[/caption]
From a pool of 500 potential applicants, Virgin Galactic has found their man. The NewSpace firm chose from some of the greatest pilots the world has to offer to work to be a pilot for their company. U.S. Air Force test pilot Keith Colmer rose to the top of the list and was selected by Virgin Galactic to join the team that is working to allow private citizens a flight into space.
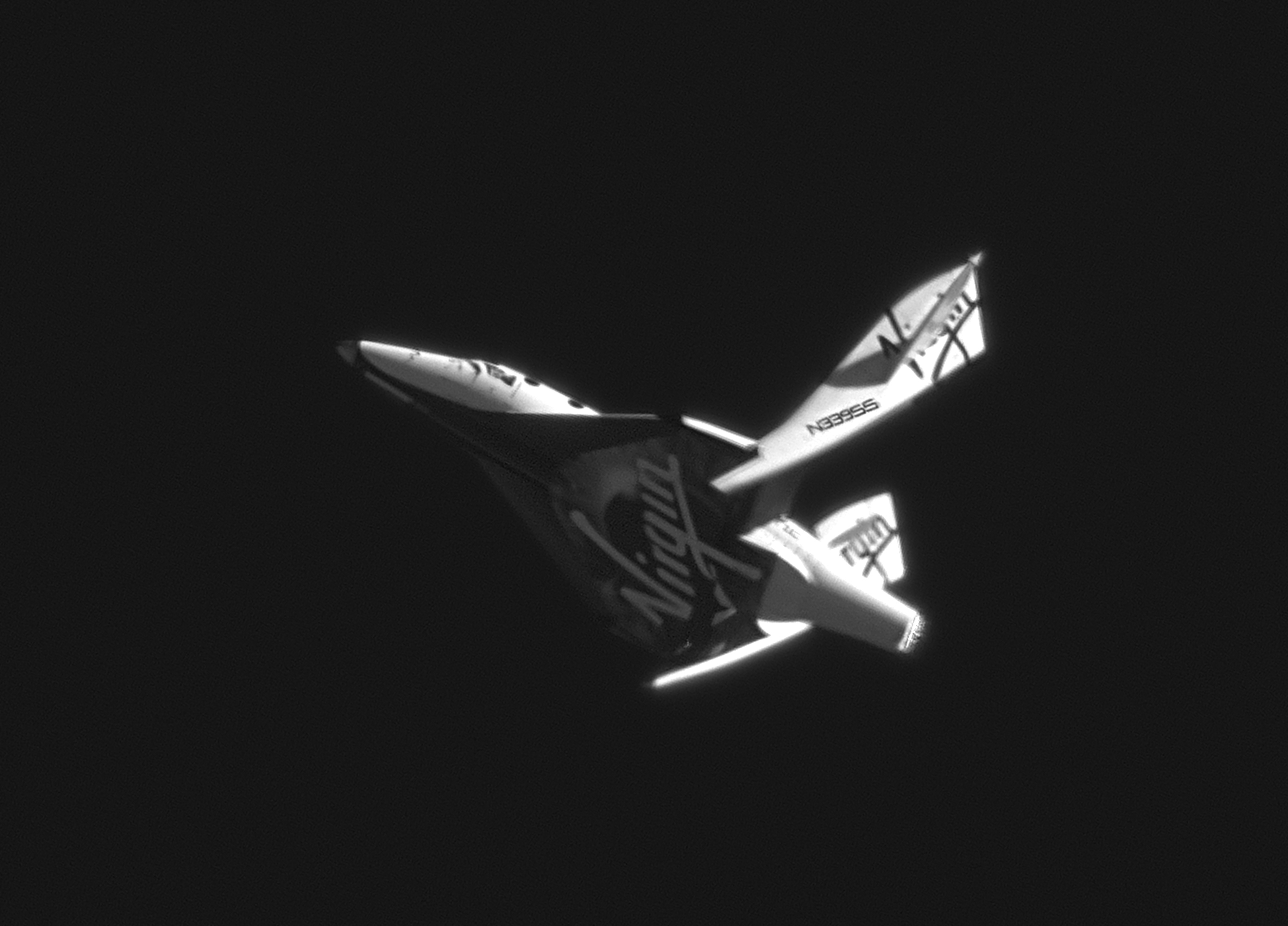
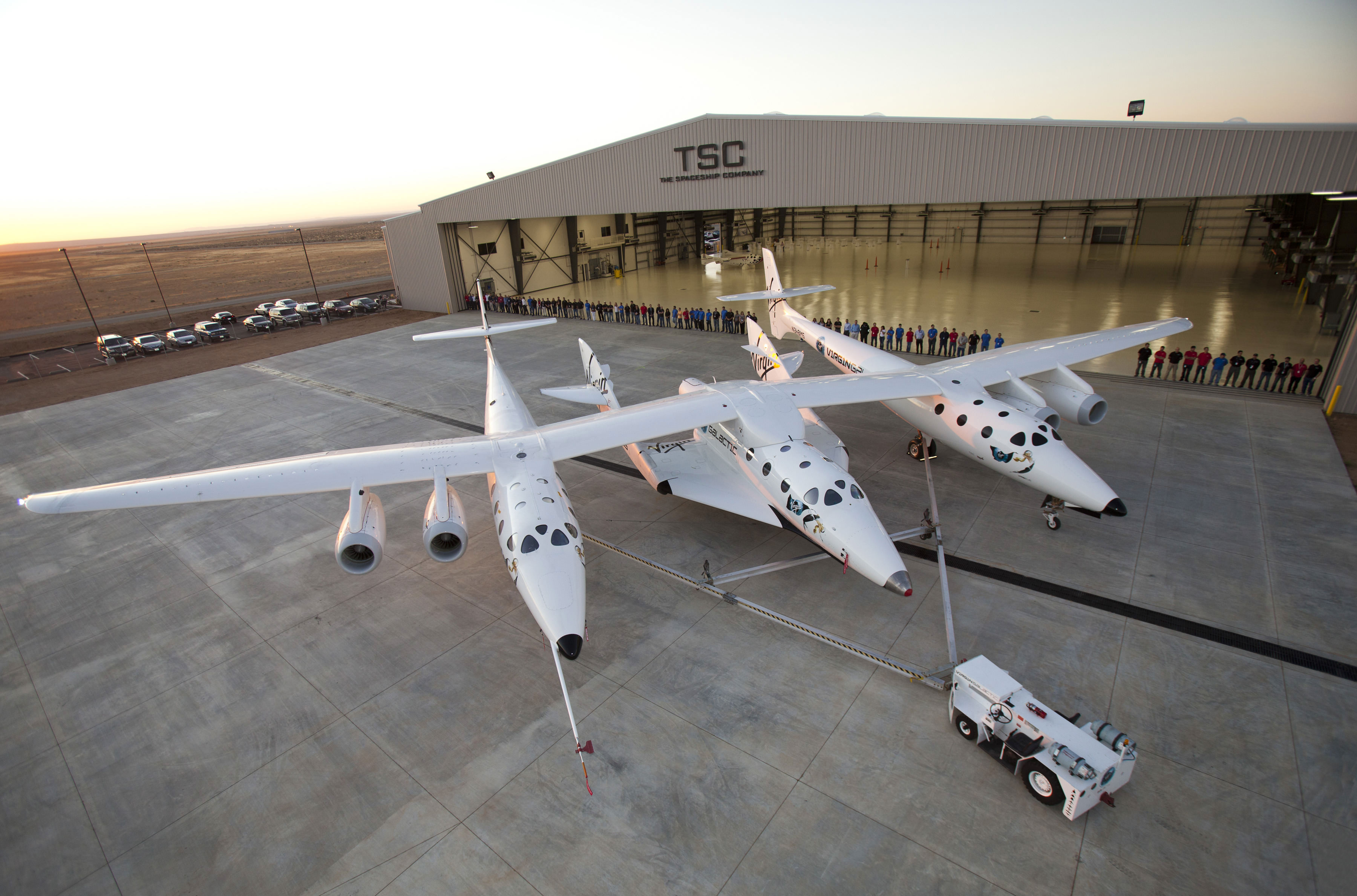
Virgin Galactic announced Colmer’s addition to the company’s space flight team on Oct. 26. He will join Virgin Galactic’s Pilot David Mackay as they work to get the company’s carrier aircraft, WhiteKnightTwo and its spacecraft SpaceShipTwo into service. They will be joined by more pilots as the company works to begin operations in 2013.

