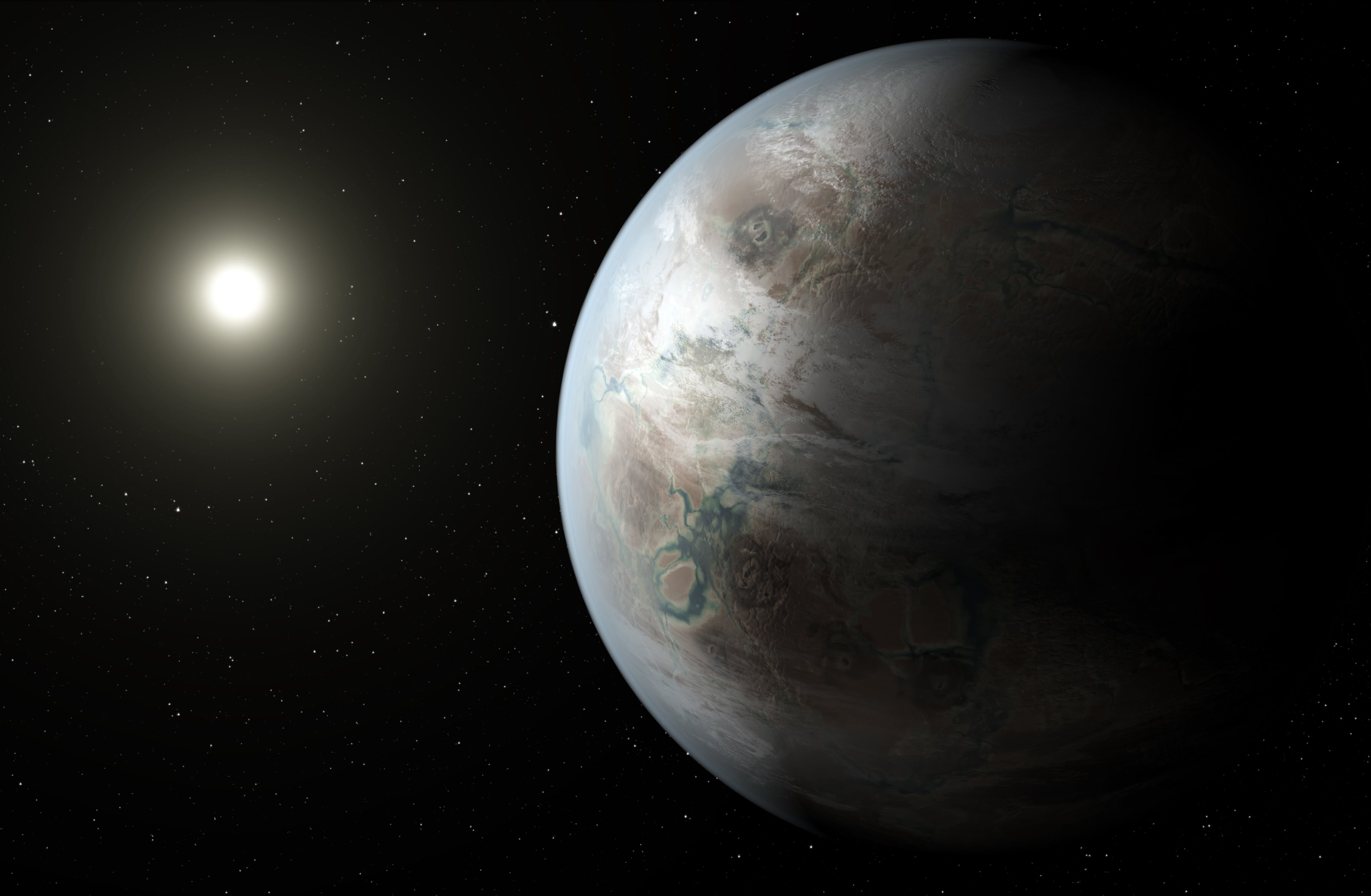
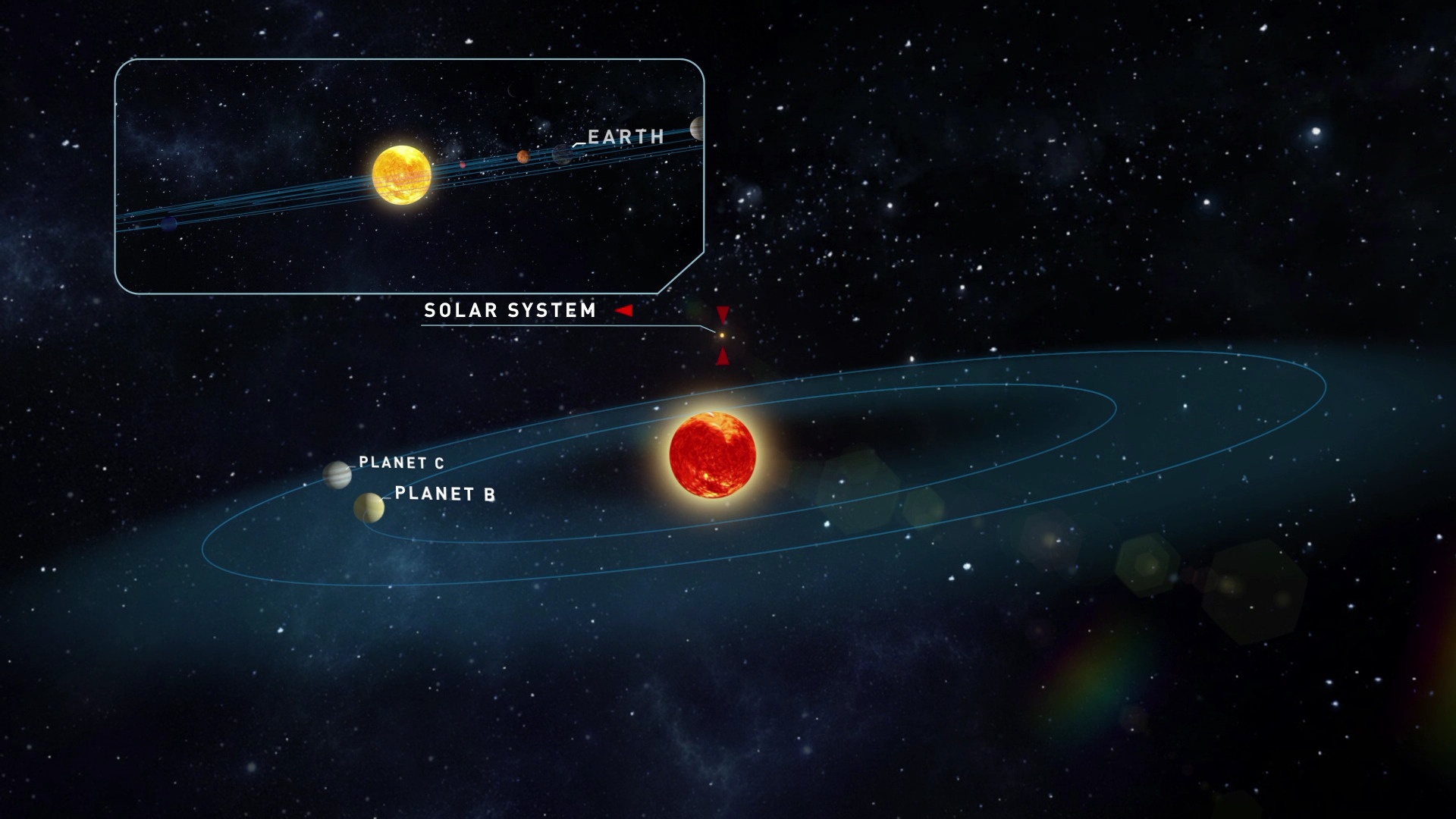
In the past few decades, there has been an explosion in the number of planets discovered beyond our Solar System. With over 4,000 confirmed exoplanets to date, the process has gradually shifted from discovery towards characterization. This consists of using refined techniques to determine just how likely a planet is to be habitable.
