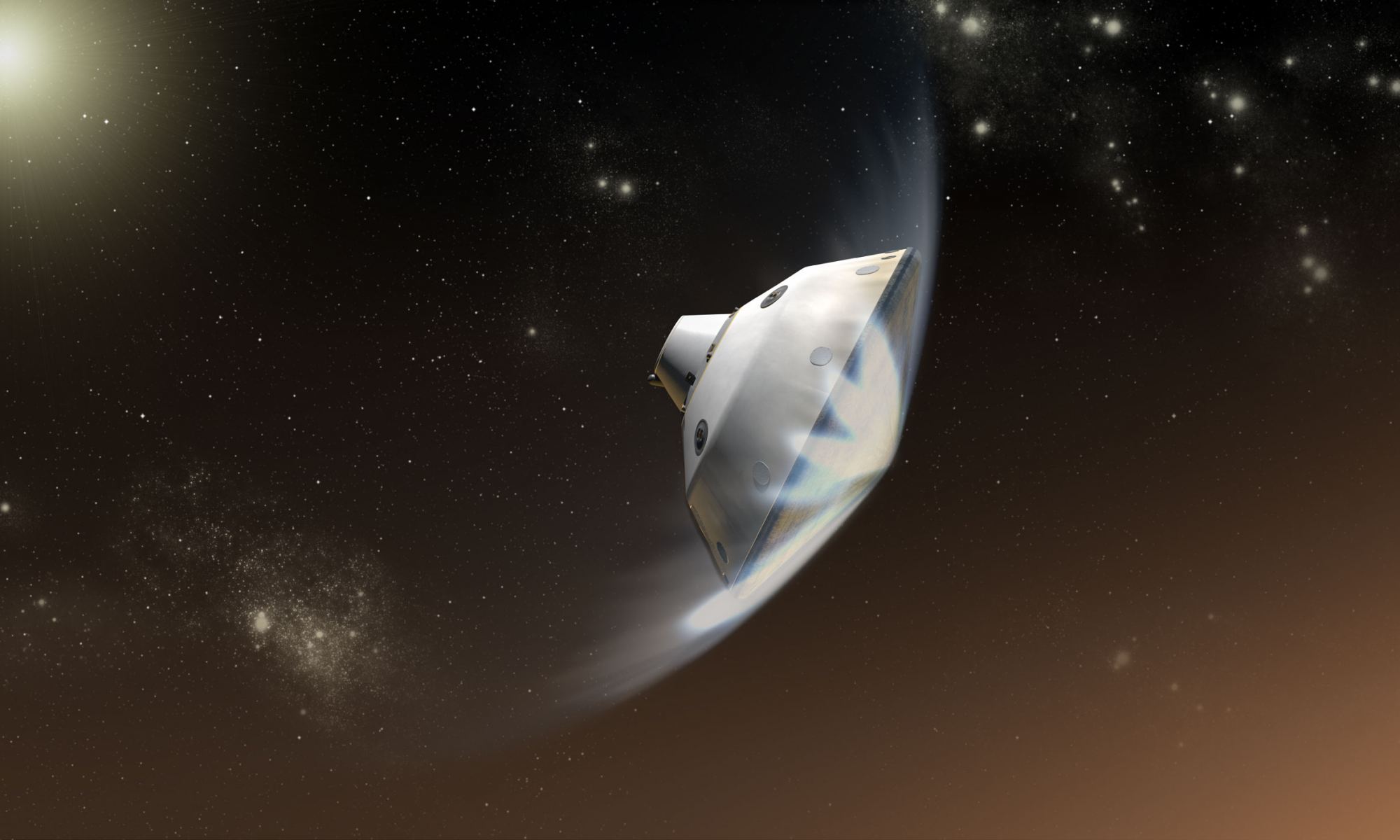
It’s too bad Mars is such an interesting place, because it’s actually one of the most difficult places to visit in the Solar System, especially if you want to bring along a lot of luggage. That planet is a graveyard of missions that didn’t quite make it.
