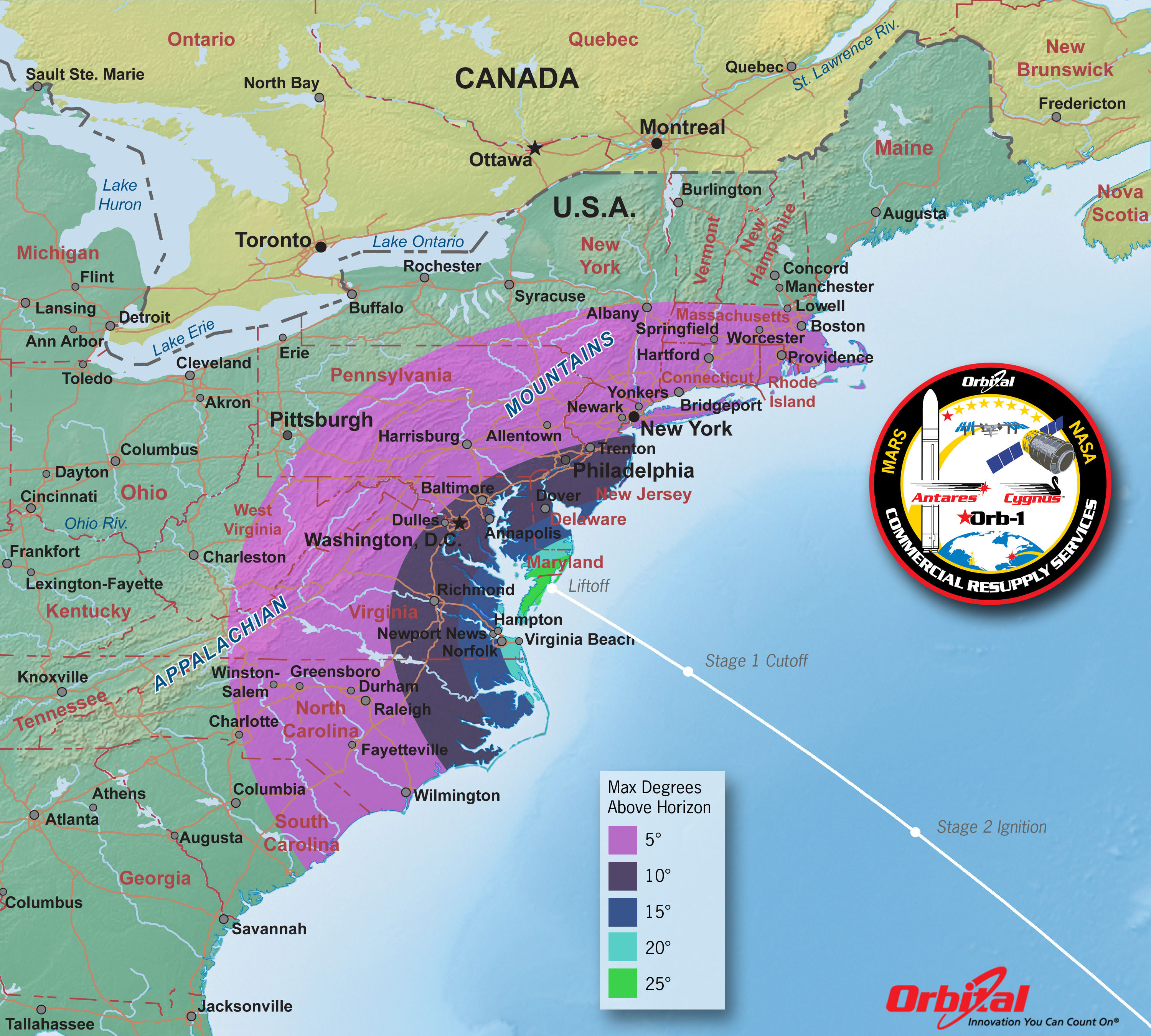
Antares Launch – Maximum Elevation Map
The Antares nighttime launch will be visible to millions of spectators across a wide area of the Eastern US -weather permitting. This map shows the maximum elevation (degrees above the horizon) that the Antares rocket will reach during the Dec 19, 2013 launch depending on your location along the US east coast. Credit: Orbital Sciences[/caption]
UPDATE: The launch of Cygnus has been delayed until no earlier than January 7, 2014 due to the coolant leak at the International Space Station and necessary spacewalks to fix the problem. You can read more about the issue here and here.
WALLOPS ISLAND, VA – Orbital Sciences Corp. is marching forward with plans for a spectacular night blastoff of the firms privately developed Antares rocket and Cygnus cargo spacecraft on Thursday, Dec. 19 from a seaside pad at Wallops Island, Virginia on a mission for NASA that’s bound for the International Space Station (ISS).
