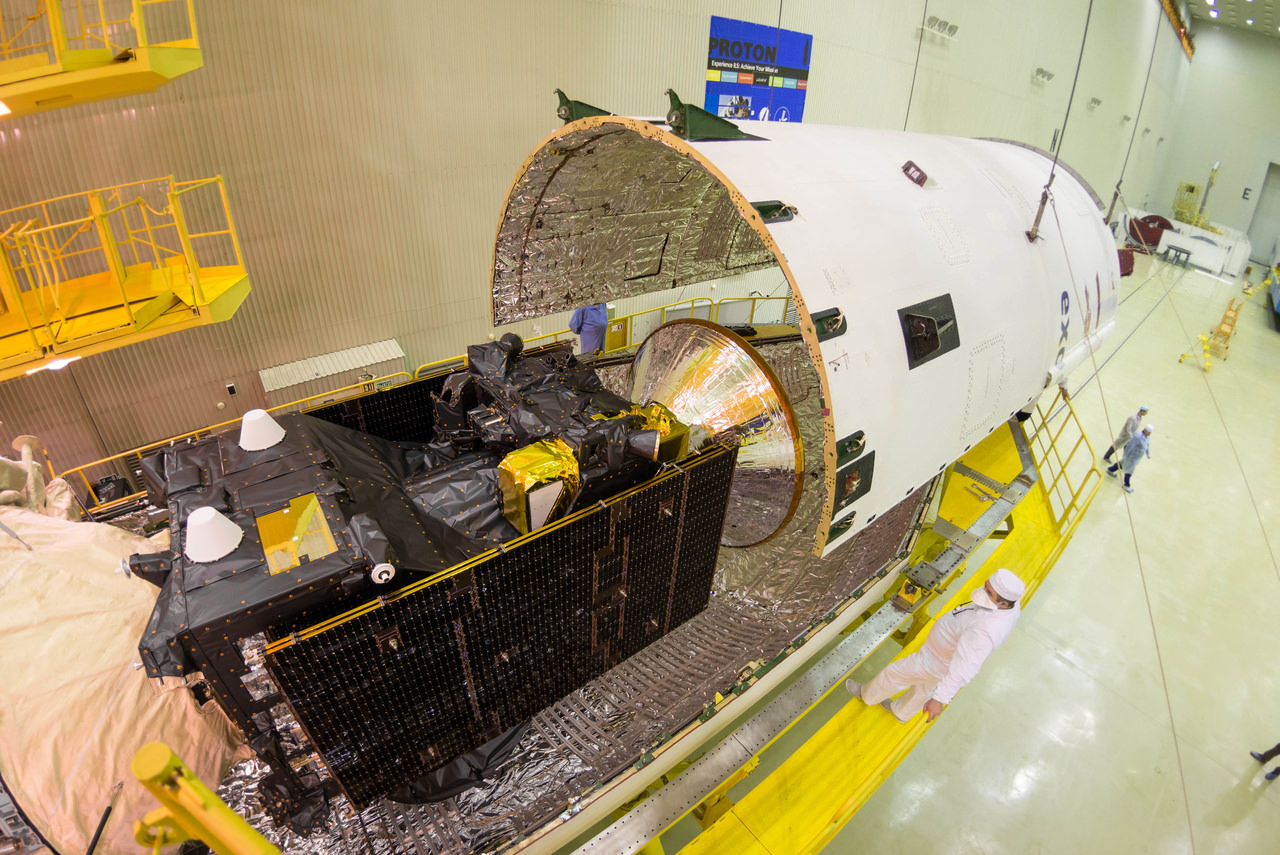
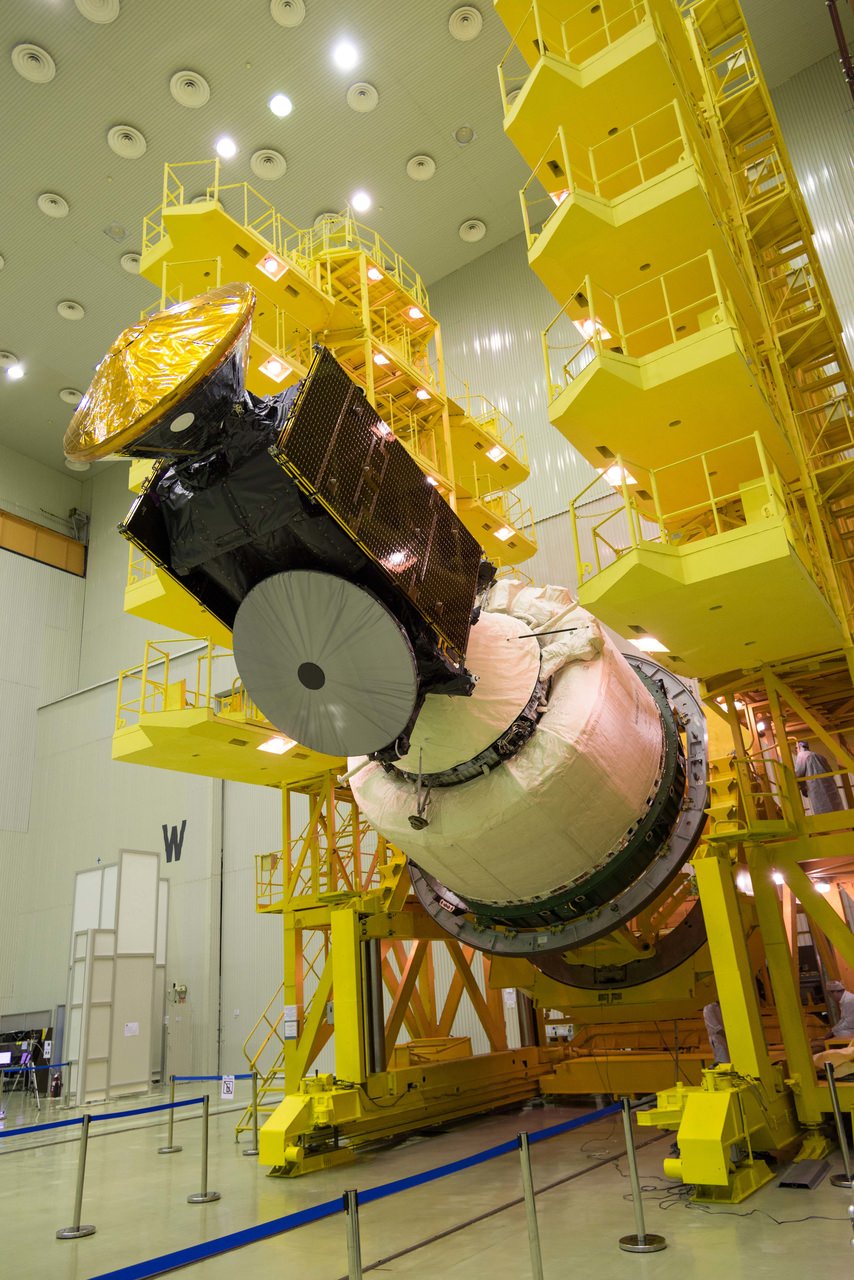
Liftoff of the ExoMars 2018 rover mission currently under development jointly by Europe and Russia has just been postponed for two years to 2020, according to an announcement today, May 2, from the European Space Agency (ESA) and the Russian space agency Roscosmos.
The delay was forced by a variety of technical and funding issues that ate up the schedule margin to enable a successful outcome for what will be Europe’s first Mars rover. The goal is to search for signs of life.
“Taking into account the delays in European and Russian industrial activities and deliveries of the scientific payload, a launch in 2020 would be the best solution,” ESA explained in a statement today.
The ambitious ExoMars rover is the second of two joint Euro-Russian missions to explore the Red Planet. It is equipped with an ESA deep driller and a NASA instrument to search for preserved organic molecules.
