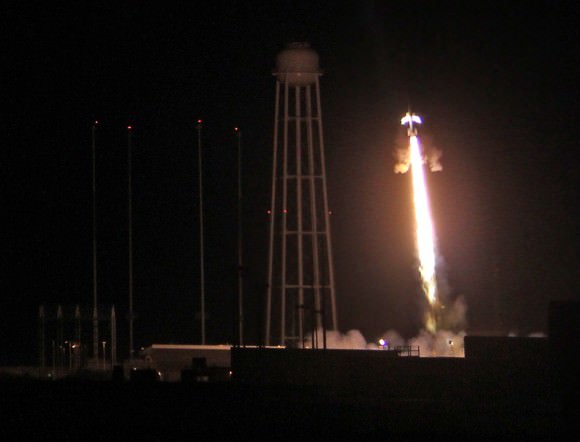
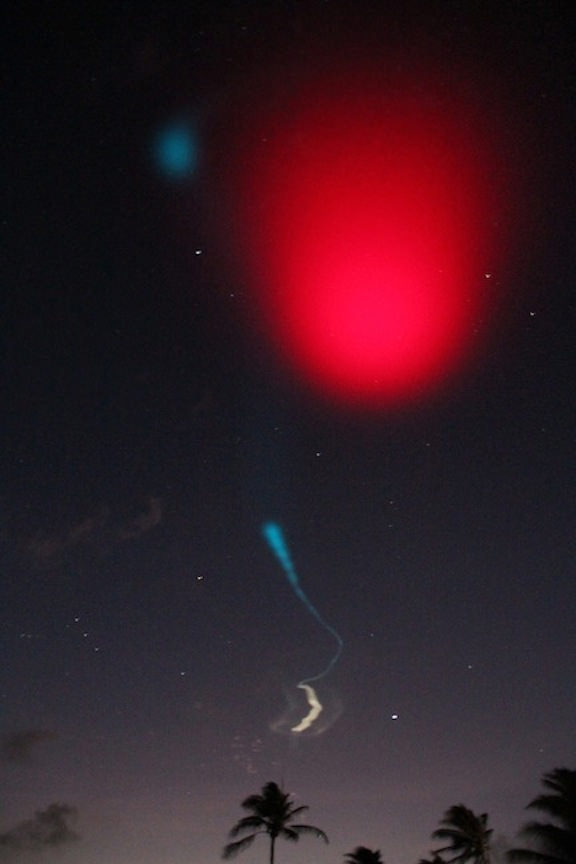
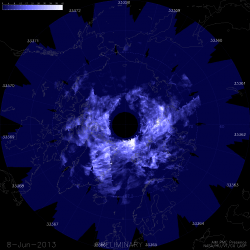
On June 24, 2013 a pair of daytime sounding rockets will launch from NASA Wallops Flight Facility (WFF) and deploy a chemical trail like the one deployed here from a sounding rocket at night. The chemical trail will help researchers track wind movement to determine how it affects the movement of charged particles in the atmosphere. All the colors in the sky shown here, the white and blue streaks, and the larger red blob overhead, are from the chemical trails. Credit: NASA
See Rocket Visibility Maps below[/caption]
NASA WALLOPS, VA – Science and space aficionados are in for rare treat on June 24 when NASA launches a two-rocket salvo from the NASA Wallops Flight Facility, Va. on a mission to study how charged particles in the ionosphere can disrupt communication signals that impact our day to day lives.
It’s a joint project between NASA and the Japanese Space Agency, or Japan Aerospace Exploration Agency, or JAXA.
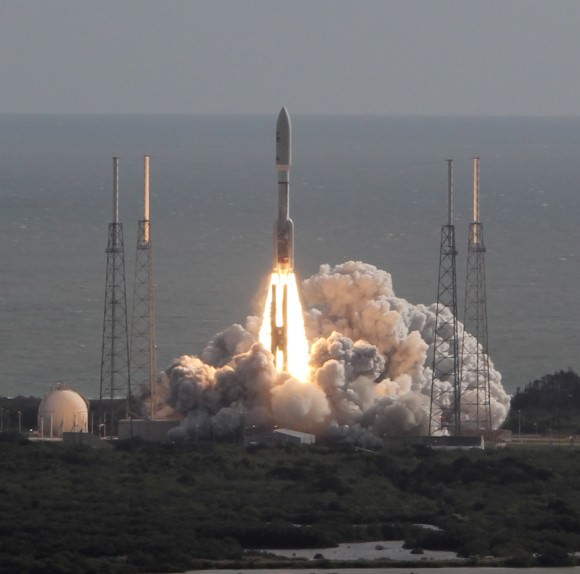
The suborbital sounding rockets will blast off merely 15 seconds apart from a beach-side launch complex directly on Virginia’s Eastern shore on a science mission named the Daytime Dynamo.
