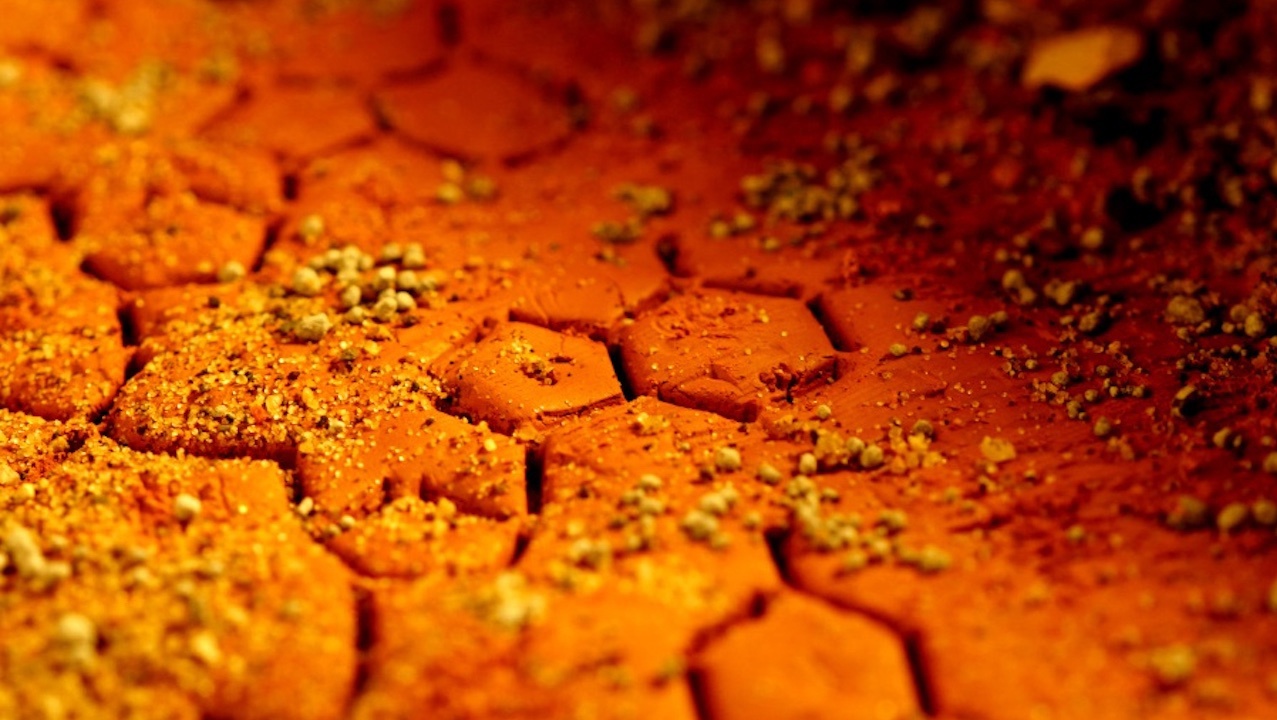
The search for life in the Universe has fascinated humans for centuries. Mars has of course been high on the list of potential habitats for alien existence but since the numerous spacecraft images that have come back showing a barren landscape, it seems Mars may not be so habitable after all. That is, until recently. The Martian regolith, the top layer of dust upon the surface has been found to be full of perchlorate salts. These chemicals are poisonous to most life on Earth but a new study suggests that some extremophile protein enzymes and RNA may just be able to survive!
Continue reading “Toxic Perchlorate on Mars Could Make Life More Interesting”Extremophiles: Why study them? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?