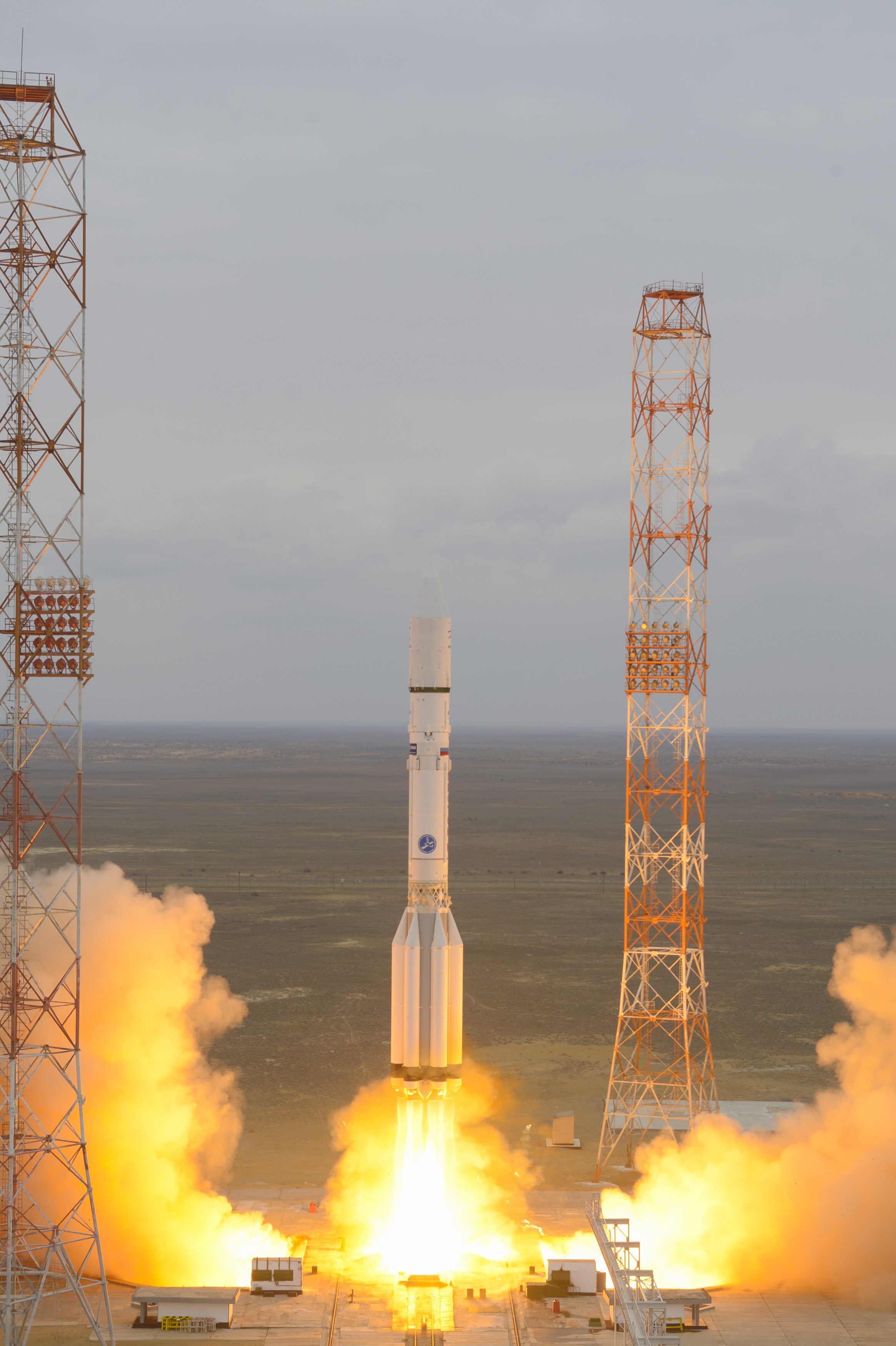
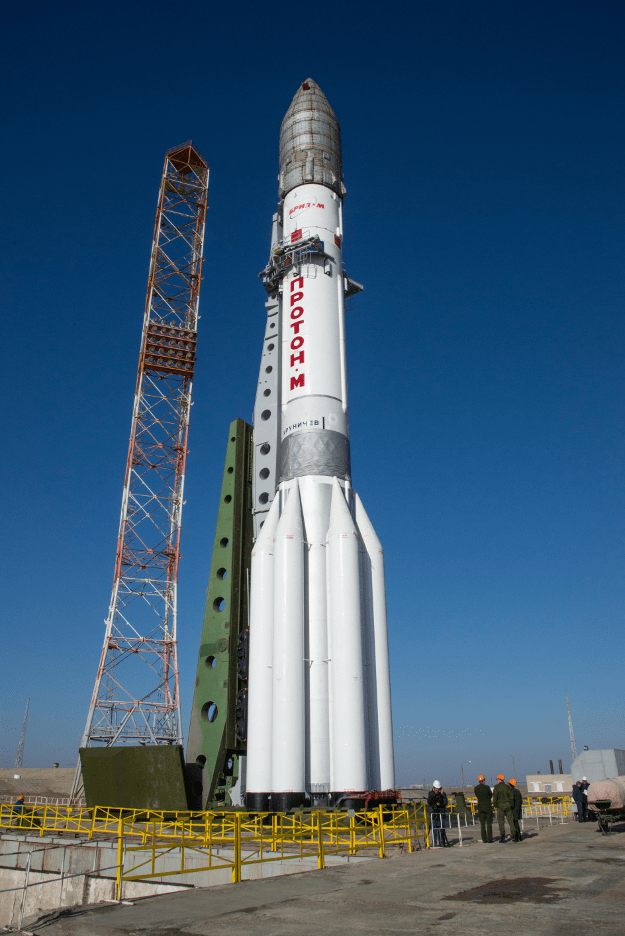
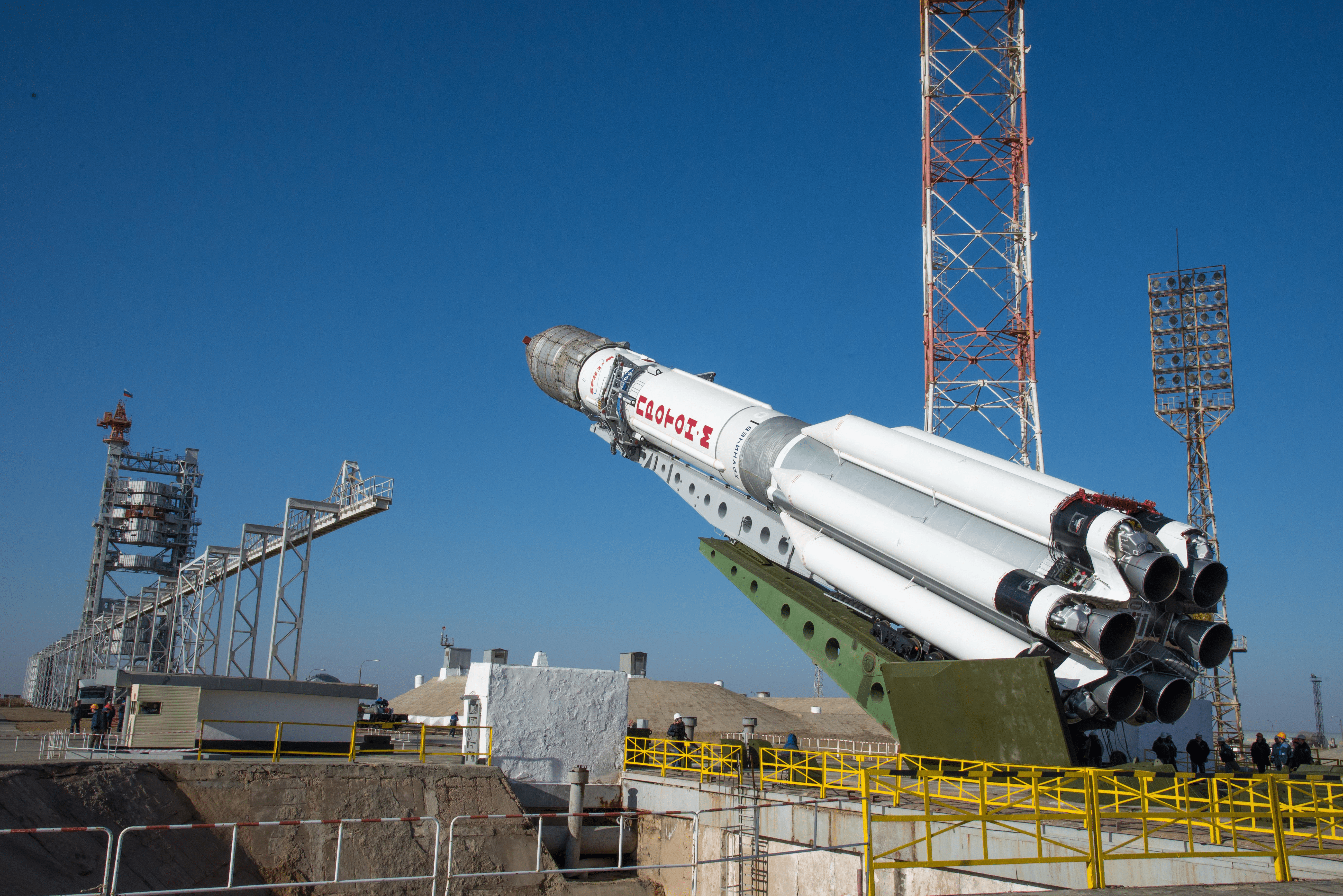
The first mission known as ExoMars 2016 was successfully launched last month from the Baikonur Cosmodrome in Kazakhstan atop a Russian Proton-M rocket on March 14.