“Keith brings the kind of tremendous multi-dimensional talent and skill set that we are looking for in our astronaut pilots,” said Virgin Galactic’s President and CEO George Whitesides. “But equally important to us are his impeccable character and his outstanding record of high caliber performance in highly demanding environments. He sets the bar very high for others to come.”
“This team in Mojave is second to none,” said Mackay about Scaled Composite’s test pilots. “Keith and I are indeed fortunate to have their expertise and body of work to build on as we enter the final phases of the test program and prepare to open space to all.”
Colmer is a veteran pilot, with 12 years worth of experience in testing experimental aircraft. He has over 5,000 hours logged in more than 90 different types of aircraft.

Former NASA Space Shuttle Manager Mike Moses recently left NASA to work as Virgin Galactic’s Vice President of Operations. Virgin Galactic is working to begin powered test flights, and after that the company will try to begin commercial operations.
“I am extremely honored to have been the first astronaut pilot selected through competition to join the team,” said Colmer. “Virgin Galactic is truly revolutionizing the way we go to space and I am looking forward to being a part of that.”
Colmer has served as a combat pilot, flying an F-16 in two tours in Iraq with the Colorado Air National Guard. According to information provided in a Virgin Galactic press release he is the first Air National Guard pilot to ever be selected to attend the USAF Test Pilot School, at Edwards Air Force Base.

Colmer has a Bachelor of Science in Aeronautics and Astronautics from the Massachusetts Institute of Technology. He holds a Masters degree in Aerospace Engineering and a Masters degree in Telecommunications from the University of Colorado, Boulder. He is a graduate of the USAF Undergraduate Space Training program, the Euro-NATO Joint Jet Pilot Training Program and USAF Test Pilot School, Class 02A.
Virgin Galactic recently dedicated its Space Port in Las Cruces, New Mexico. The company is part of the London-based Virgin Group which is owned by Sir Richard Branson. The company formed after Scaled Composites one the $10 million Ansari X-PRIZE back in 2004. The flights of WhiteKnightOne and SpaceShipOne paved the way for the development of the vehicles that Virgin Galactic is planning on utilizing to begin suborbital space flight operations. Tickets for flights on the commercial space plane are set to cost approximately $200,000.