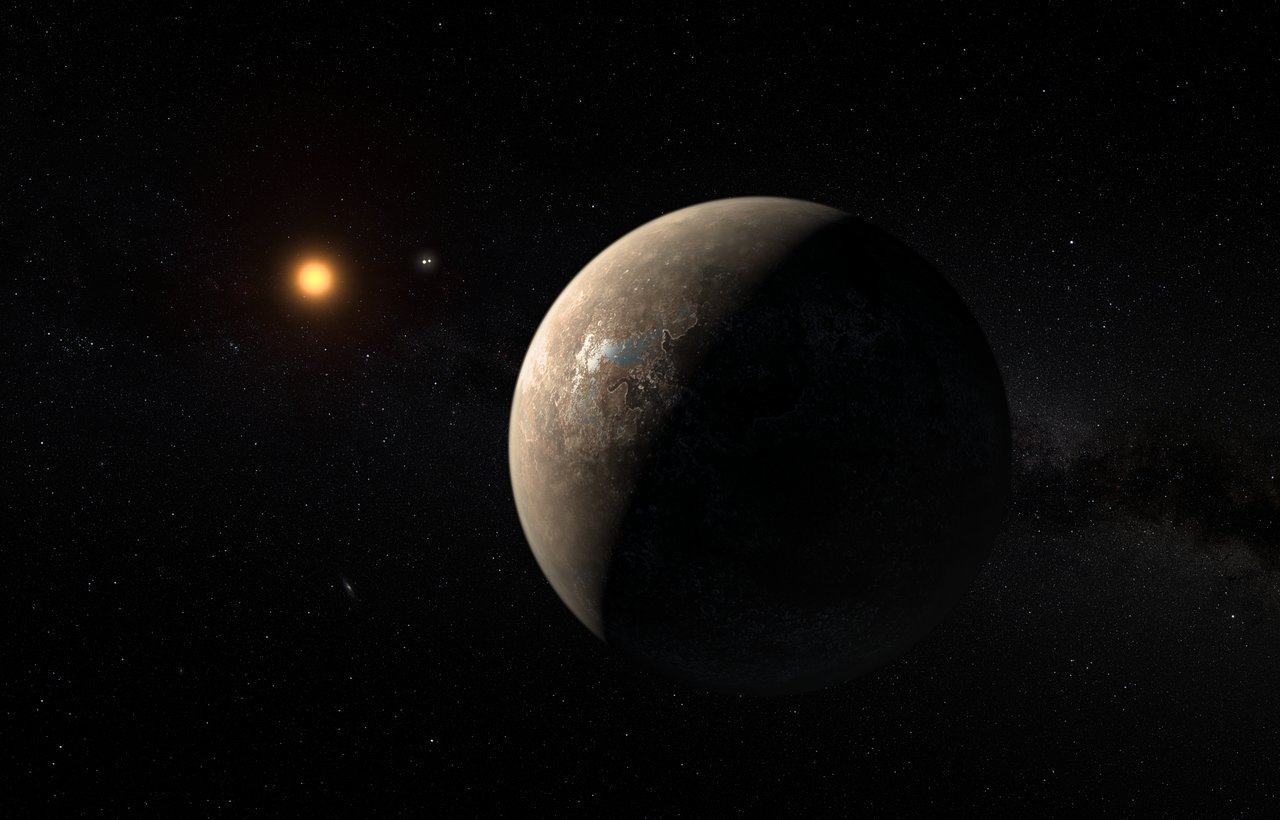
At the same time, astronomers continue to make discoveries regularly, some of which are right in our cosmic backyard. For instance, an international team of researchers recently detected two new Earth-like planets orbiting Teegarden’s Star, an M-type (red dwarf) star located just 12.5 light-years from the Solar System in the direction of the Aries constellation.
Continue reading “Two Earth-Like Worlds Found Orbiting a Red Dwarf Only 12.5 Light-Years Away”