The renamed ExoMars 2020 mission involves a European-led rover and a Russian-led surface platform and is also slated to blastoff on an Russian Proton rocket.
Roscosmos and ESA jointly decided to move the launch to the next available Mars launch window in July 2020. The costs associated with the delay are not known.
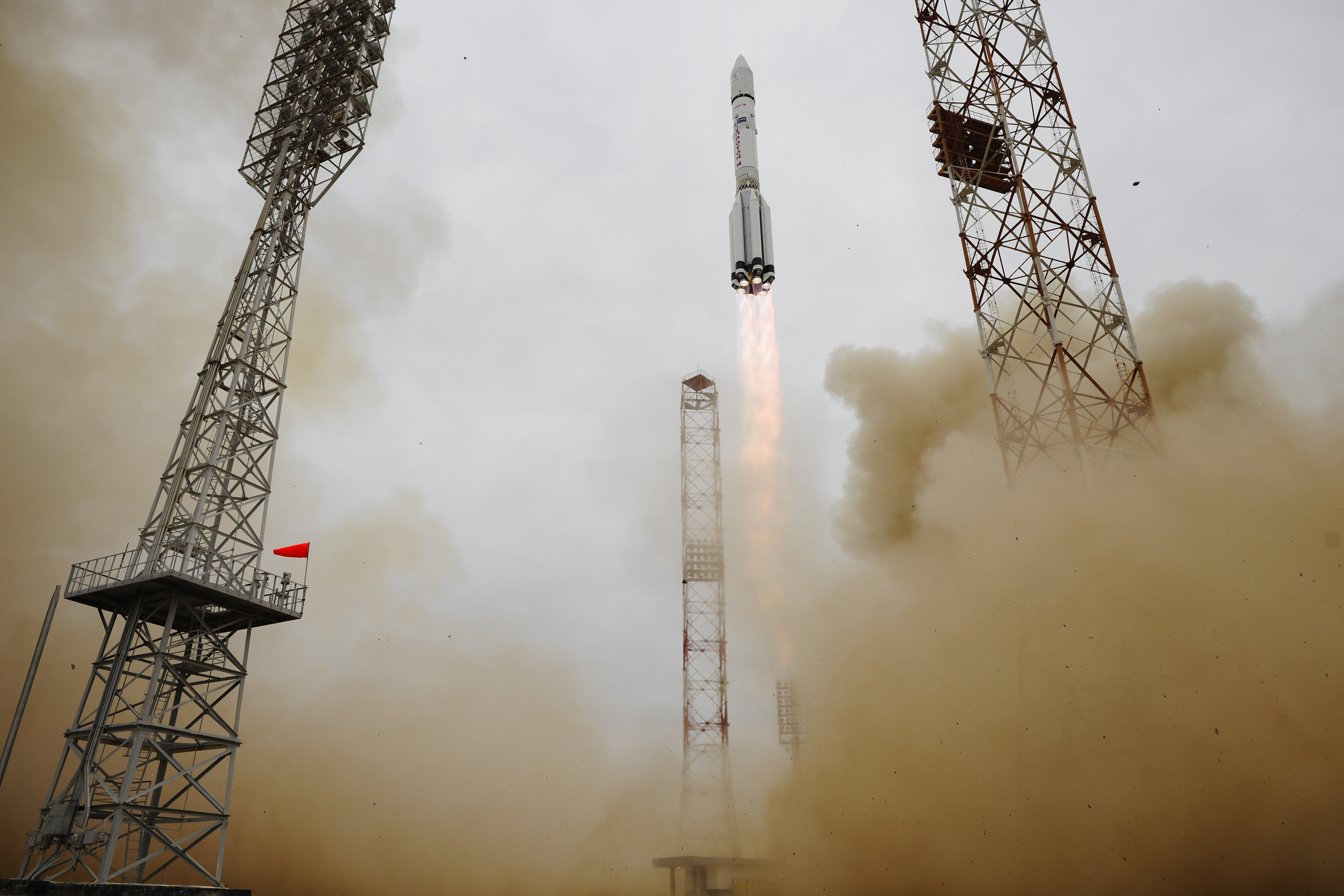

The delay means that the Euro-Russian rover mission will launch the same year as NASA’s 2020 rover.
The rover is being built by prime contractor Airbus Defense and Space in Stevenage, England.
The descent module and surface science package are provided by Roscosmos with some contributions by ESA.
