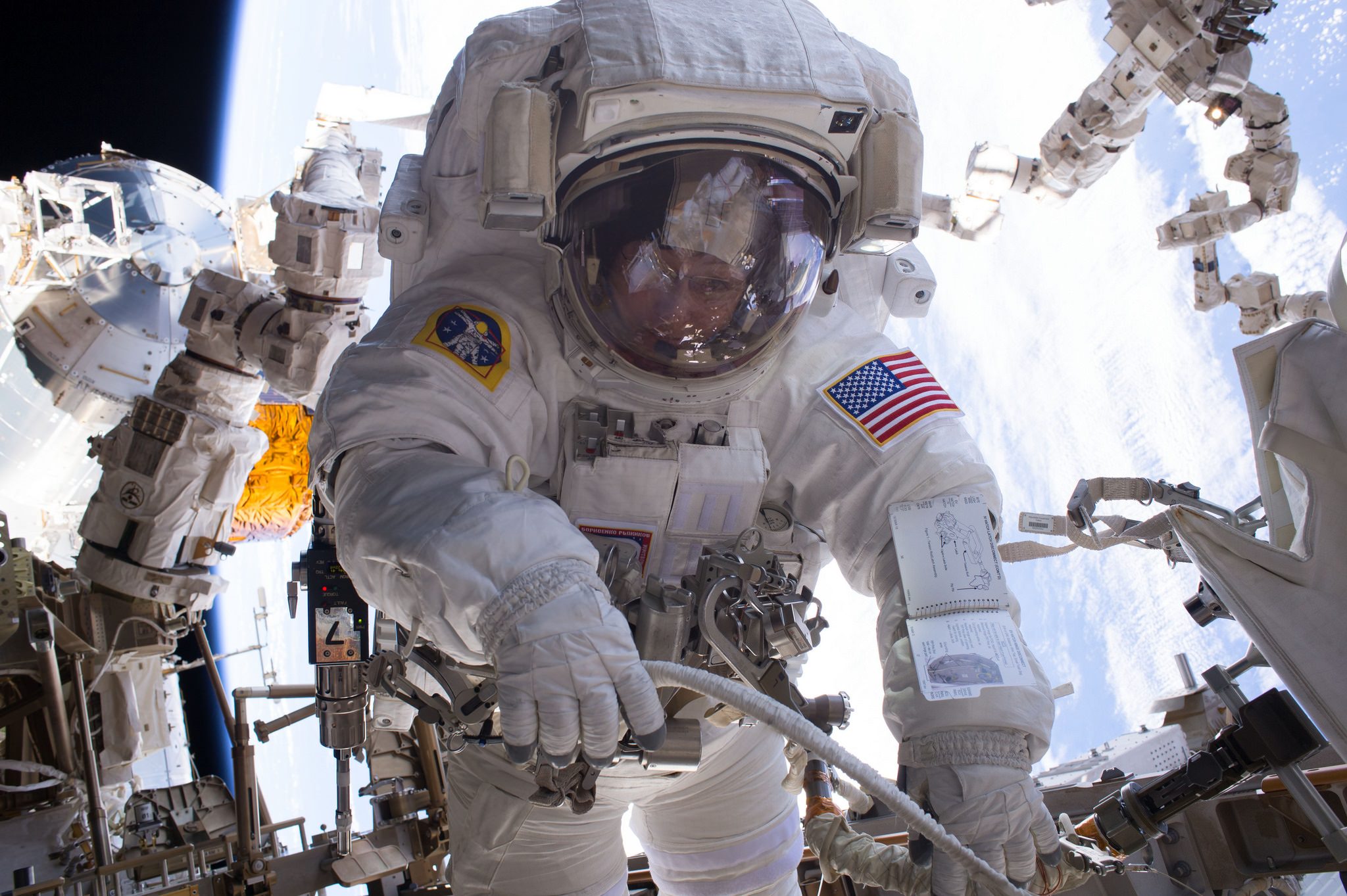

“This is an inspirational record Peggy is setting today, and she would be the first to tell you this is a record that’s absolutely made to be broken as we advance our knowledge and existence as both Americans and humans,” said NASA acting Administrator Robert Lightfoot, in a statement.
