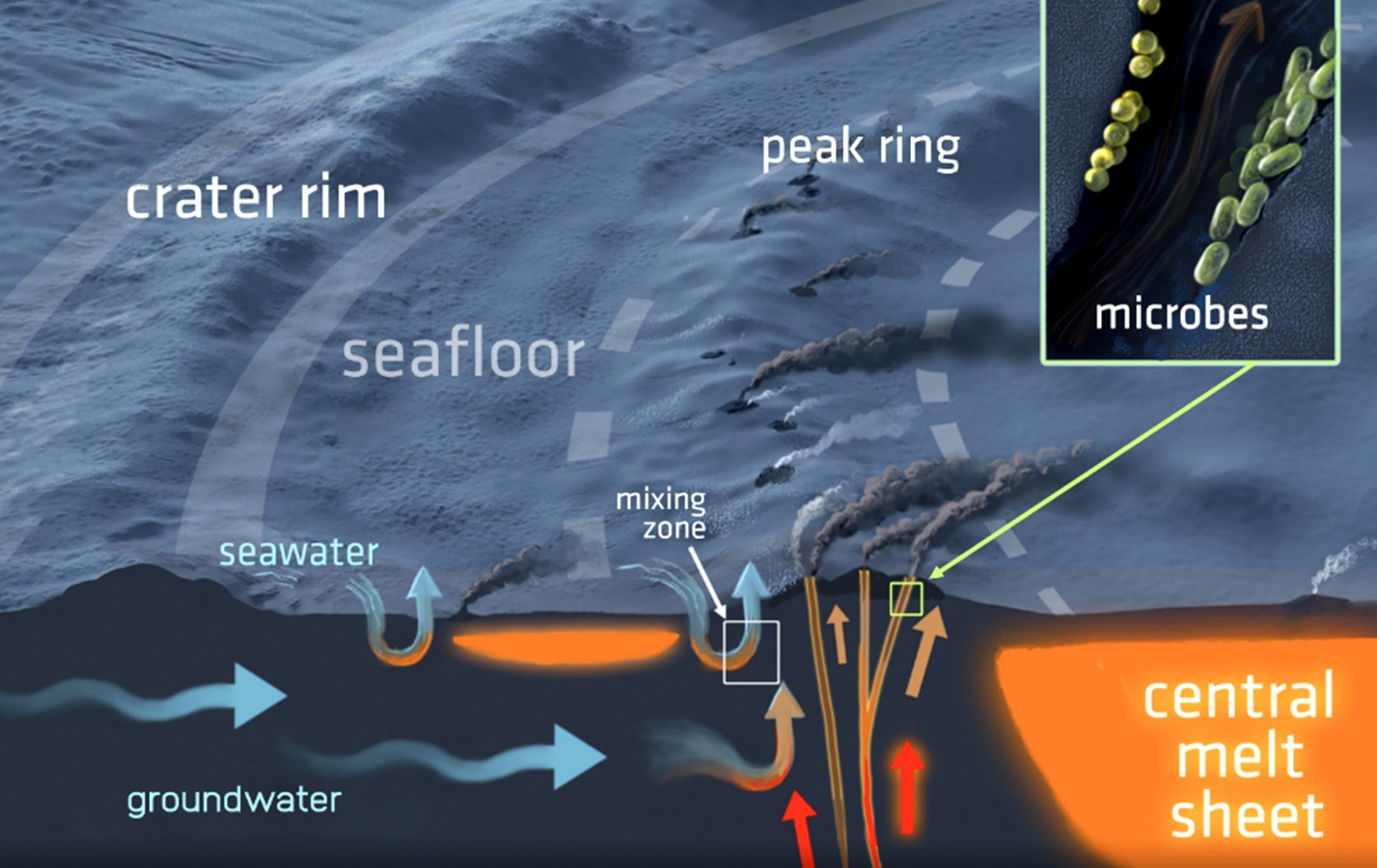
The Chicxulub impact event was an enormous catastrophe that left a huge imprint on the Earth’s surface. Not only did it cause the mass extinction of the dinosaurs, it left a crater 180 km (112 miles) in diameter, and deposited a worldwide layer of concentrated iridium in the Earth’s crust.
But a new study shows that the impact also left its mark deep underground, in the form of a vast hydrothermal system that modified a massive chunk of the Earth’s crust.
Continue reading “The Meteor Impact that Wiped Out the Dinosaurs Created a Vast Underground Hydrothermal System”