Recognizing the potential for a delay, ESA and Roscosmos set up a tiger team in late 2015 to assess the best options.
“Russian and European experts made their best efforts to meet the 2018 launch schedule for the mission, and in late 2015, a dedicated ESA-Roscosmos Tiger Team, also including Russian and European industries, initiated an analysis of all possible solutions to recover schedule delays and accommodate schedule contingencies,” said ESA in the statement.
The tiger team reported their results to ESA Director General Johann-Dietrich Woerner and Roscosmos Director General Igor Komarov.
Woerner and Komarov then “jointly decided to move the launch to the next available Mars launch window in July 2020, and tasked their project teams to develop, in cooperation with the industrial contactors, a new baseline schedule aiming towards a 2020 launch. Additional measures will also be taken to maintain close control over the activities on both sides up to launch.”
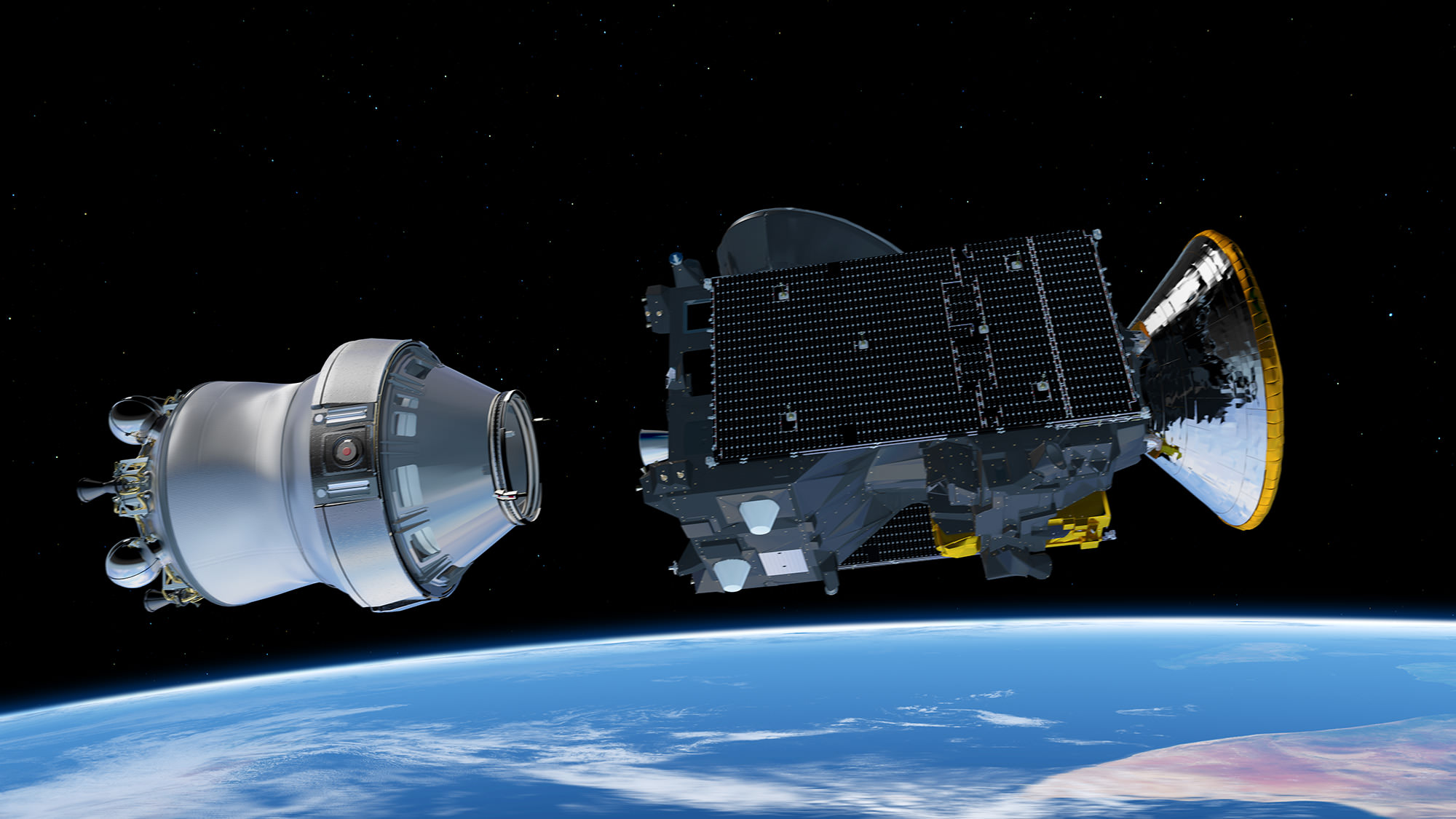
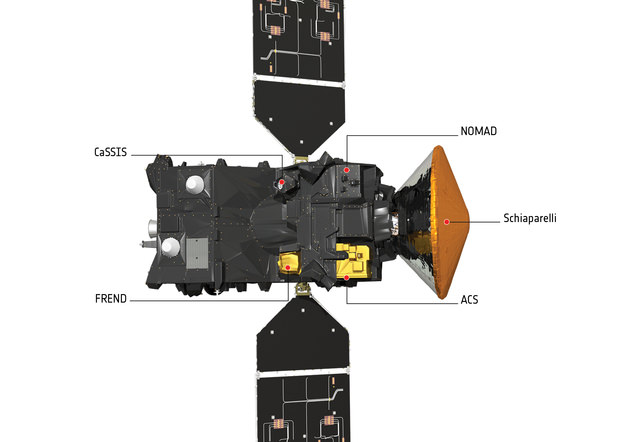
The ExoMars 2016 interplanetary mission is comprised of the Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and the Schiaparelli lander. The spacecraft are due to arrive at Mars in October 2016.