The nighttime Antares liftoff is currently scheduled for prime time – at 9:19 p.m. EST from Launch Pad 0A at the Mid-Atlantic Regional Spaceport (MARS) at NASA Wallops Island, Virginia. It should be easily visible to tens of millions of residents along a wide swath of the US East Coast spanning from South Carolina to southern Maine – weather permitting.
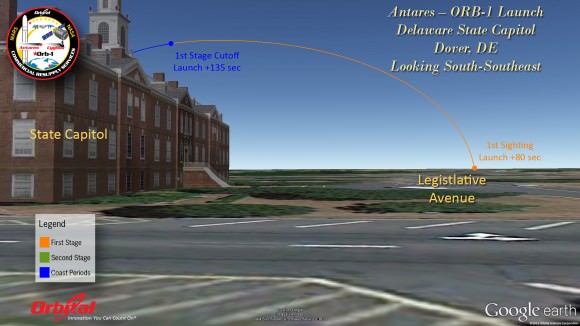
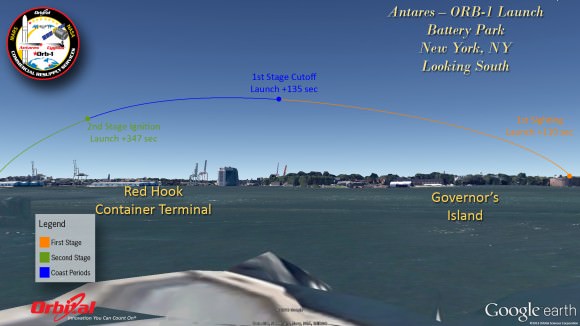
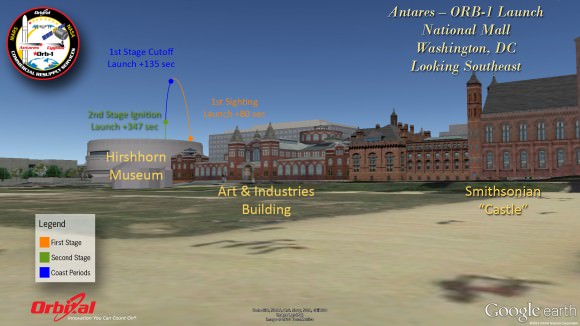
Here’s our guide on “How to See the Antares/Cygnus Dec. 19 Night Launch” – with your own eyes – complete with viewing maps and trajectory graphics from a variety of prime viewing locations; including Philadelphia, NYC, Baltimore and historic landmarks in Washington, DC.
Update: launch postponed to mid-January 2014 to allow NASA astronauts to conduct 3 EVA’s to swap out the ammonia pump module and restore full cooling capacity to the ISS
It will be visible to spectators inland as well, stretching possibly into portions of West Virginia and western Pennsylvania.
For example; Here’s the expected view from Rocky’s famous workout on the steps of the Philadelphia Art Museum.

The viewing maps are courtesy of Orbital Sciences, the private company that developed both the Antares rocket and Cygnus resupply vessel aimed at keeping the ISS fully stocked and operational for science research.
Up top is the map showing the maximum elevation the rocket will reach in the eastern United States.

The flight is designated the Orbital-1, or Orb-1 mission.
Orb-1 is the first of eight commercial cargo resupply missions to the ISS by Orbital according to its Commercial Resupply Services (CRS) contract with NASA.
Of course you can still view the launch live via the NASA TV webcast.
This marks the maiden night launch of the two stage Antares rocket following a pair of daytime test and demonstration launches earlier this year, in April and September.
It’s important to note that the Dec. 19 liftoff is still dependent on NASA engineers resolving the significant issue with the ammonia cooling system that popped up late last week when a critical flow control valve malfunctioned.
If the pump valve can’t be brought back online, two American astronauts may make two or three unscheduled spacewalks starting later this week.
So in the event spacewalks are required, Antares launch could still slip a few days to the end of the launch window around Dec. 21 or Dec. 22. Thereafter the launch would be postponed until January 2014.
Here’s your chance to witness a mighty rocket launch – from the comfort of your home and nearby locations along the east coast.
And its smack dab in the middle of the Christmas and holiday season resplendent with shining bright lights.
Weather outlook appears rather promising at this time – 95% favorable chance of lift off.
The rocket was rolled out to the Wallops launch pad this morning by Orbital’s technicians.
Cygnus is loaded with approximately 1465 kg (3,230 lbs.) of cargo for the ISS crew for NASA.
NASA Television coverage of the Antares launch will begin at 8:45 p.m. on Dec. 19 – www.nasa.gov/ntv
Stay tuned here for Ken’s Antares launch reports from NASA Wallops Flight Facility, VA.