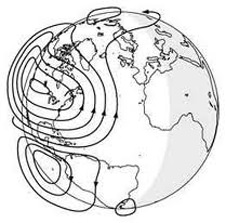
The goal is to study the global electrical current called the dynamo, which sweeps through the ionosphere, a layer of charged particles that extends from about 30 to 600 miles above Earth.
Why should you care?
Because disruptions in the ionosphere can scramble radio wave signals for communications and navigations transmissions from senders to receivers – and that can impact our every day lives.
The experiment involves launching a duo of suborbital rockets and also dispatching an airplane to collect airborne science measurements.
Mission control and the science team will have their hands full coordinating the near simultaneous liftoffs of two different rockets with two different payloads while watching the weather to make sure its optimal to collect the right kind of data that will answer the research proposal.
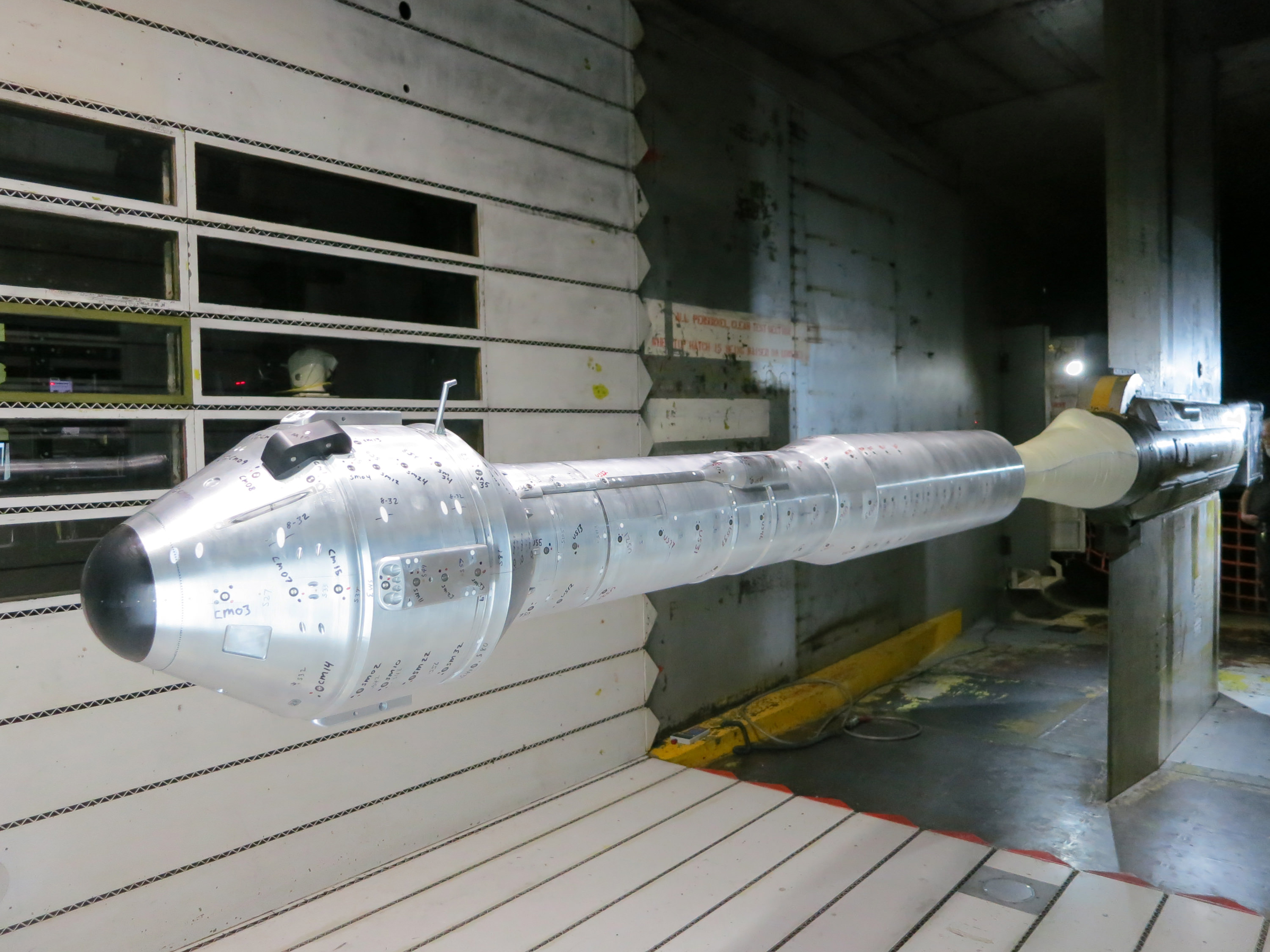
A single-stage Black Brant V will launch first. The 35 foot long rocket will carry a 600 pound payload to collect the baseline data to characterize the neutral and charged particles as it swiftly travels through the ionosphere.
