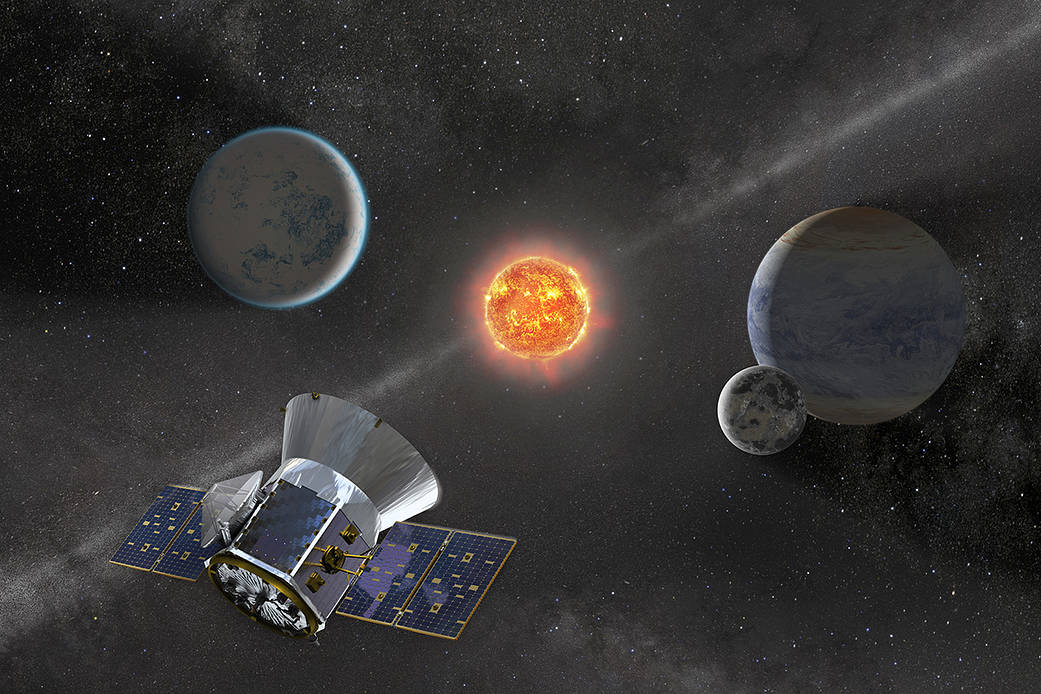
The field of extrasolar planet studies continues to grow by leaps and bounds. Currently, 5,090 exoplanets have been confirmed in 3,816 systems, and another 8,933 candidates are awaiting confirmation. The majority of these have been Neptune-like gas giants (1,779), gas giants comparable to Jupiter or Saturn (1,536), and rocky planets many times the size of Earth (1,582). The most effective means for finding exoplanets has been the Transit Method (aka. Transit Photometry), where periodic dips in a star’s brightness are seen as an indication of a planet passing in front of its star (transiting) relative to the observer.
Using data from NASA’s Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite (TESS), an international team of astronomers has discovered a three-planet system orbiting a Sun-like star (HD 22946, or TOI 11) located about 205.5 light-years. Based on size estimates yielded from their transits, the team theorizes that these exoplanets consist of a rocky planet several times the size of Earth (a Super-Earth) and two gas giants smaller than Neptune. Given its proximity, this system could be ideal for follow-up studies and characterization with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST).
Continue reading “TESS Finds a Super-Earth and two Mini-Neptunes in a Single System”