[/caption]
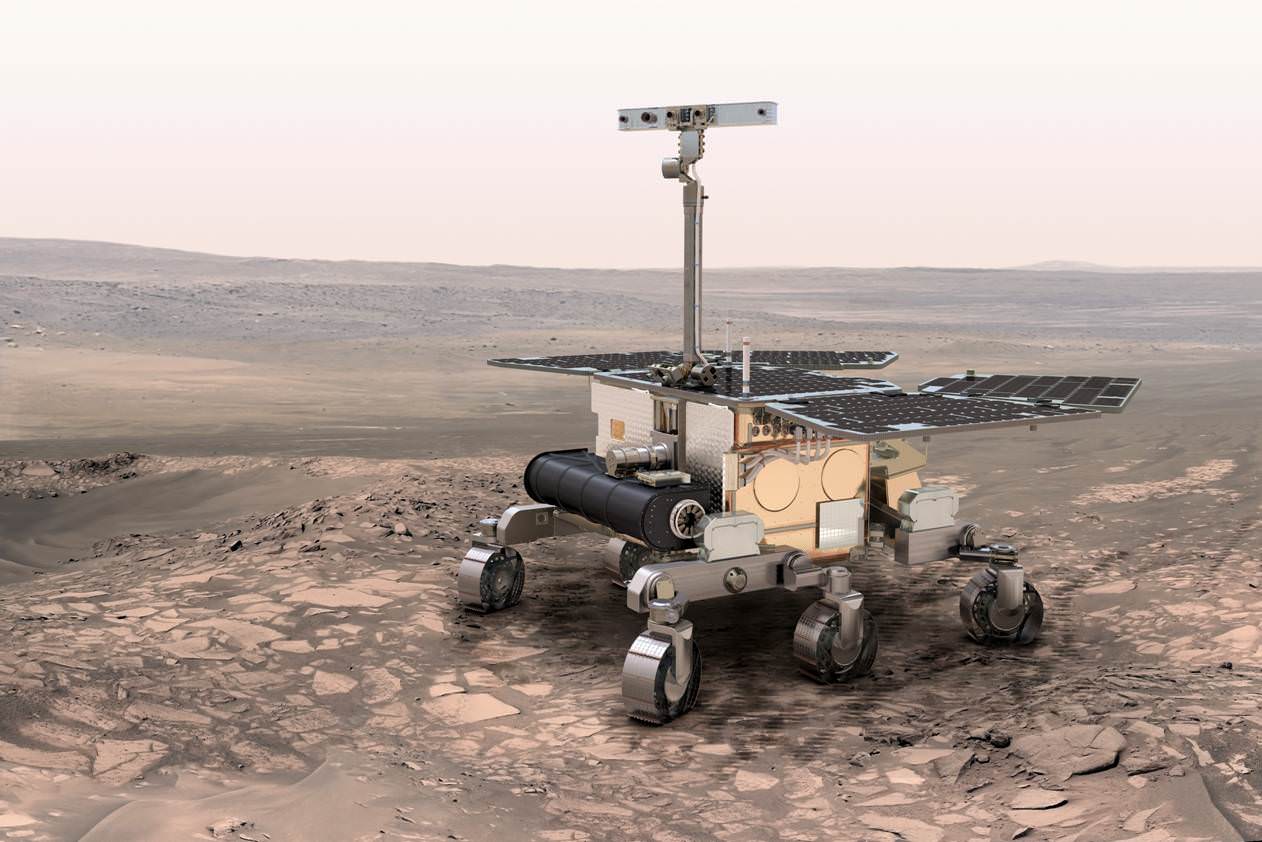
A Phoenix-like lander that would mine the deepest hole yet into Mars– to a depth of 5 meters – and unveil the nature of the mysterious deep interior and central core of the Red Planet is under consideration by NASA for a 2016 launch and sports a nifty new name – InSight.
The stationary “InSight” lander would be an international science mission and a near duplicate of NASA’s proven Phoenix spacecraft, Bruce Banerdt told Universe Today. Banerdt is the Principal Investigator of the proposed InSight mission.
“InSight is essentially built from scratch, but nearly build-to-print from the Phoenix design,” Banerdt, of NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) in Pasadena , Calif, told me. The team can keep costs down by re-using the blueprints pioneered by Phoenix instead of creating an entirely new spacecraft.
“The robotic arm is similar (but not identical) to the Phoenix arm.”
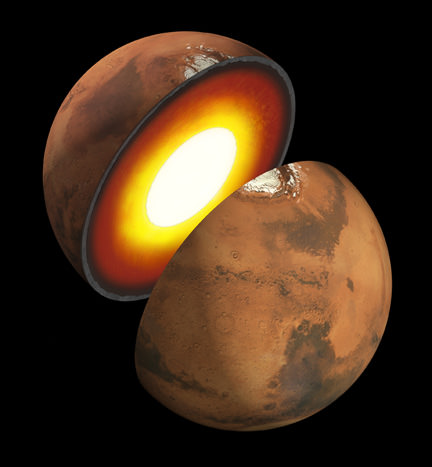

Insight’s goal is to investigate and deduce the nature of the interior of the Red Planet. Credit: JPL/NASA
However, the landing site and science goals for InSight are quite different from Phoenix.
