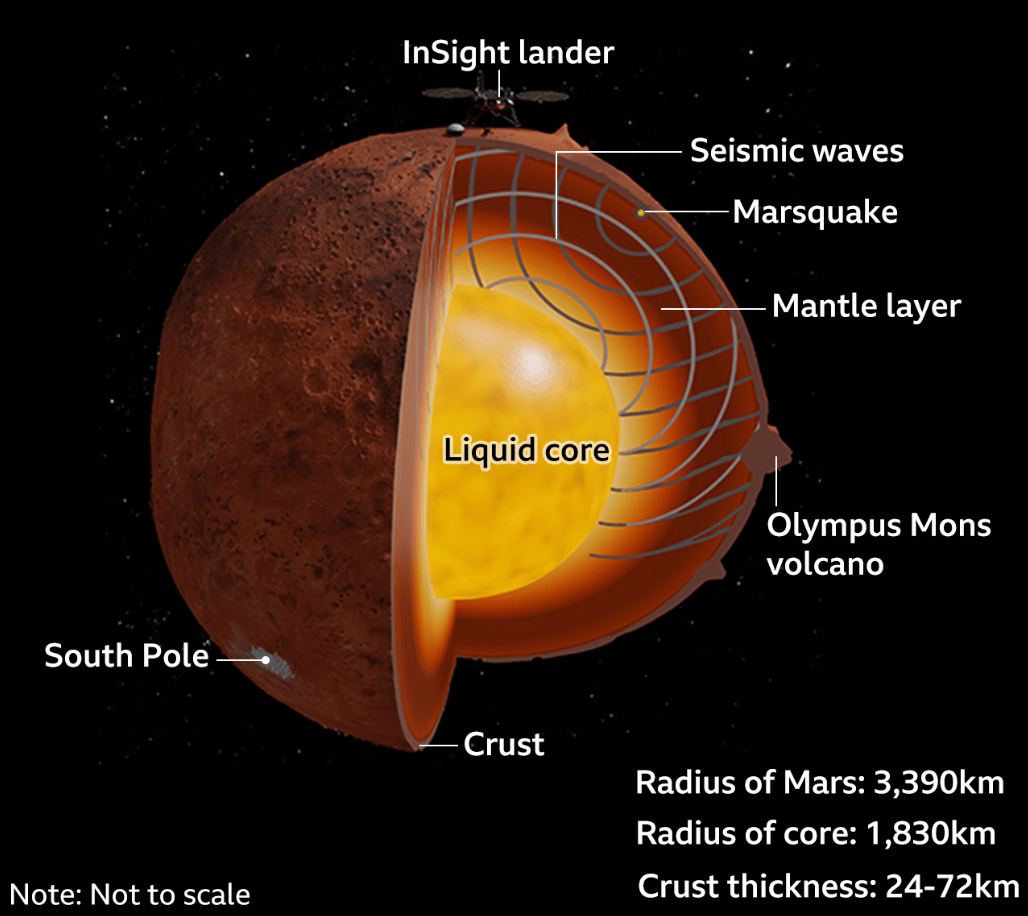
Within Jupiter’s massive system of satellites, four large moons really stand out. They’re known as the “Galilean Moons” in honor of Galileo Galilee, who made the first recorded observations of them in 1610. The innermost of these moons is the rocky moon Io, which is slightly larger than Earth’s Moon and slightly denser. With more than 400 active volcanoes on its surface, it is the most geologically active body in the Solar System.