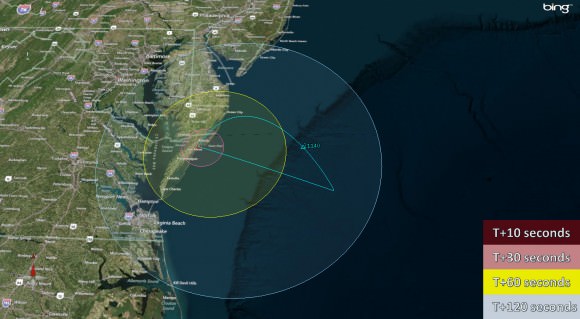
A two-stage Terrier-Improved Orion blasts off just 15 seconds later. The 33 foot long rocket carries a canister of lithium gas. It will shoot out a long trail of lithium gas that creates a chemical trail that will be tracked to determine how the upper atmospheric wind varies with altitude. These winds are believed to be the drivers of the dynamo currents.
Both rockets will fly for about five minutes to an altitude of some 100 miles up in the ionosphere.
Since its daytime the lithium trails will be very hard to discern with the naked eye. That’s why NASA is also using a uniquely equipped NASA King Air airplane outfitted with cameras with special new filters optimized to detect the lithium gas and how it is moved by the winds that generate the global electrical current.
The new technology to make the daytime measurements was jointly developed by NASA, JAXA and scientists at Clemson University.

Sounding rockets are better suited to conduct these studies of the ionosphere compared to orbiting satellites which fly to high.
“The manner in which neutral and ionized gases interact is a fundamental part of nature,” said Robert Pfaff, the principle investigator for the Dynamo sounding rocket at NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center in Greenbelt, Md.
“There could very well be a dynamo on other planets. Jupiter, Saturn, Uranus and Neptune are all huge planets with huge atmospheres and huge magnetic fields. They could be setting up dynamo currents galore.”
The launch window opens at 9:30 a.m. and extends until 11:30 a.m. Back up opportunities are available on June 25 and from June 28 to July 8.
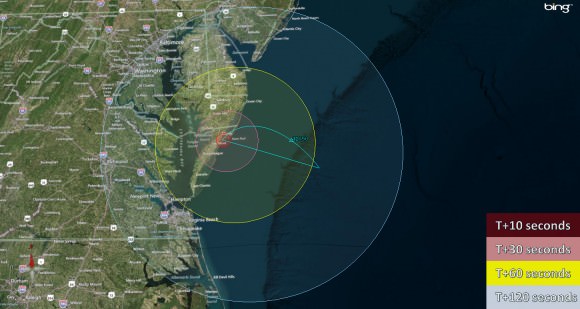
The rockets will be visible to residents in the Wallops region – and also beyond to the US East Coast from parts of North Carolina to New Jersey.
The NASA Wallops Visitor Center will open at 8 a.m. on launch day for viewing the launches.
Live coverage of the June 24 launch is available via NASA Wallops UStream beginning at 8:30 a.m. at: http://www.ustream.tv/channel/nasa-tv-wallops
I will be onsite at Wallops for Universe Today.
And don’t forget to “Send Your Name to Mars” aboard NASA’s MAVEN orbiter- details here. Deadline: July 1, 2013. Launch: Nov. 18, 2013
…………….
Learn more about Earth, Mars, Curiosity, Opportunity, MAVEN, LADEE, Sounding rockets and NASA missions at Ken’s upcoming presentation
June 23: “Send your Name to Mars on MAVEN” and “CIBER Astro Sat, LADEE Lunar & Antares Rocket Launches from Virginia”; Rodeway Inn, Chincoteague, VA, 8 PM