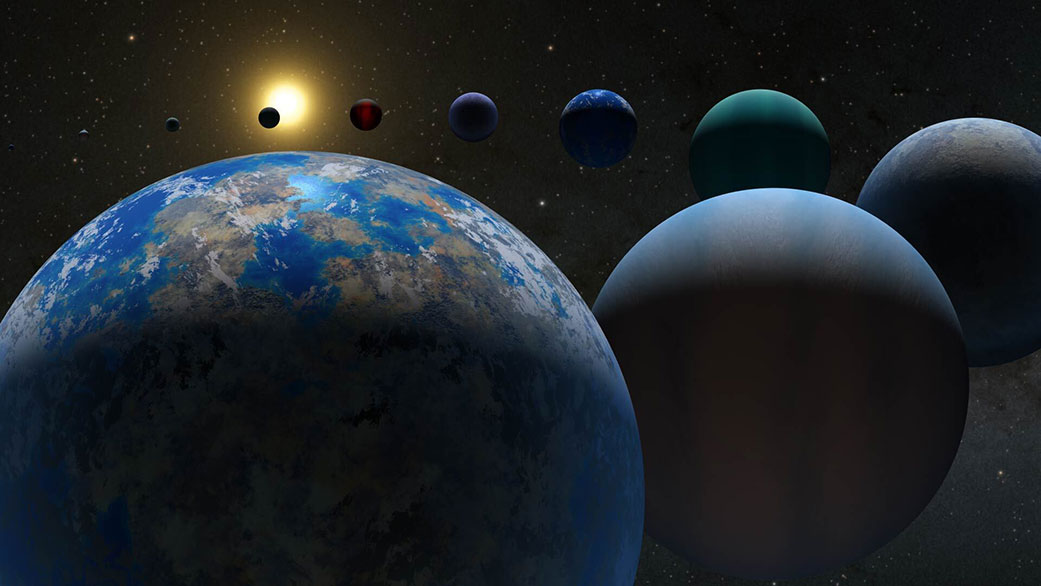
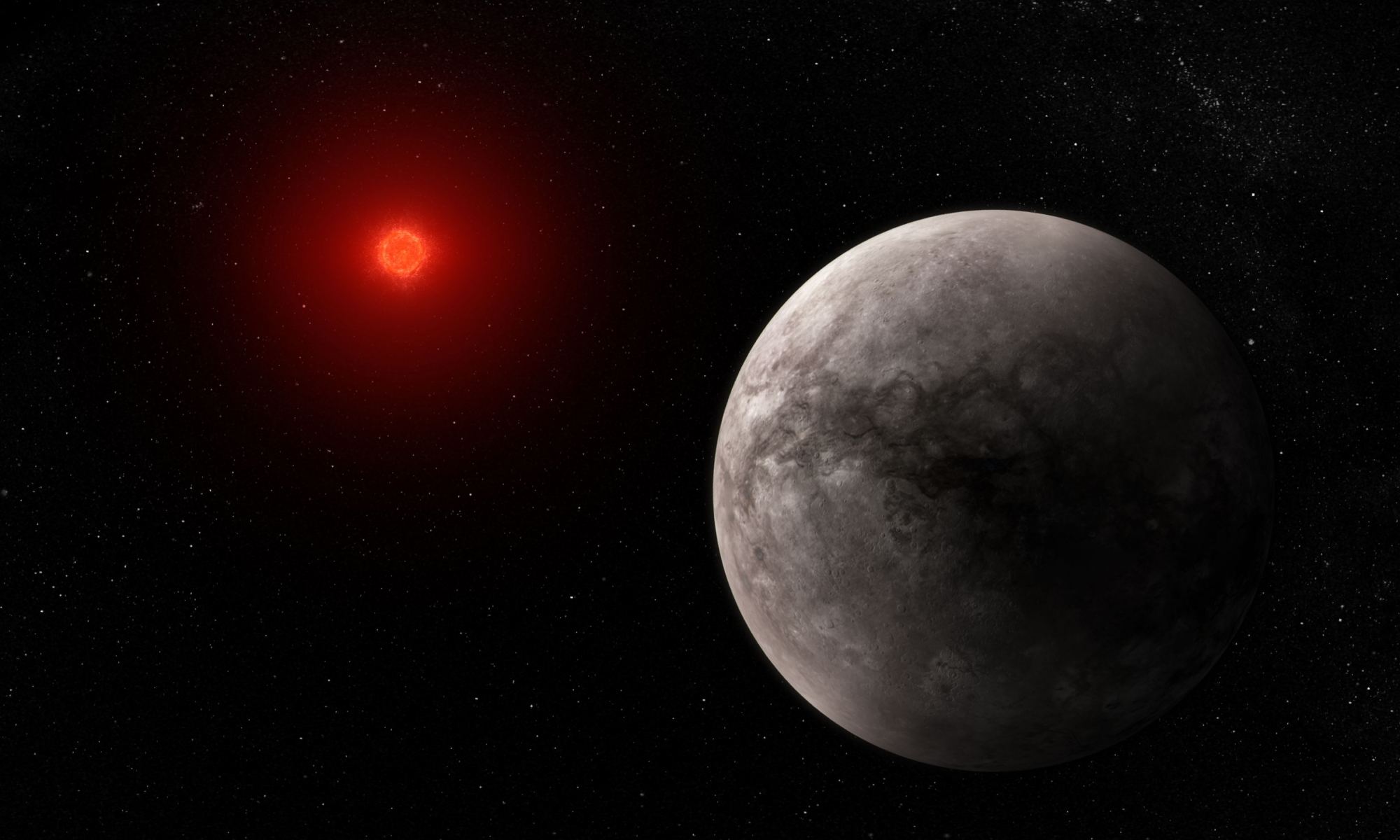
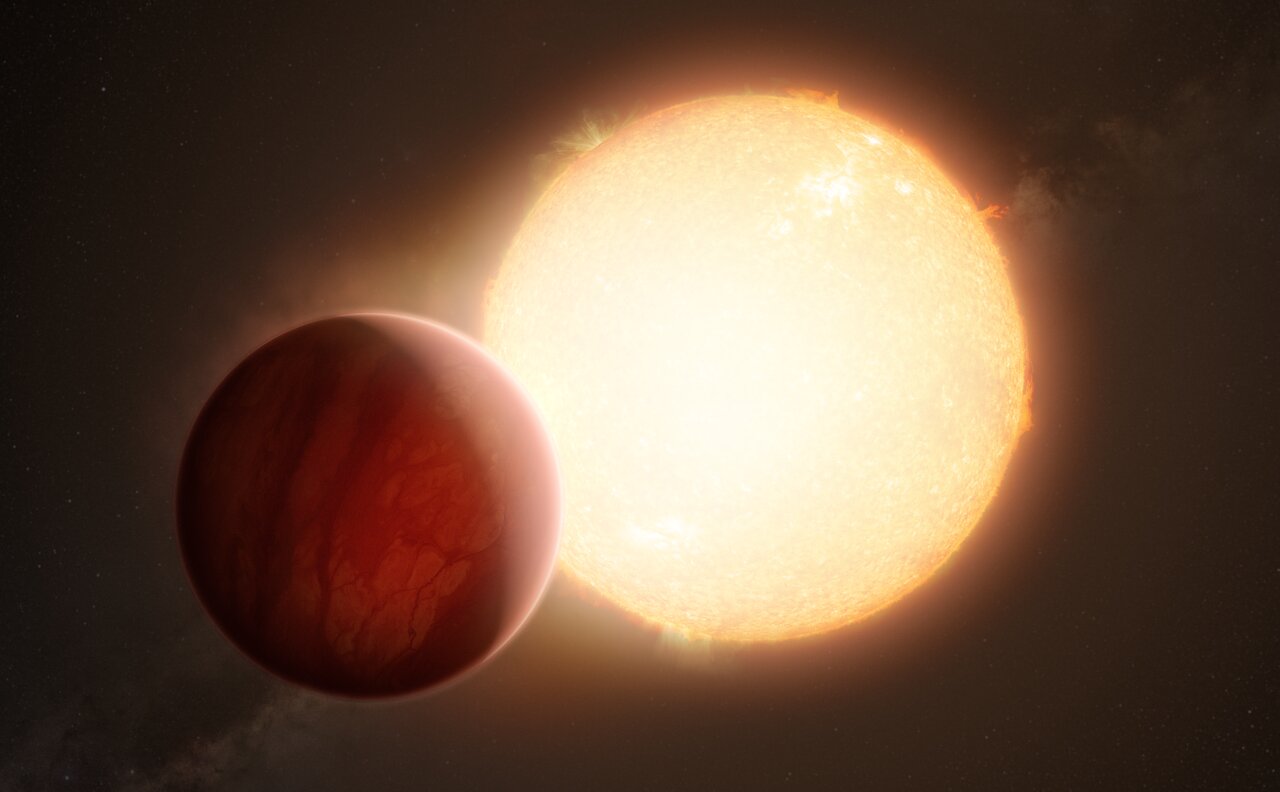
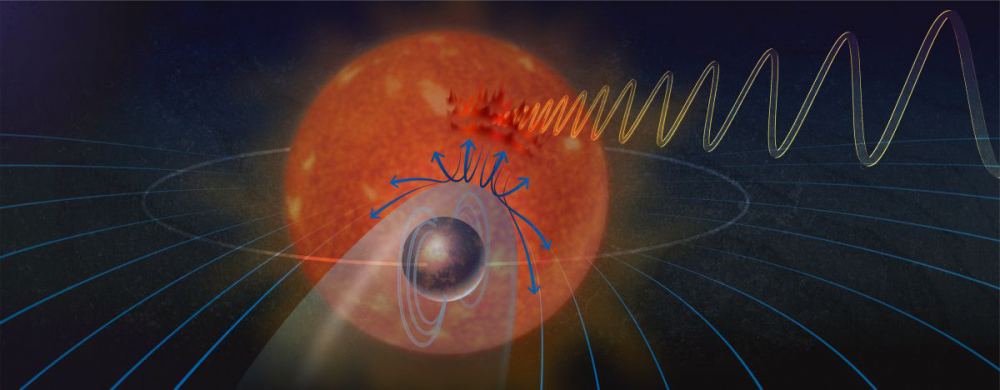
In the hunt for habitable worlds around other stars, planetary atmospheres provide fertile places to look. But, as a group of scientists at the Max-Planck Institute for Solar System Studies in Germany found, maybe astronomers should focus on a star’s metallicity, too. That’s because there seems to be a direct link between their metallicity, how much UV radiation they give off, and the atmospheres of rocky planets orbiting them. It turns out that metal-poor stars provide better conditions for life on their planets than metal-rich ones do.
Continue reading “If a Star Has Less Metals, it Might Have a Better Chance to Spark Life”If a Star Has Less Metals, it Might Have a Better Chance to Spark Life