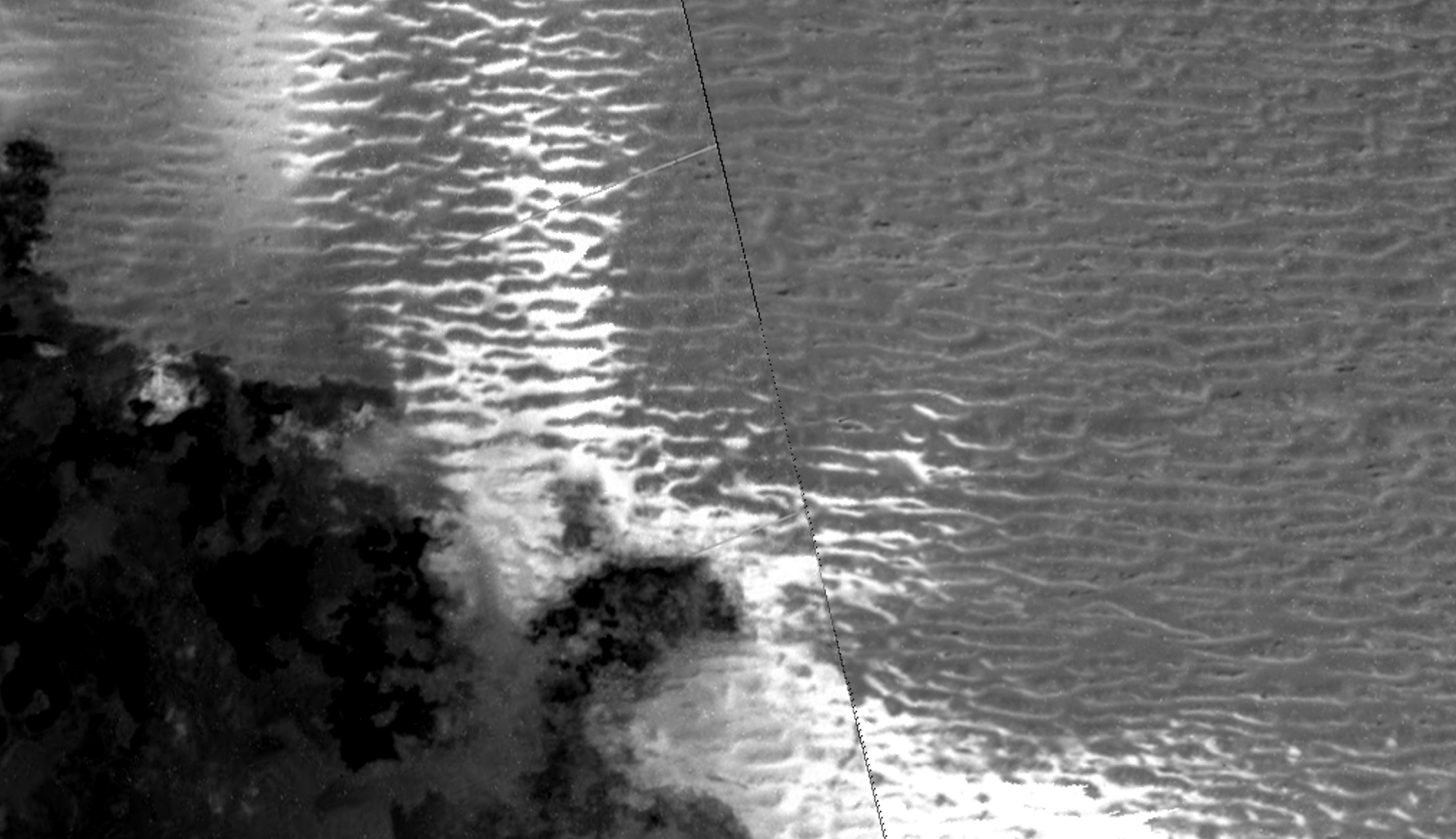
Add to that the intense radiation it gets from Jupiter’s magnetic field, and it’s arguably one of the most hellish environments in the Solar System! Nevertheless, scientists have long been puzzled by the meandering ridges visible on the surface, which are as large as any seen here on Earth. Thanks to a recent study led by Rutgers University, there’s now an explanation for how these formations can exist on a surface as icy and volcanic as Io’s.
Continue reading “Jupiter’s Moon Io has Dunes. Dunes!?”