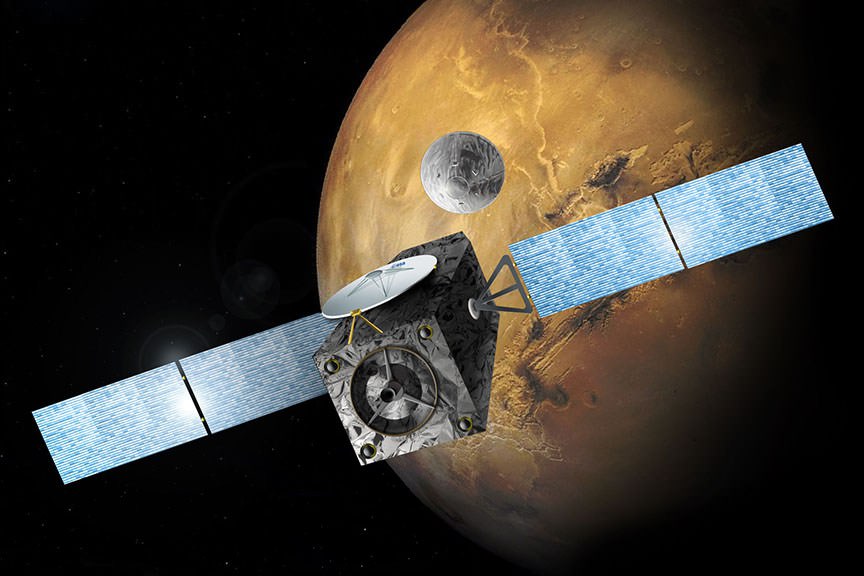

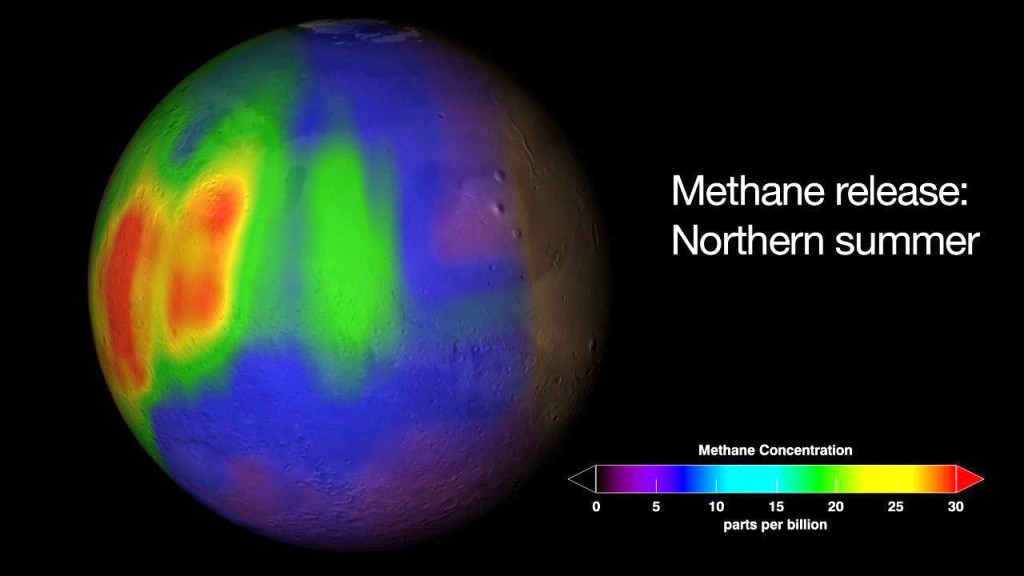
The goal of TGO is to search for possible signatures of life in the form of trace amounts of atmospheric methane on the Red Planet.
