The study of extrasolar planets has really exploded in recent years. Currently, astronomers have been able to confirm the existence of 4,104 planets beyond our Solar System, with another 4900 awaiting confirmation. The study of these many planets has revealed things about the range of possible planets in our Universe and taught us that there are many for which there are no analogs in our Solar System.
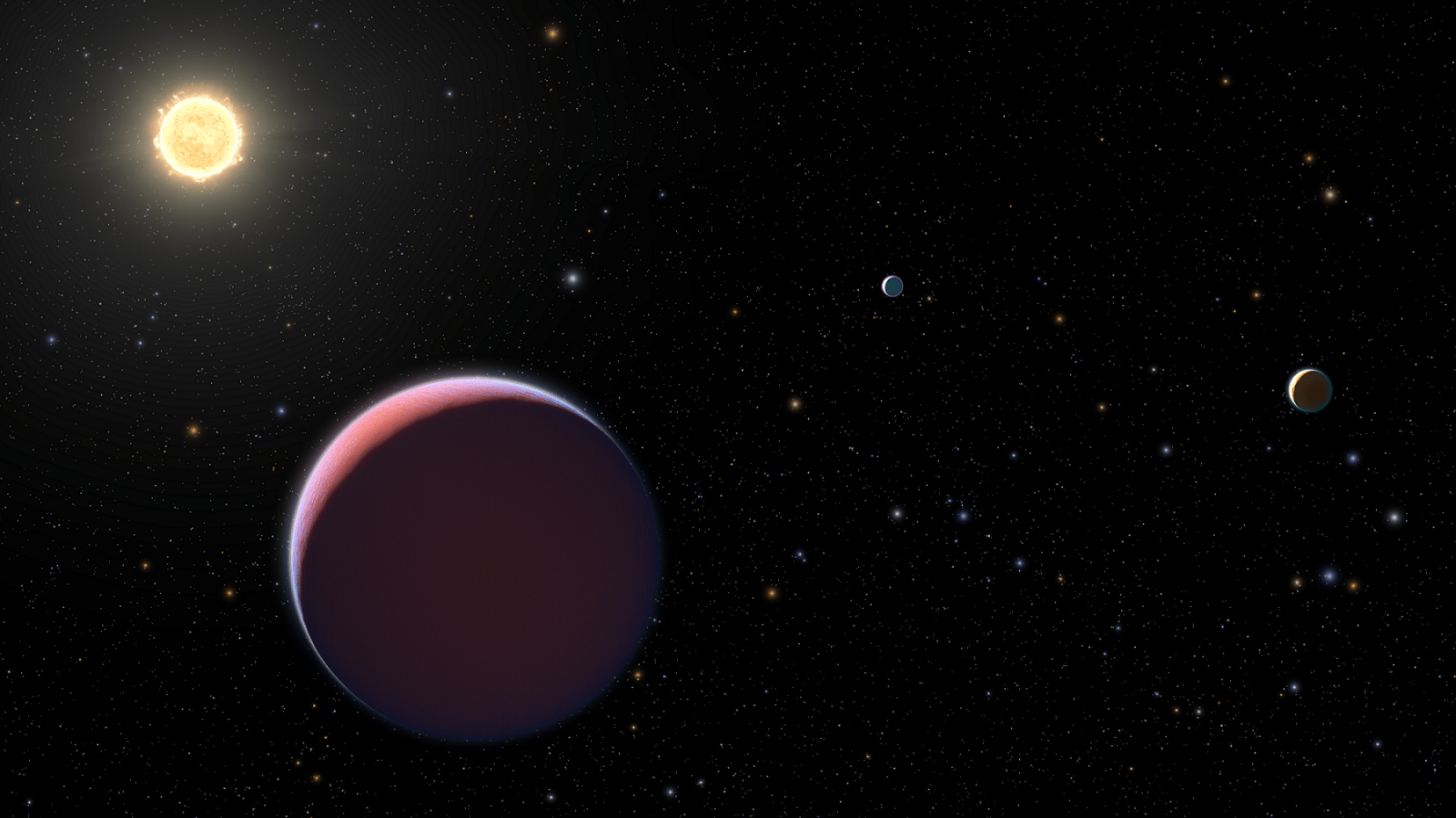
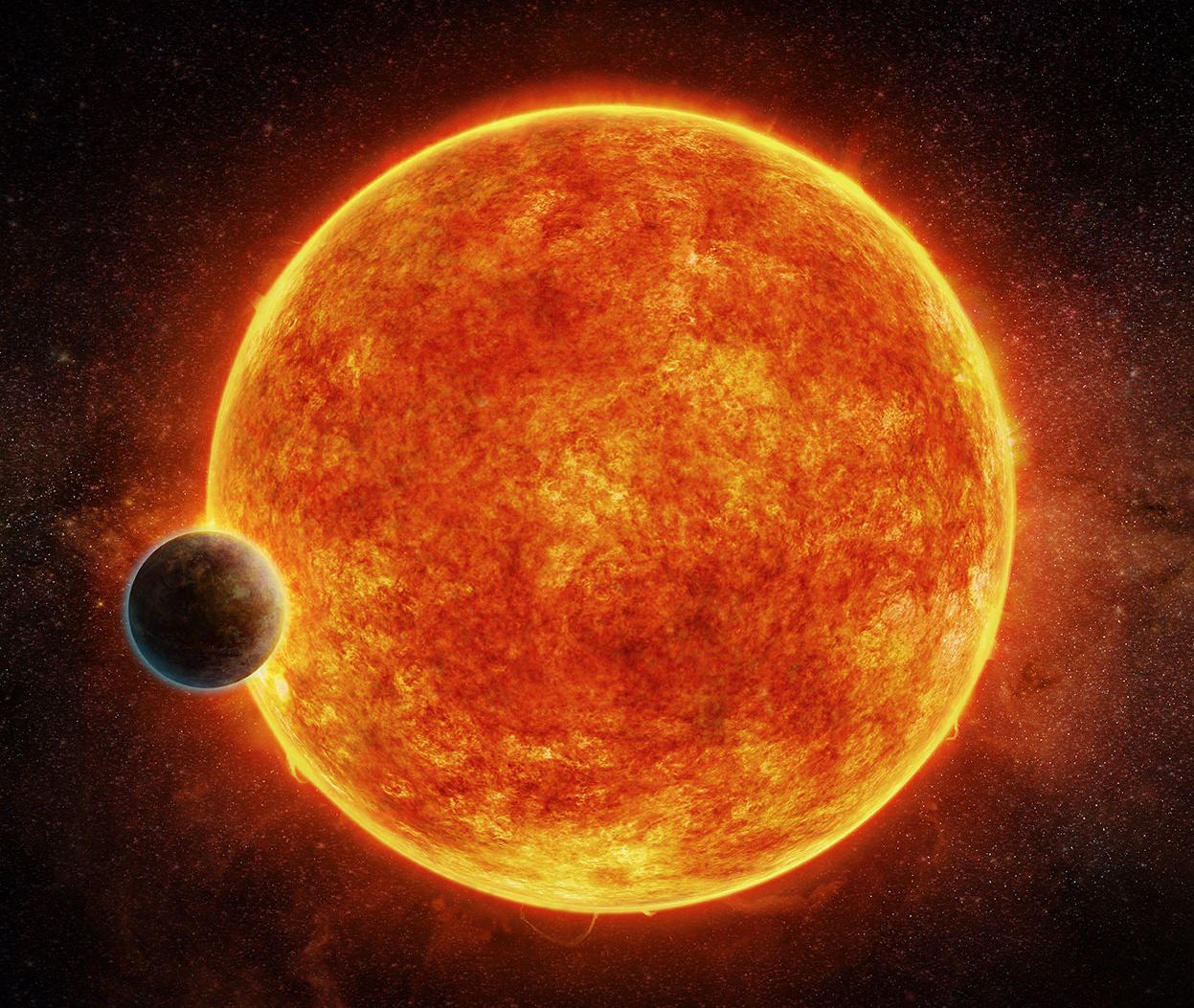
For example, thanks to new data obtained by the Hubble Space Telescope, astronomers have learned more about a new class of exoplanet known as “super-puff” planets. Planets in this class are essentially young gas giants that are comparable in size to Jupiter but have masses that are just a few times greater than that of Earth. This results in their atmospheres having the density of cotton candy, hence the delightful nickname!
Continue reading ““Super-Puff” Exoplanets Aren’t Like Anything We’ve Got in the Solar System”