Universe Today has conducted some incredible examinations regarding a plethora of scientific fields, including impact craters, planetary surfaces, exoplanets, astrobiology, solar physics, comets, planetary atmospheres, planetary geophysics, cosmochemistry, meteorites, and radio astronomy, and how these disciplines can help scientists and the public gain greater insight into searching for life beyond Earth. Here, we will discuss the immersive field of extremophiles with Dr. Ivan Paulino-Lima, who is a Senior Research Investigator at Blue Marble Space Institute of Science and the Co-Founder and Chief Science Officer for Infinite Elements Inc., including why scientists study extremophiles, the benefits and challenges, finding life beyond Earth, and proposed routes for upcoming students. So, why is it so important to study extremophiles?
Continue reading “Extremophiles: Why study them? What can they teach us about finding life beyond Earth?”Could Earth Life Survive on a Red Dwarf Planet?
Even though exoplanet science has advanced significantly in the last decade or two, we’re still in an unfortunate situation. Scientists can only make educated guesses about which exoplanets may be habitable. Even the closest exoplanet is four light-years away, and though four is a small integer, the distance is enormous.
That doesn’t stop scientists from trying to piece things together, though.
Continue reading “Could Earth Life Survive on a Red Dwarf Planet?”Life on Earth Uses Water as a Solvent. What are Some Other Options for Life as We Don't Know it?
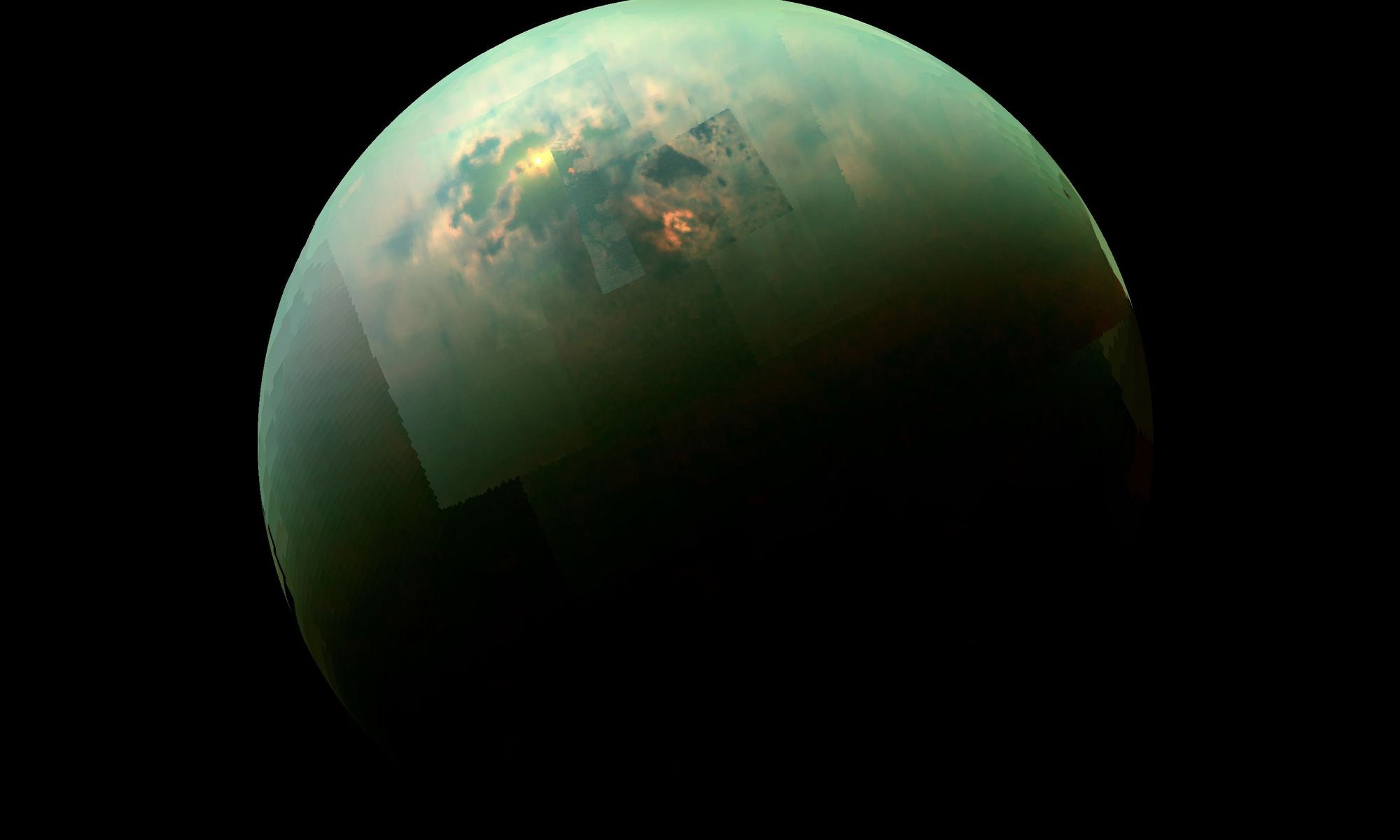

There is a vast menagerie of potentially habitable worlds in the cosmos, which means the Universe could be home to a diversity of life beyond what we can imagine. Creatures built on silicon rather than carbon, or organisms that breathe hydrogen instead of oxygen. But regardless of how strange and wondrous alien life may be, it is still governed by the same chemistry as life on Earth, and that means it needs a chemical solvent.
Continue reading “Life on Earth Uses Water as a Solvent. What are Some Other Options for Life as We Don't Know it?”Microbes Can Survive in Saltier Water than Previously Believed
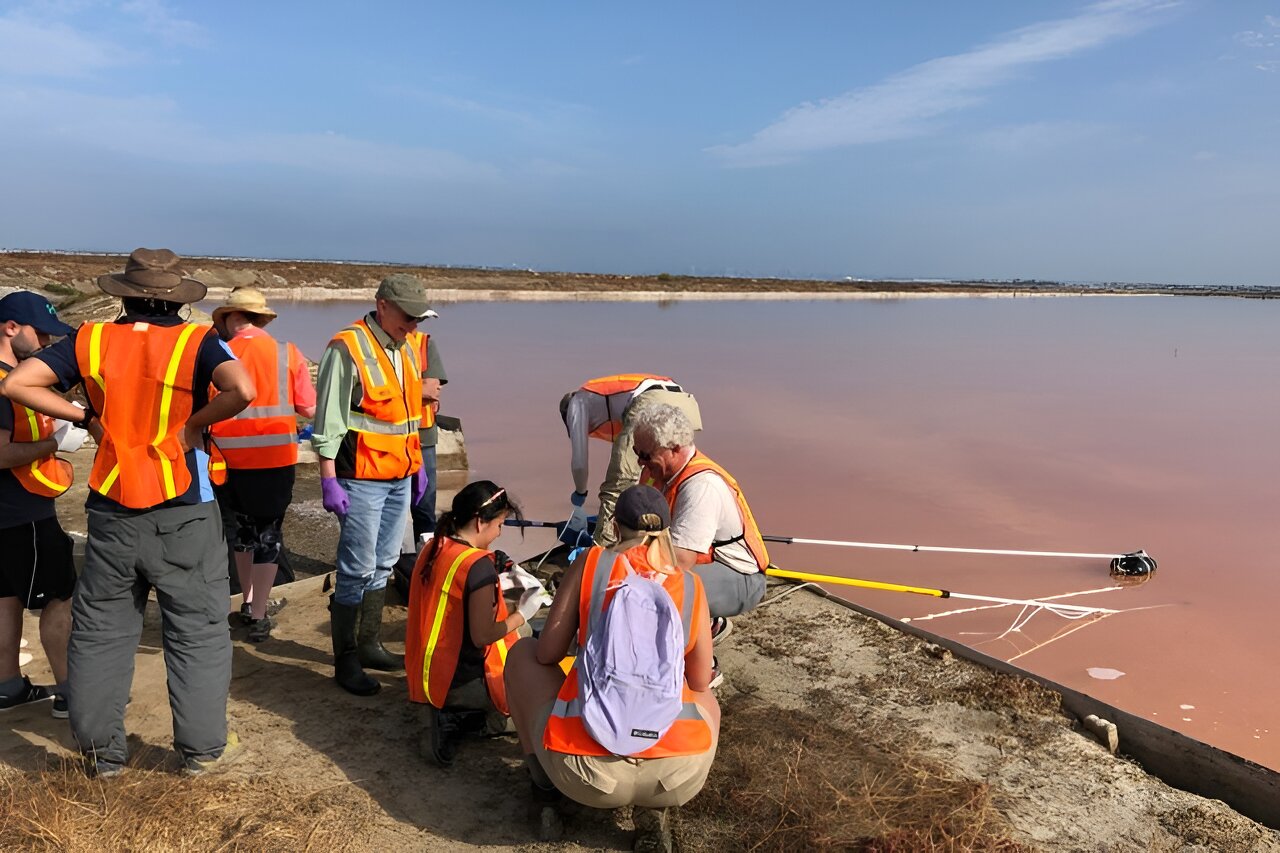

On Earth, it seems to be true that life will find a way; in the deepest ocean, the saltiest ocean or the highest mountain, live seems to find a way to get a foothold. One of the key ingredients for life seems to be the necessity for water. Until now, it was thought that there was a limit to the level of salinity within which life