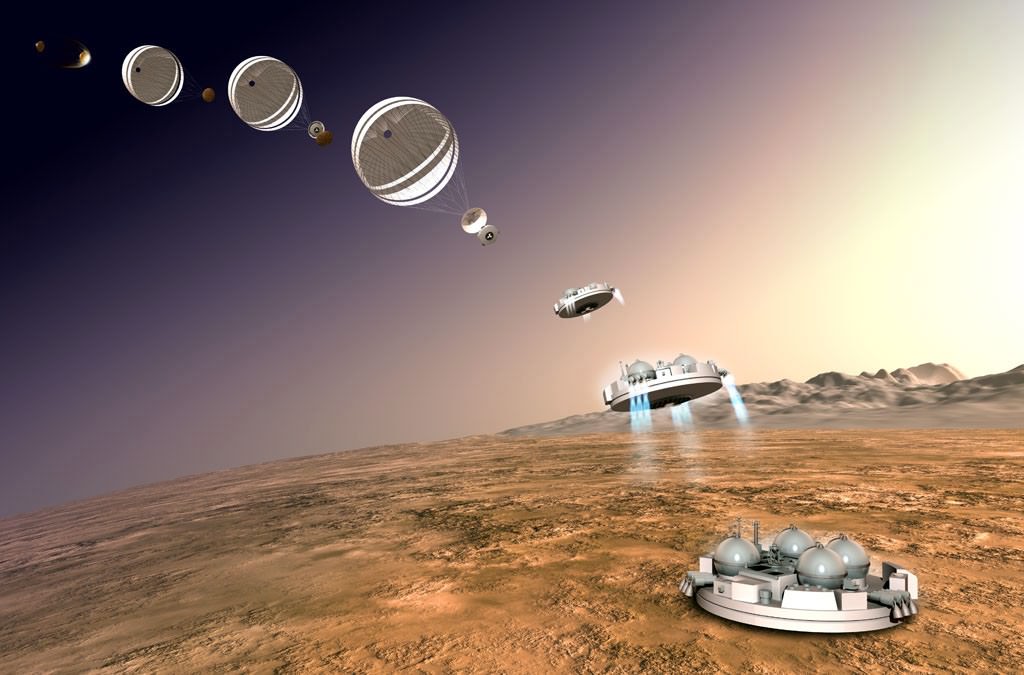
The main purpose of Schiaparelli is to demonstrate key entry, descent, and landing technologies for the follow on 2nd ExoMars mission that will land the first European rover on the Red Planet.
The now planned 2020 ExoMars mission will deliver an advanced rover to the Red Planet’s surface. It is equipped with the first ever deep driller that can collect samples to depths of 2 meters (seven feet) where the environment is shielded from the harsh conditions on the surface – namely the constant bombardment of cosmic radiation and the presence of strong oxidants like perchlorates that can destroy organic molecules.
ExoMars was originally a joint NASA/ESA project.
But thanks to hefty cuts to NASA’s budget by Washington DC politicians, NASA was forced to terminate the agencies involvement after several years of extremely detailed work and withdraw from participation as a full partner in the exciting ExoMars missions.
NASA is still providing the critical MOMA science instrument that will search for organic molecules.
Thereafter Russia agreed to take NASA’s place and provide the much needed funding and rockets for the pair of launches in March 2016 and May 2018.
TGO will also help search for safe landing sites for the ExoMars 2020 lander and serve as the all important data communication relay station sending signals and science from the rover and surface science platform back to Earth.
ExoMars 2016 is Europe’s most advanced mission to Mars and joins Europe’s still operating Mars Express Orbiter (MEX), which arrived back in 2004, as well as a fleet of NASA and Indian probes.
The Trace Gas Orbiter (TGO) and Schiaparelli lander arrive at Mars on October 19, 2016.
Stay tuned here for Ken’s continuing Earth and planetary science and human spaceflight news.