Messier 81 – the Bode Galaxy
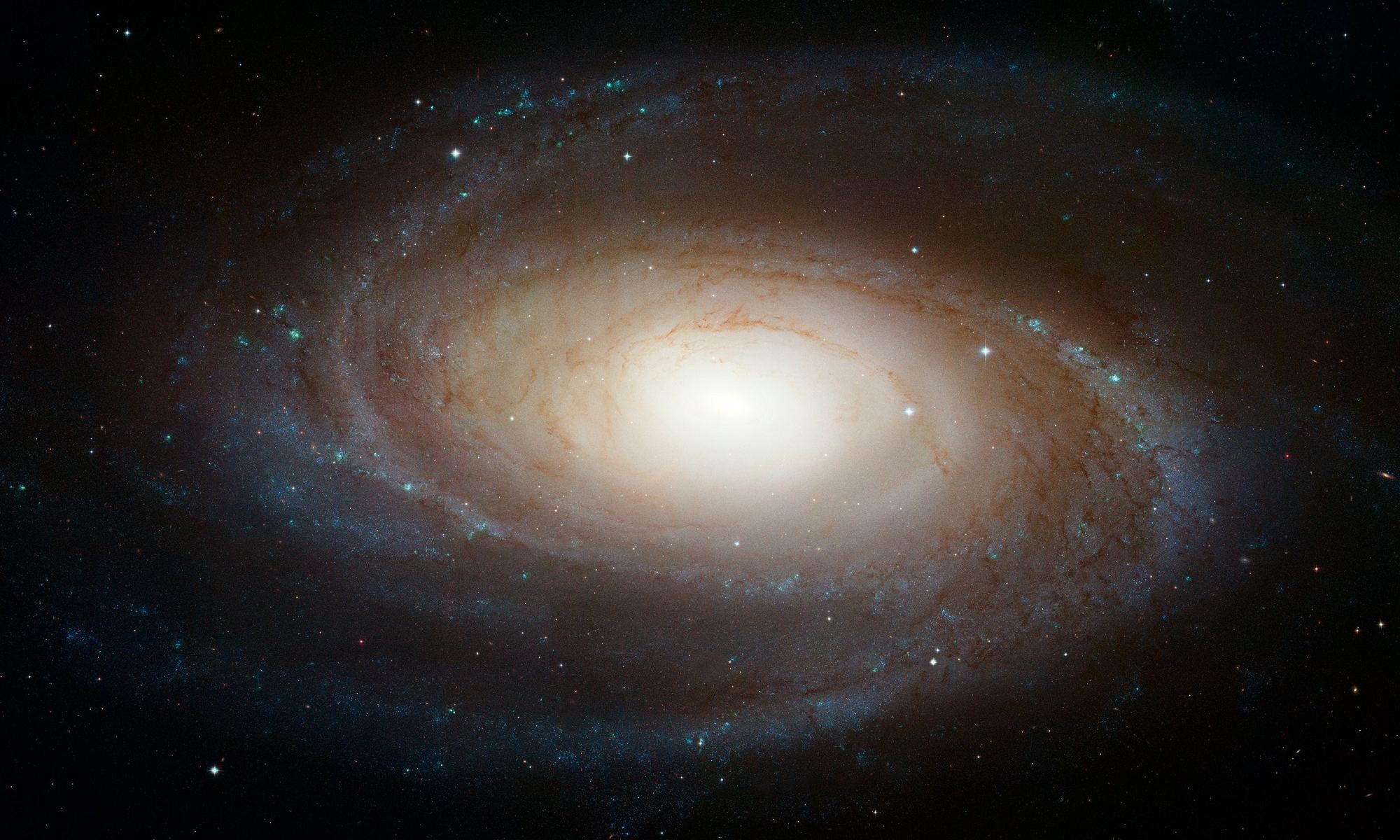

Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the Bode’s Galaxy – also known as Messier 81!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
One of these objects is the galaxy known as Messier 81 (aka. Bode’s Galaxy), a spiral galaxy located about 12 million light-years from our Solar System. Measuring about 90,000 light-years in diameter (half the size of the Milky Way), this galaxy’s proximity, large size, and active galactic nuclear (AGN) makes its a favorite among professional and amateur astronomers alike.