could thrive. A team of biologists have found bacterial life thrives in salty ponds where the water evaporates leaving high levels of salt. This only serves to expand the likely envrionments across the Universe that life could evolve.
Continue reading “Microbes Can Survive in Saltier Water than Previously Believed”NASA Tests a Robotic Snake That Could Explore Other Worlds
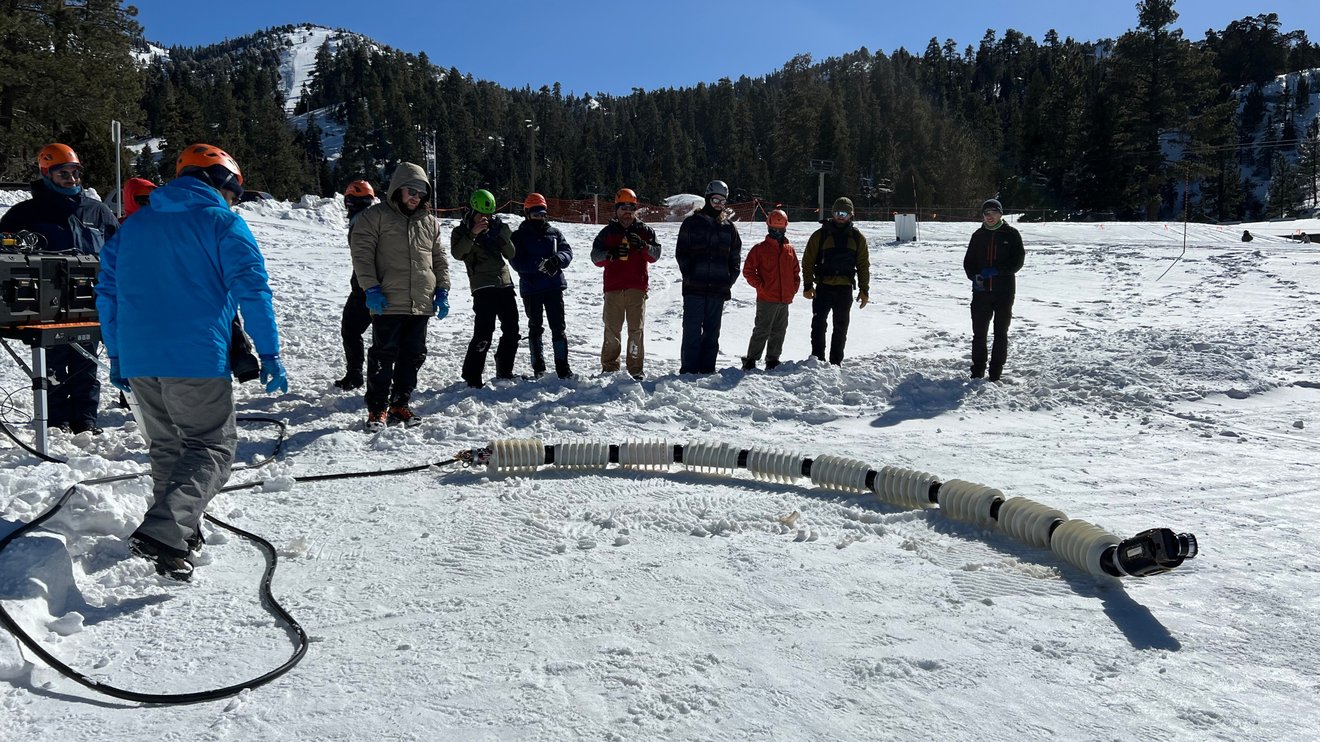

Rovers have enabled some amazing explorations of other worlds like the Moon and Mars. However, rovers are limited by the terrain they can reach. To explore inaccessible terrain, NASA is testing a versatile snake-like robot that could crawl up steep slopes, slither across ice, and even slide into lava tubes. Called Exobiology Extant Life Surveyor (or EELS), this robot could cross different terrains and create a 3D map of its surrounding to autonomously pick its course, avoiding hazards to reach its destination.
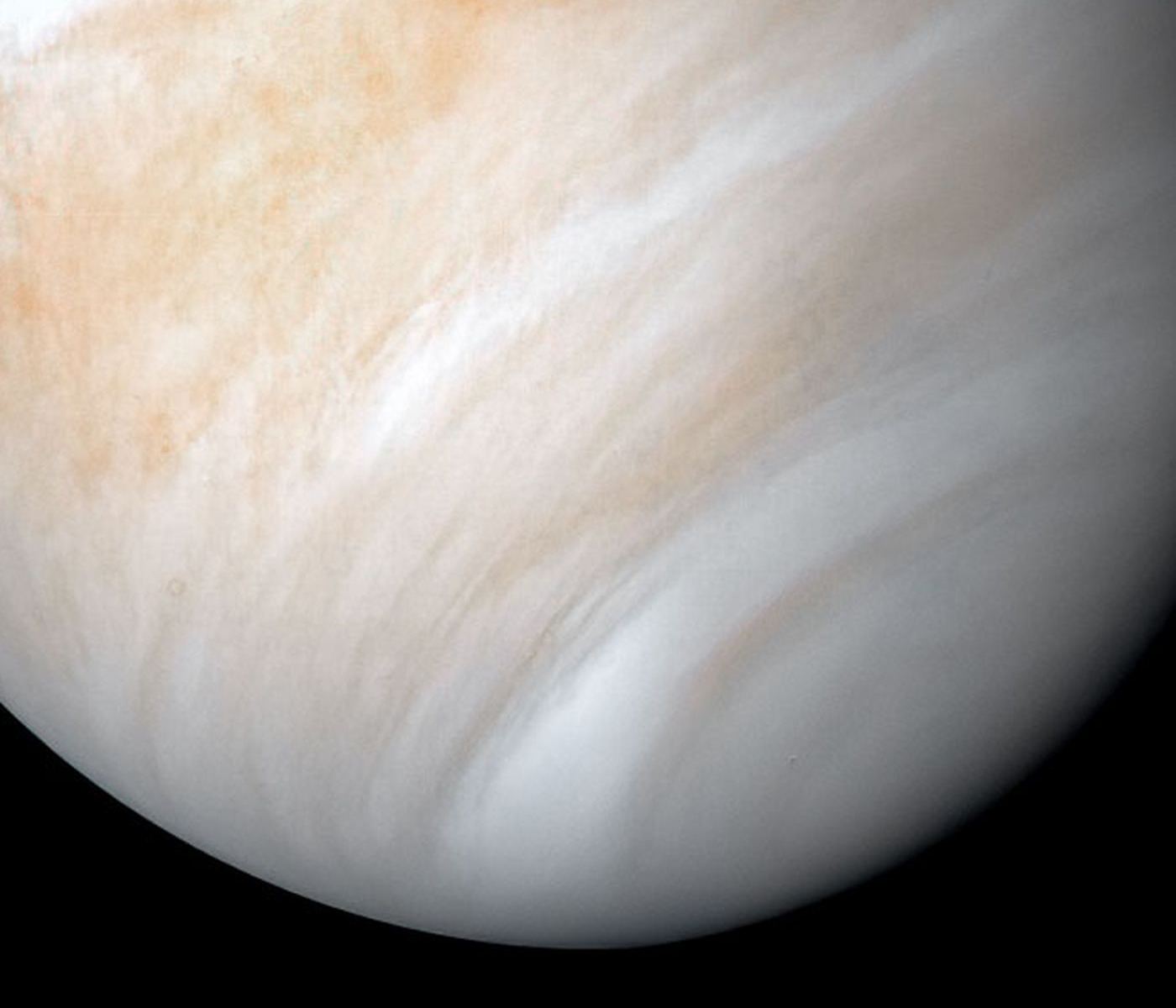
Continue reading “NASA Tests a Robotic Snake That Could Explore Other Worlds”Scientists Have Re-Analyzed Their Data and Still See a Signal of Phosphine at Venus. Just Less of it
