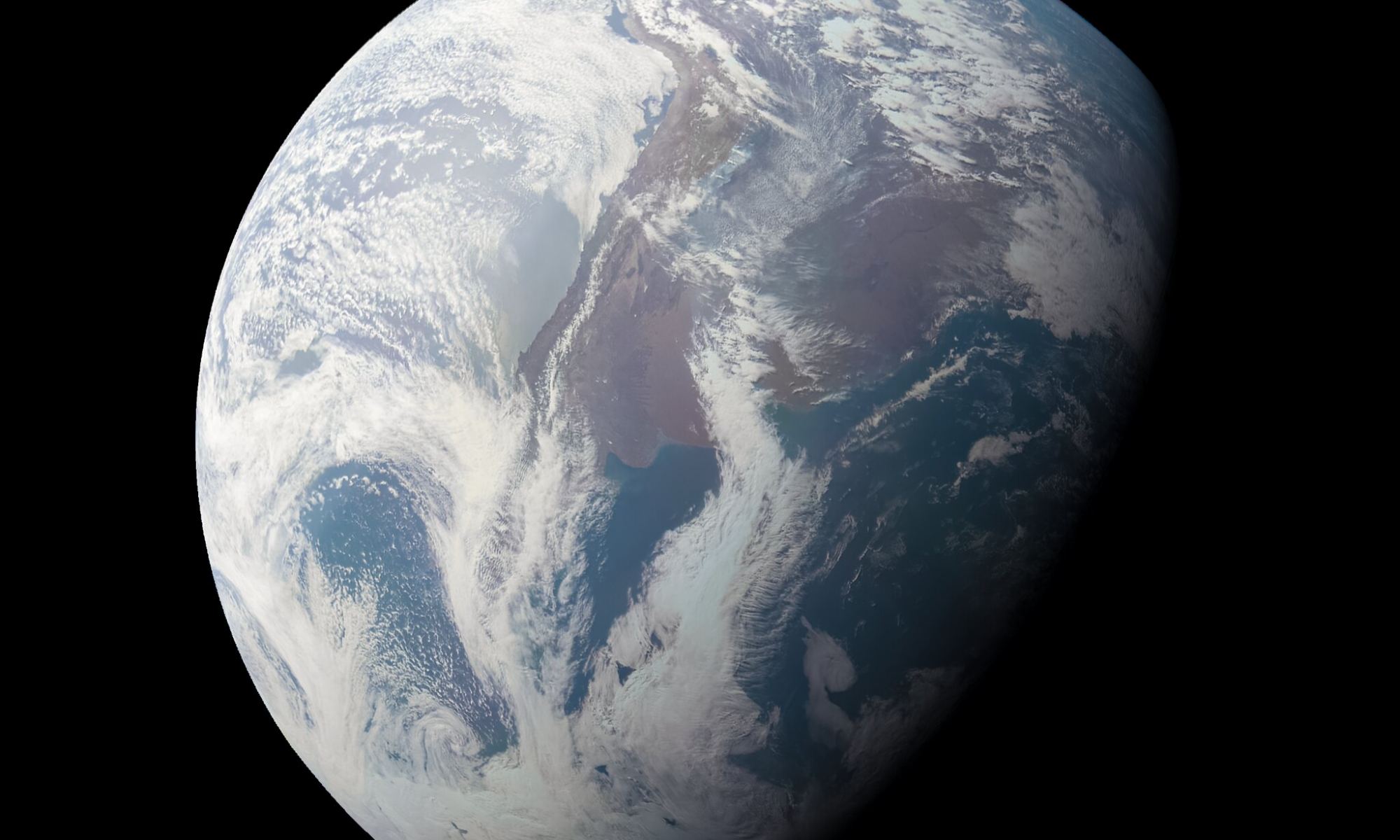
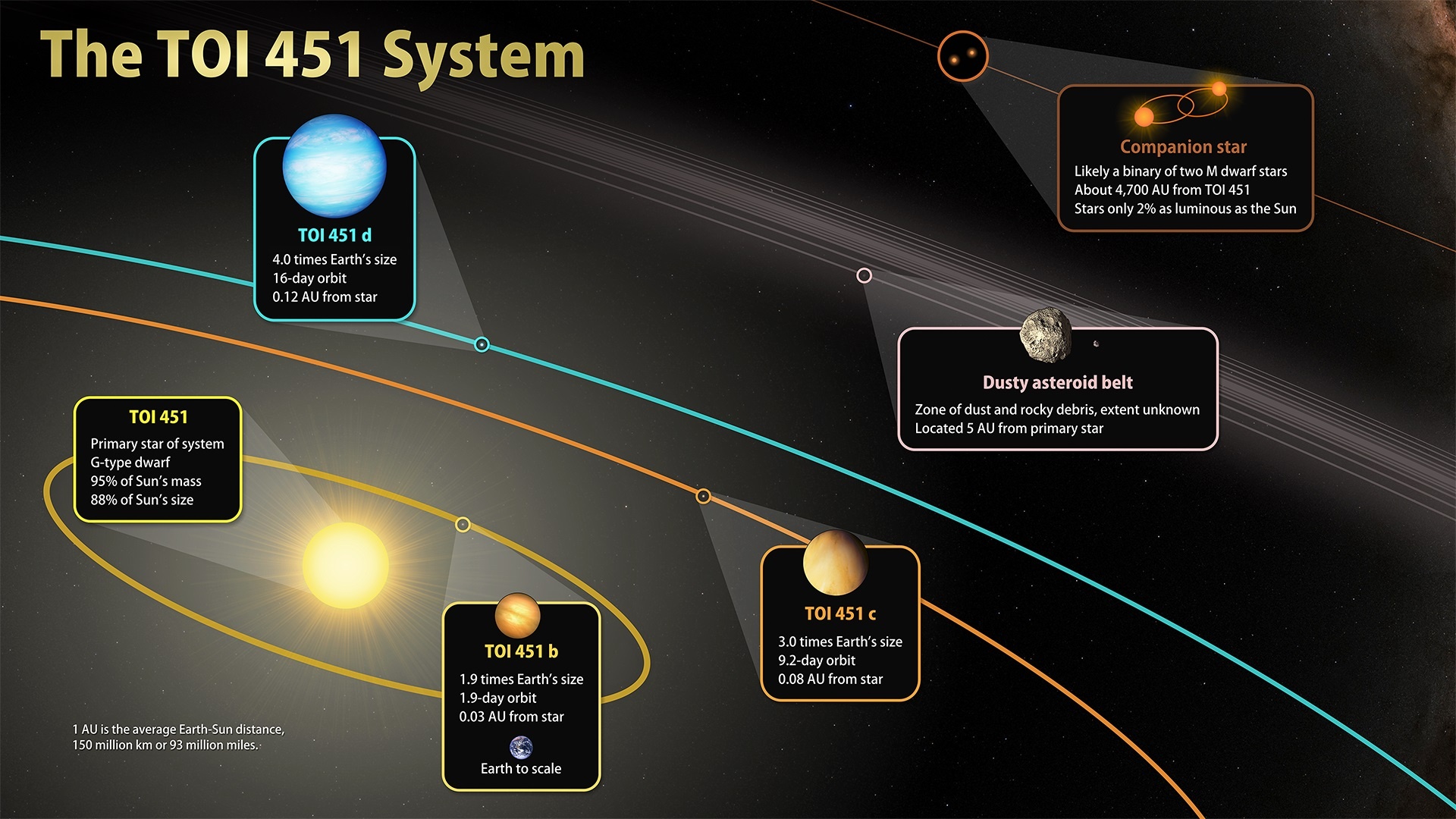
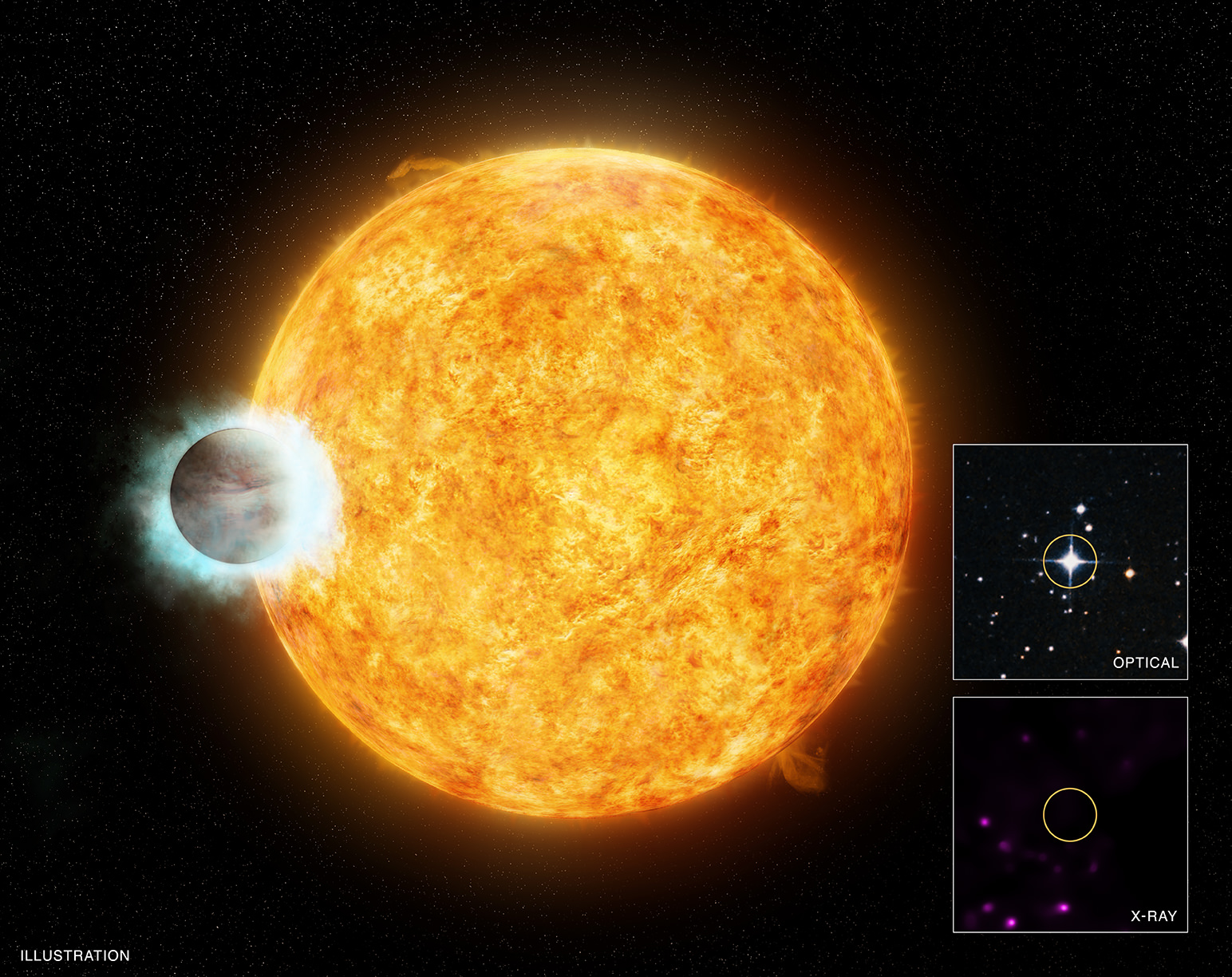
Between 2021 and 2024, the James Webb (JWST) and Nancy Grace Roman (RST) space telescopes will be launched to space. As the successors to multiple observatories (like Hubble, Kepler, Spitzer, and others), these missions will carry out some of the most ambitious astronomical surveys ever mounted. This will range from the discovery and characterization of extrasolar planets to investigating the mysteries of Dark Matter and Dark Energy.
In addition to advanced imaging capabilities and high sensitivity, both instruments also carry coronagraphs – instruments that suppress obscuring starlight so exoplanets can be detected and observed directly. According to a selection of papers recently published by the Journal of Astronomical Telescopes, Instruments, and Systems (JATIS), we’re going to need more of these instruments if we truly want to really study exoplanets in detail.
Continue reading “To Take the Best Direct Images of Exoplanets With Space Telescopes, we’re Going to Want Starshades”