“The cutting-edge research and technology demonstrations on the International Space Station will help us go farther into our solar system and stay there longer, as we explore the mysteries of deep space first-hand. Congratulation to Peggy, and thank you for inspiring not only women, but all Americans to pursue STEM careers and become leaders.”
When she returns to Earth in September she will have accumulated some 666 days in space.
Trump made note of the science and commercial industrial work being carried out aboard the station.
“Many American entrepreneurs are racing into space. I have many friends that are so excited about space. They want to get involved in space from the standpoint of entrepreneurship and business,” said President Trump.
“And I’m sure that every student watching wants to know, what is next for Americans in space.”
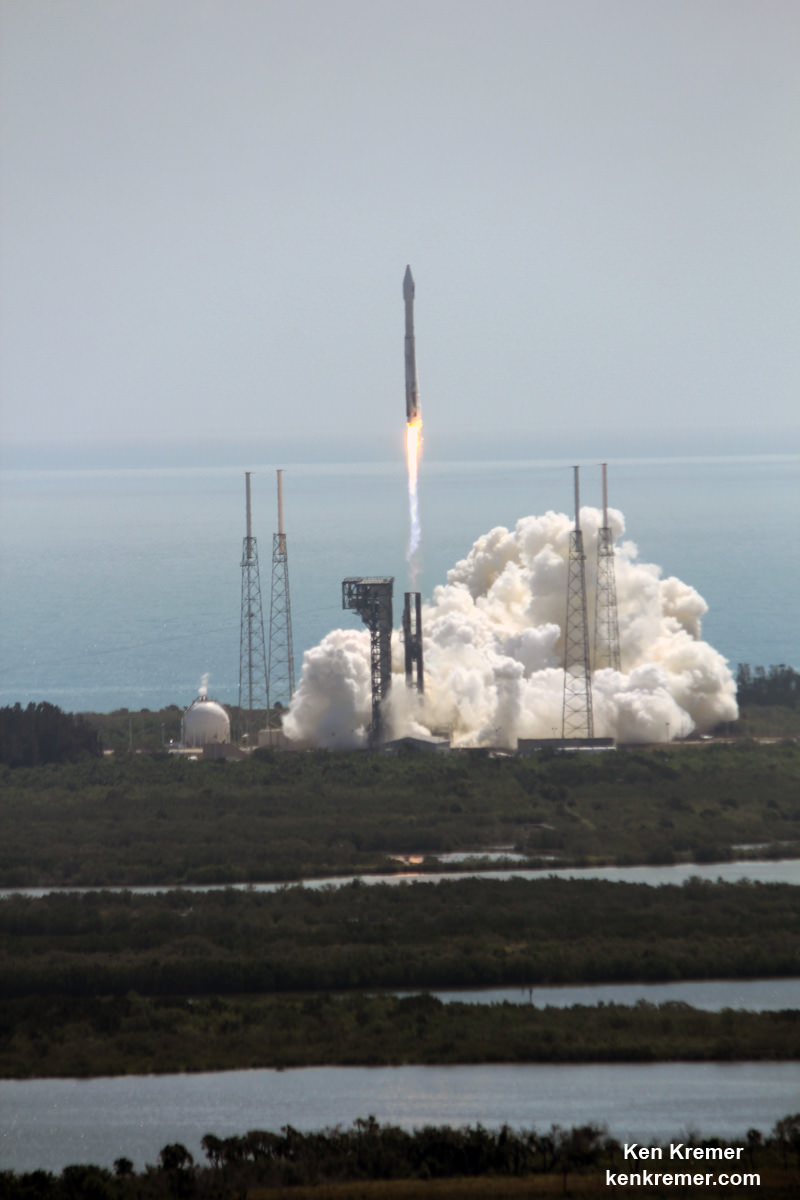
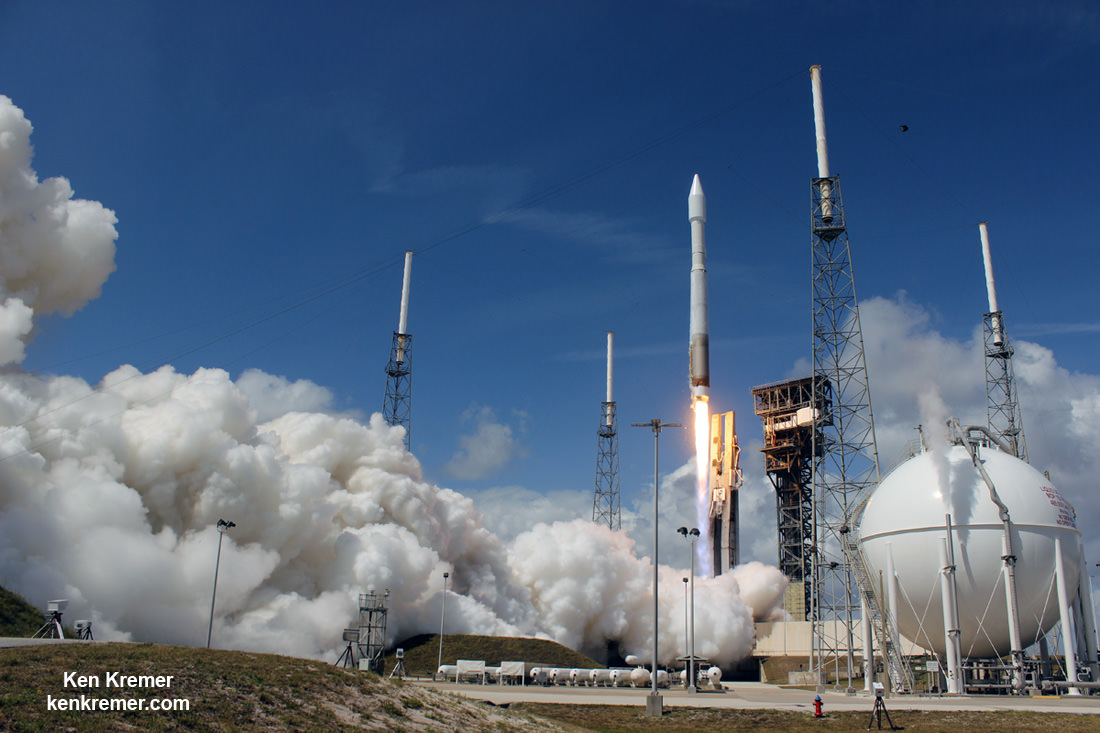
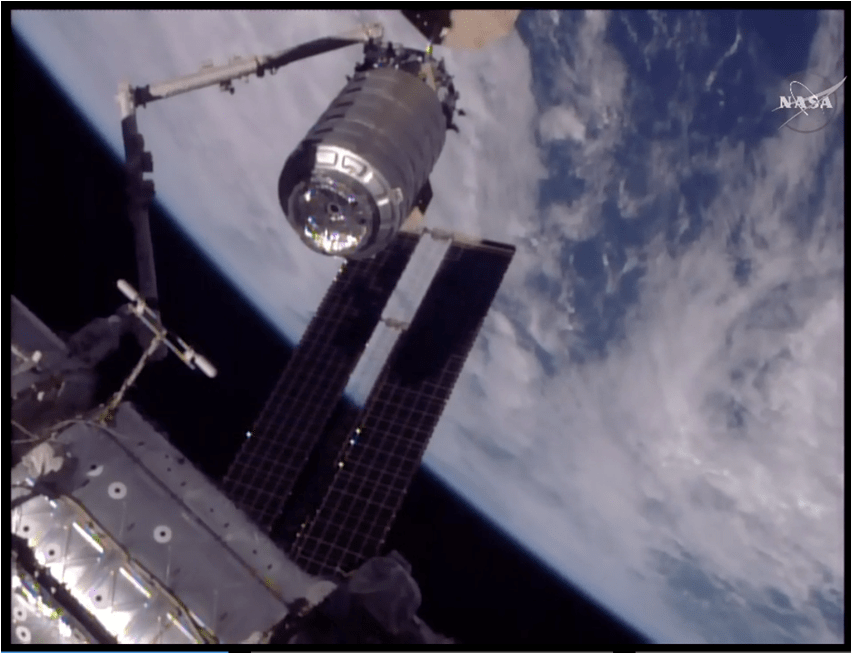
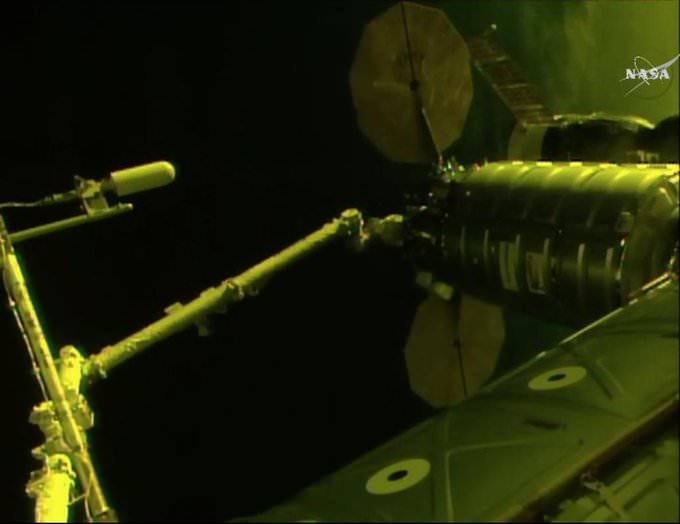
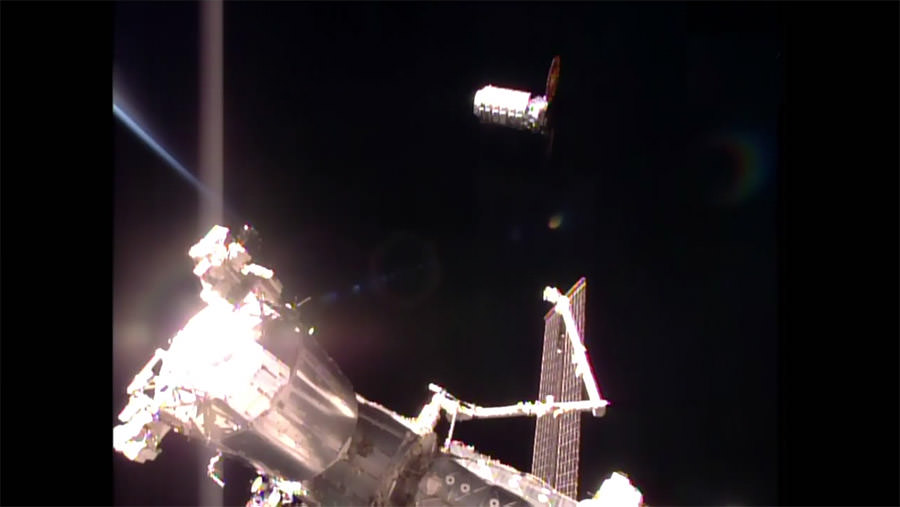
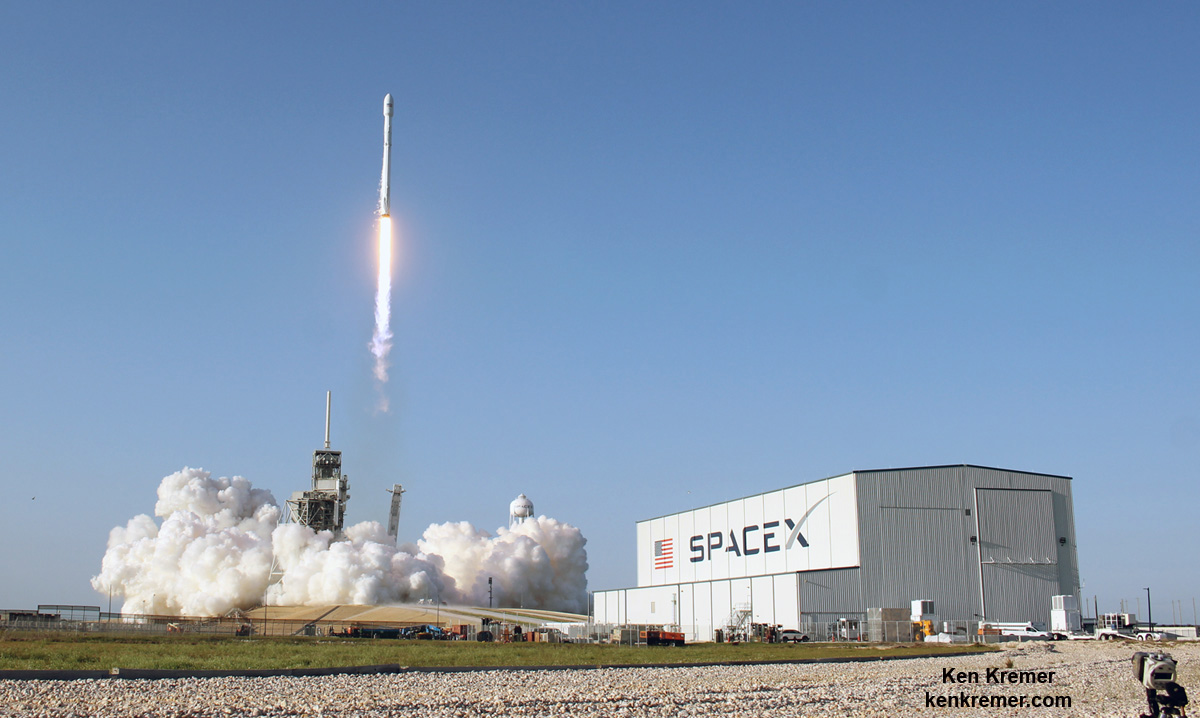
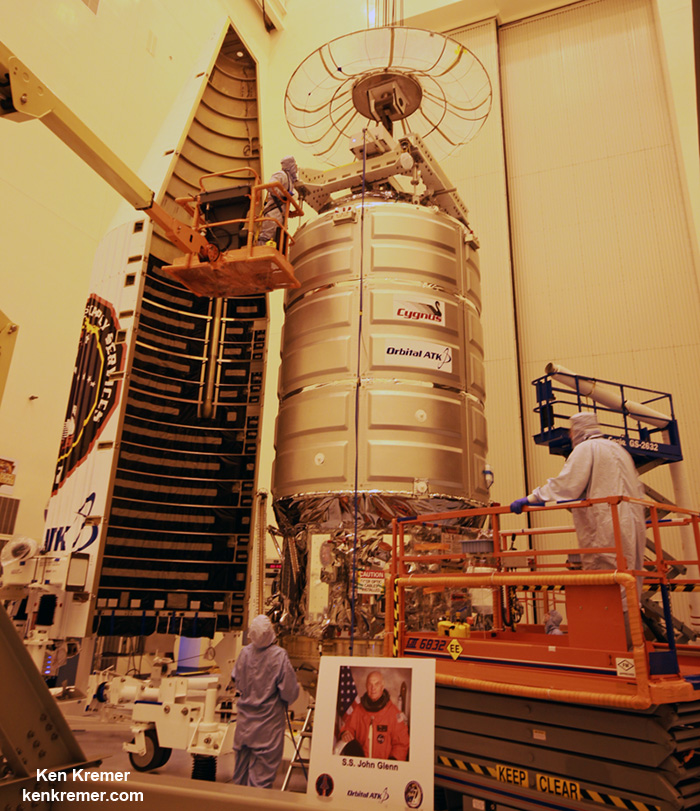
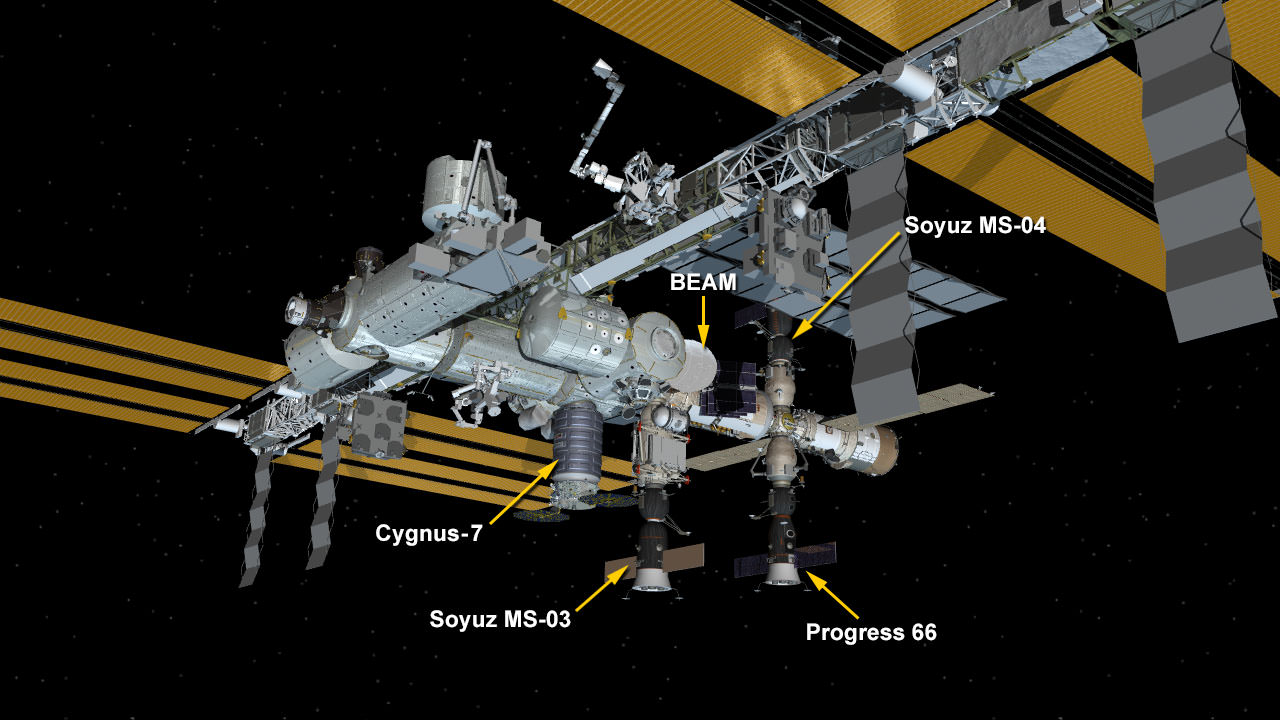
Indeed the private SS John Glenn Cygnus cargo freighter just arrived at the ISS on Saturday, April 22, carrying nearly 4 tons or science experiments, hardware, parts and provisions.
Whitson was one of two ISS astronauts involved in capturing Cygnus with the Canadian built robotic arm for attachment to the stations Unity node.
Trump also mentioned his strong support for sending humans on a mission to Mars in the 2030s and for NASA’s development of the SLS heavy lift rocket and Orion deep space capsule.
“I’m very proud that I just signed a bill committing NASA to the aim of sending America astronauts to Mars. So we’ll do that. I think we’ll do it a lot sooner than we’re even thinking.”
“Well, we want to try and do it during my first term or, at worst, during my second term. So we’ll have to speed that up a little bit, okay?”
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and Planetary science and human spaceflight news.