In September, an international team announced that based on data obtained by the Atacama Millimeter-submillimeter Array (ALMA) in Chile and the James Clerk Maxwell Telescope (JCMT) in Hawaii, they had discovered phosphine gas (PH3) in the atmosphere of Venus. The news was met with its fair share of skepticism and controversy since phosphine is considered a possible indication of life (aka. a biosignature).
Shortly thereafter, a series of papers were published that questioned the observations and conclusions, with one team going as far as to say there was “no phosphine” in Venus’ atmosphere at all. Luckily, after re-analyzing the ALMA data, the team responsible for the original discovery concluded that there is indeed phosphine in the cloud tops of Venus – just not as much as they initially thought.
Continue reading “Scientists Have Re-Analyzed Their Data and Still See a Signal of Phosphine at Venus. Just Less of it”Could There Be a Form of Life Inside Stars?

Are we alone in the universe?
It is one of the most profound questions posed in modern astronomy. But although our understanding of the cosmos has grown significantly, the question remains unanswered. We know that Earth-like planets are common, as are the building blocks necessary for terrestrial life, and yet we still haven’t found definitive evidence for life beyond Earth. Perhaps part of our problem is that we are mostly looking for life similar to our own. It is possible that alien life is so radically different from that of Earth it goes unnoticed.
Continue reading “Could There Be a Form of Life Inside Stars?”An ocean floor bacteria has been found with a totally bizarre metabolism
Bacteria come in two basic forms: the kinds that use a lot of hydrogen, and the kinds that don’t. And recently researchers think they’ve found a new bacteria that appear to do both at the same time, allowing it to live in a variety of extreme environments, like the ocean floor.
Its name is Acetobacterium woodii, often shortened to A. woodii, and it seems like it’s a superhero of the small-sized world.
Continue reading “An ocean floor bacteria has been found with a totally bizarre metabolism”Nutrient-Poor and Energy-Starved. How Life Might Survive at the Extremes in the Solar System

Our growing understanding of extremophiles here on Earth has opened up new possibilities in astrobiology. Scientists are taking another look at resource-poor worlds that appeared like they could never support life. One team of researchers is studying a nutrient-poor region of Mexico to try to understand how organisms thrive in challenging environments.
Continue reading “Nutrient-Poor and Energy-Starved. How Life Might Survive at the Extremes in the Solar System”