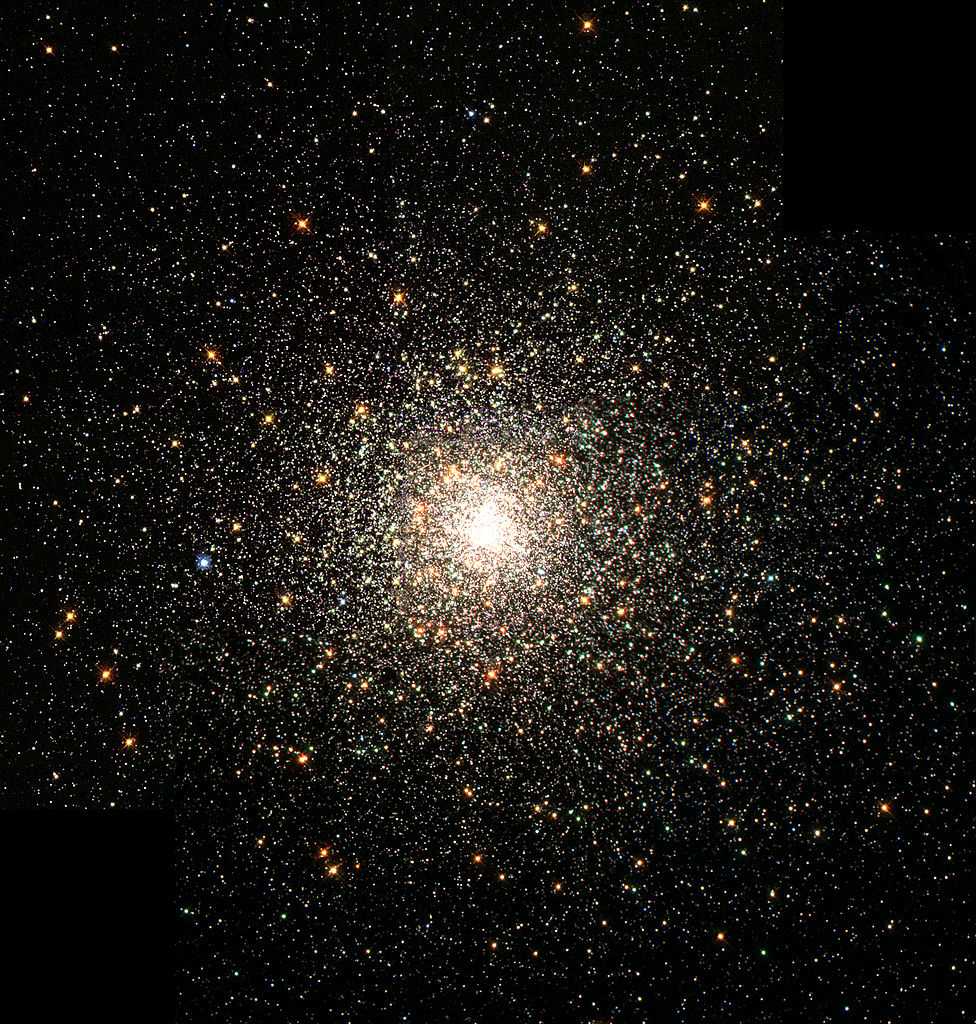
Messier 80 – the NGC 6093 Globular Cluster
Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the globular cluster known as Messier 80!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
One of these objects is Messier 80, a globular star cluster located about 32,600 light years from Earth in the constellation Scorpius. This cluster is one of the most densely populated in our galaxy and is located about halfway between the bright stars Antares, Alpha Scorpii, Akrab and Beta Scorpii – making it relatively easy to find.
Continue reading “Messier 80 – the NGC 6093 Globular Cluster”
Messier 79 – the NGC 1904 Globular Cluster
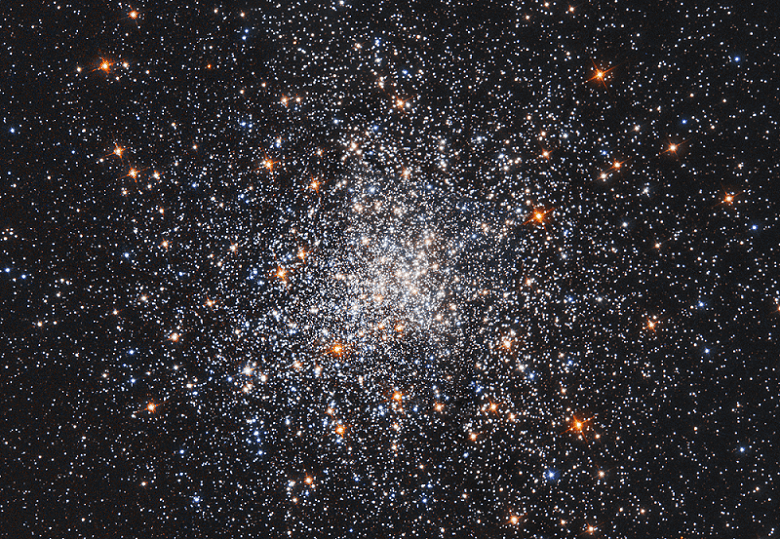
Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the globular cluster known as Messier 79!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
One of these objects is Messier 79 (aka. NGC 1904), a globular cluster in the constellation Lepus. Located about 42,000 light years from Earth, and 60,000 light years from the Galactic Center, this cluster is believed to not be native to the Milky Way itself. One possibility is that it arrived in our galaxy as part of the Canis Major Dwarf Galaxy, which is currently the closest galaxy to our own (though this remains the subject of debate).