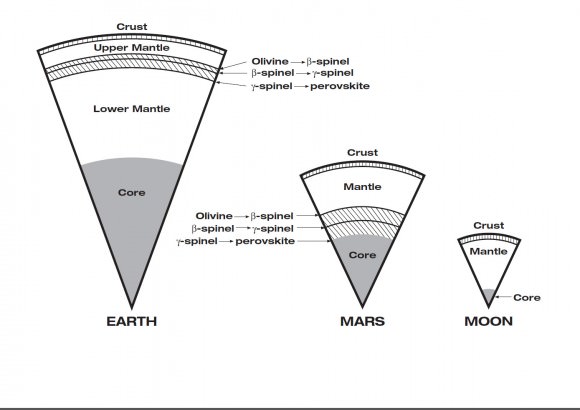
InSight will have an entirely new suite of three science instruments, including two from Europe, designed to peer to the center of Mars and detect the fingerprints of the processes by which the terrestrial planets formed. It will determine if there is any seismic activity, the amount of heat flow from the interior, the size of Mars core and whether the core is liquid or solid.
NASA’s twin GRAIL lunar gravity probes are set to begin their own investigation into the interior and core of Earth’s Moon in early March 2012, and several science team members are common to GRAIL and InSight.
“The seismometer (SEIS, stands for Seismic Experiment for Interior Structure) is from France (built by CNES and IPGP) and the heat flow probe (HP3, stands for Heat flow and Physical Properties Probe) is from Germany (built by DLR),” Banerdt explained.
Phoenix successfully landed in the frigid northern polar regions of Mars in 2008 in search of potential habitats for life and quickly discovered water ice and salty soils that could be favorable for the genesis and support of extraterrestrial life.

Phoenix thrusters blasted away Martian soil and exposed water ice. Proposed Mars InSight mission will build a new Phoenix-like lander from scratch to peer deep into the Red Planet and investigate the nature and size of the mysterious Martian core. Credit: Kenneth Kremer, Marco Di Lorenzo, Phoenix Mission, NASA/JPL/UA/Max Planck Institute
InSight will intentionally land in a far warmer and sunnier location nearer the moderate climate of the equator to enable a projected lifetime of 2 years (or 1 Mars year) vs. the 5 months survival of Phoenix extremely harsh arctic touchdown zone.
“Our planned landing site is in Elysium Planitia,” Banerdt told me. “It was chosen for optimizing engineering safety margins for landing and power.”
The more equatorial landing site affords far more sun for the life giving solar arrays to power the instruments and electronics.
“We have global objectives and can do our science anywhere on the planet.”
Elysium Planitia is not too far from the landing sites of the Spirit and Curiosity rovers. The Elysium Mons volcano is also in the general area, but it’s a long way from precise site selection.
InSight is a geophysical lander targeted to delve deep beneath the surface into the Martian interior, check its “vital signs”; like “pulse” though seismology, “temperature”, though a heat flow probe, and “reflexes”, through precision tracking.
The purpose is to answer one of science’s most fundamental questions: How were the planets created?
InSight will accomplish much of its science investigations through experiments sitting directly in contact with the Martian surface. The robotic arm will pluck two of the instruments from the lander deck and place them onto Mars.
“The arm will pick the SEIS seismometer and HP3 heat flow probe off the deck and place each on the ground next to the lander. The arm doesn’t have a drill, but the heat flow probe itself will burrow down as deep as 5 meters,” Banerdt elaborated.
The third experiment named RISE (Rotation and Interior Structure Experiment) is to be provided by JPL and will use the spacecraft communication system to provide precise measurements of Mars planetary rotation and elucidate clues to its interior structure and composition.
Right now on Mars, NASA’s Opportunity rover is conducting a Doppler radio tracking experiment similar to what is planned for RISE, but InSight will have a big advantage according to Banerdt.
“The RISE experiment will be very similar to what we are doing right now on Opportunity, but will be able to do much better, said Banerdt. “The differences are that we will get more tracking every week (Opportunity is power-limited during the winter months; that’s why she is currently stationary!) and will make measurements for an entire Mars year – we will likely only get a handful of months from Opportunity.”
Insight will also be equipped with 2 cameras and make some weather measurements.
“We have a camera on the arm and one fixed to the deck, both primarily to support placing the instruments on the surface, although they will be able to scan the landscape around the spacecraft. Both are Black & White,” Banerdt told me.
“We will measure pressure, temperature and wind, mostly to support noise analysis on the seismic data, but will also supply information on the weather.”
InSight is one of three missions vying to be selected for flight in NASA’s Discovery Program, a series of low cost NASA missions to understand the solar system by exploring planets, moons, and small bodies such as comets and asteroids. All three mission teams are required to submit concept study reports to NASA on March 19.
Banerdt’s team is working hard to finalize the concept study report.
“It describes the mission design as we have refined it over the past 9 months since the NASA Step-1 selection.”
So there is no guarantee that InSight will fly. Because of severe budget cuts to NASA’s Planetary Science Division, NASA had to cancel its scheduled participation in two other Mars missions dubbed ExoMars and jointed planned with ESA, the European Space Agency, for launch in 2016 and 2018.