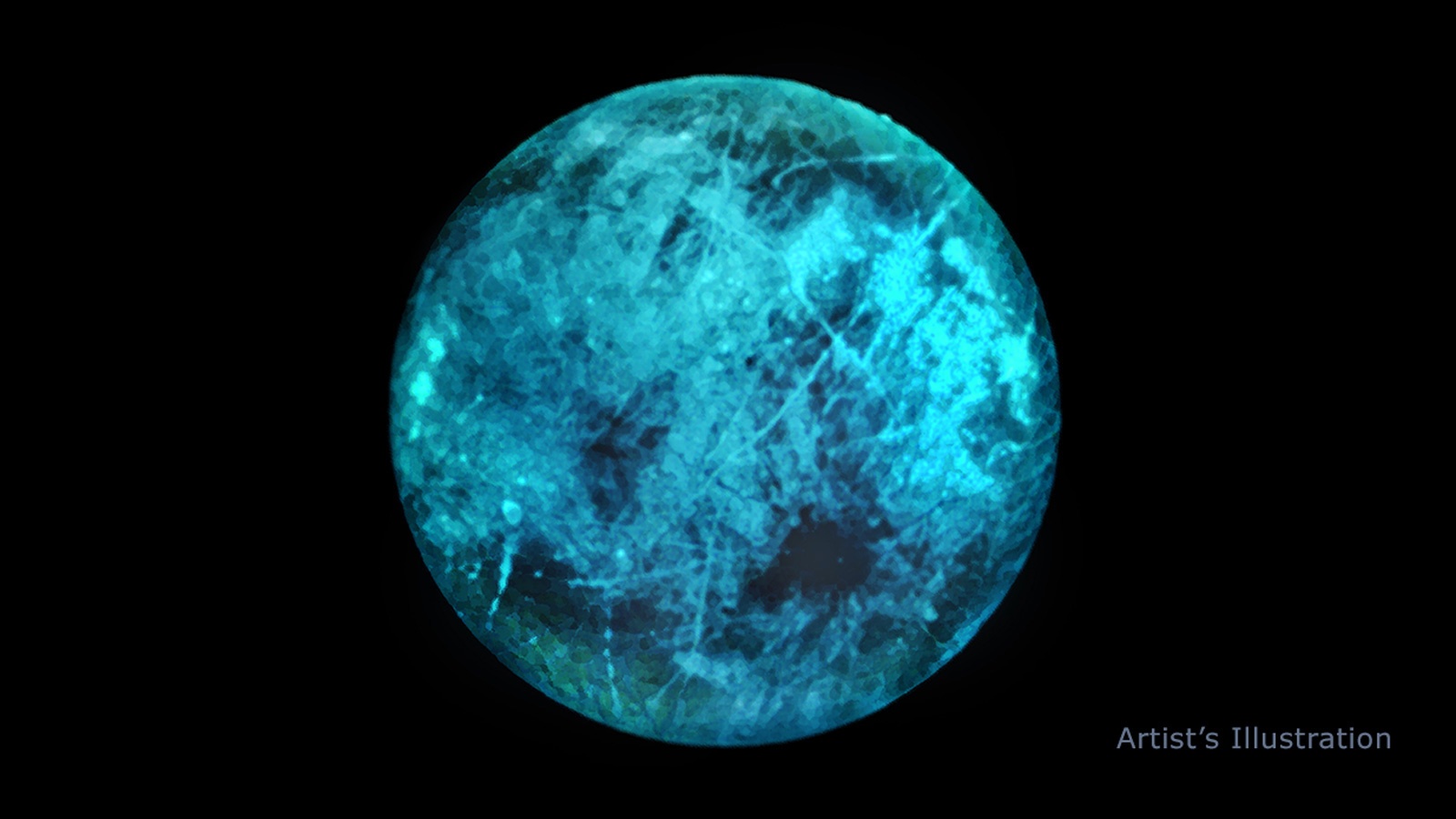
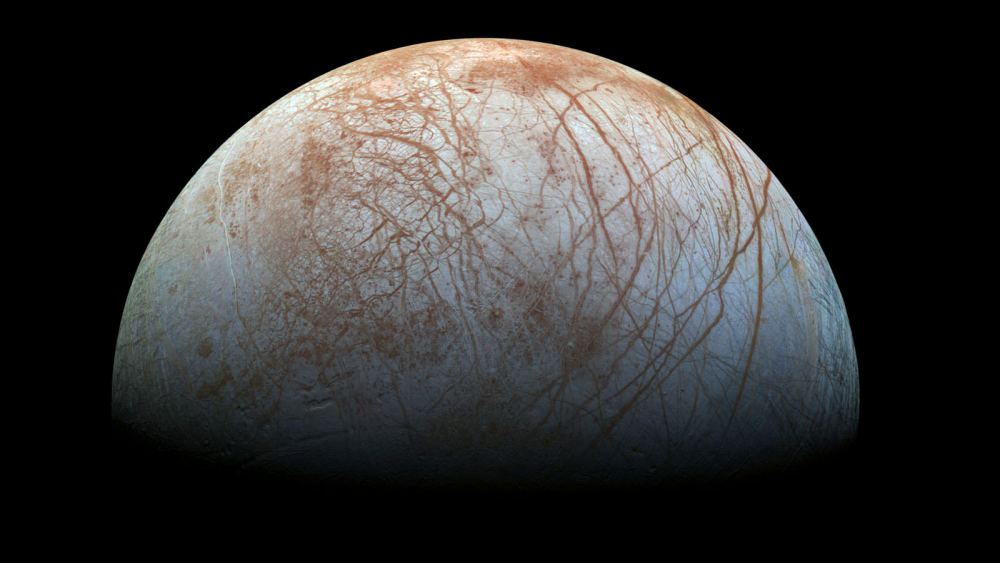
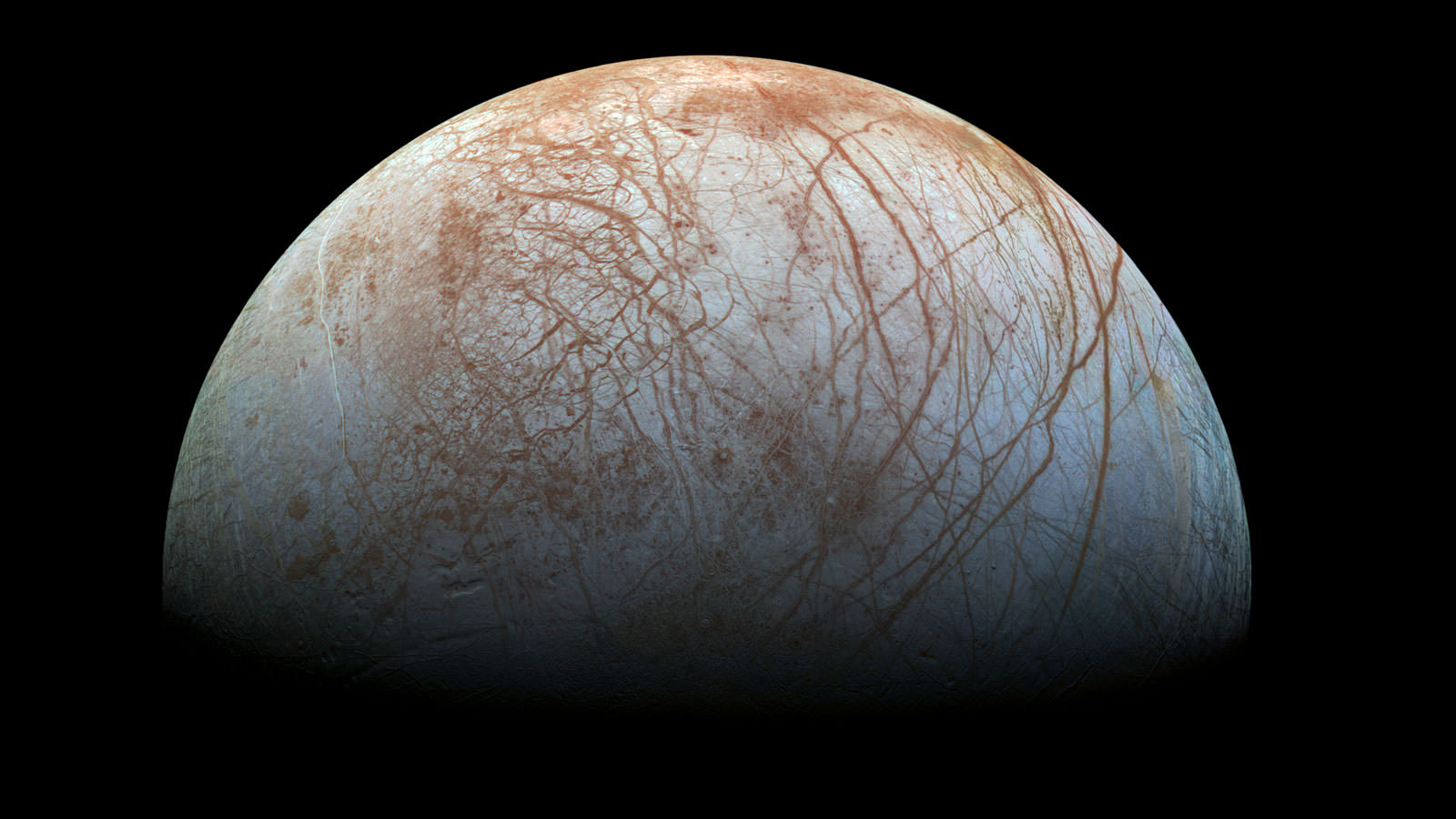
In about three years, NASA plans to launch a robotic orbiter that will study Jupiter’s mysterious moon Europa. It’s called the Europa Clipper mission, which will spend four years orbiting Europa to learn more about its ice sheet, interior structure, chemical composition, and plume activity. In the process, NASA hopes to find evidence that will help resolve the ongoing debate as to whether or not Europa harbors life in its interior.
Naturally, scientists are especially curious about what the Clipper mission might find, especially in Europa’s interior. According to new research and modeling supported by NASA, it’s possible that volcanic activity occurred on the seafloor in the recent past – which could be happening still. This research is the most detailed and thorough 3D modeling on how internal heat is produced and transferred and what effect this will have on a moon.
Continue reading “There Might be Volcanoes at the Bottom of Europa’s sub-ice Oceans”