Continue reading “Messier 79 – the NGC 1904 Globular Cluster”
Messier 78 – the NGC 2068 Reflection Nebula
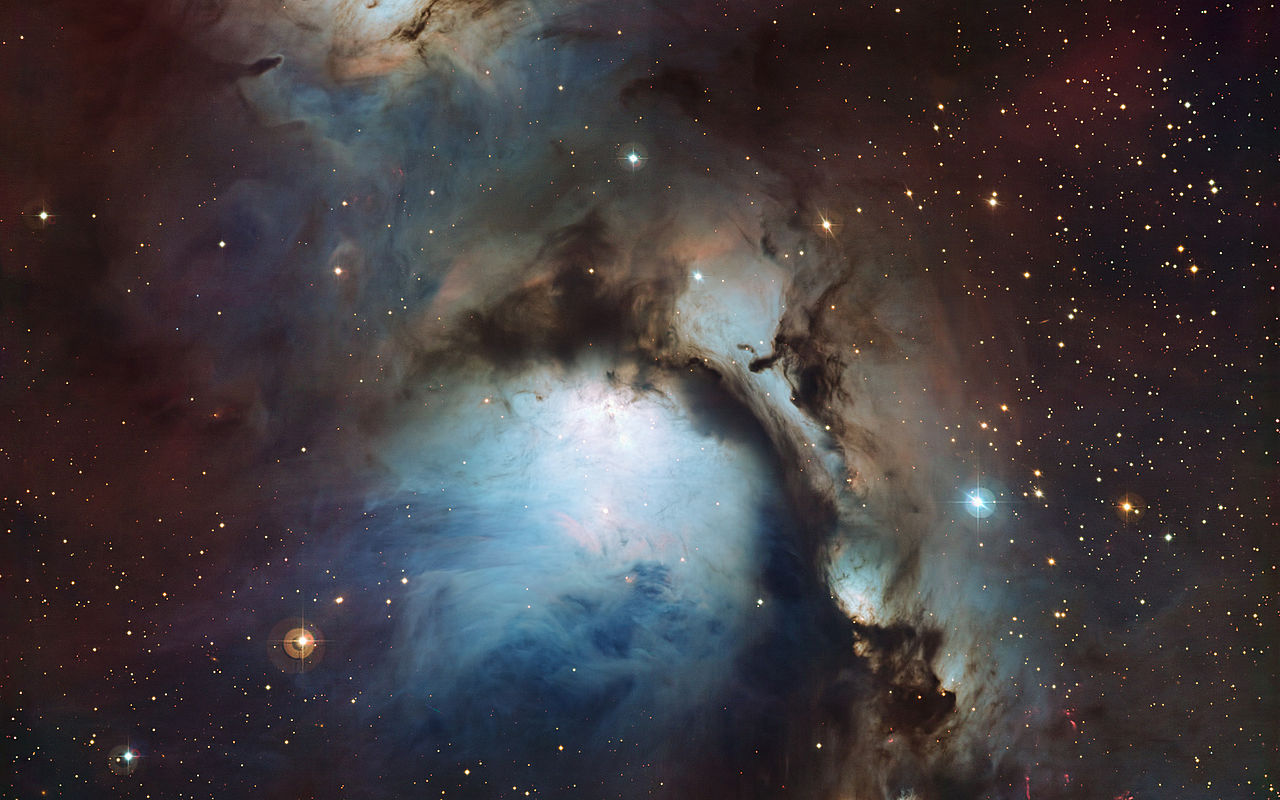

Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the bright reflection nebula known as Messier 78!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
Continue reading “Messier 78 – the NGC 2068 Reflection Nebula”
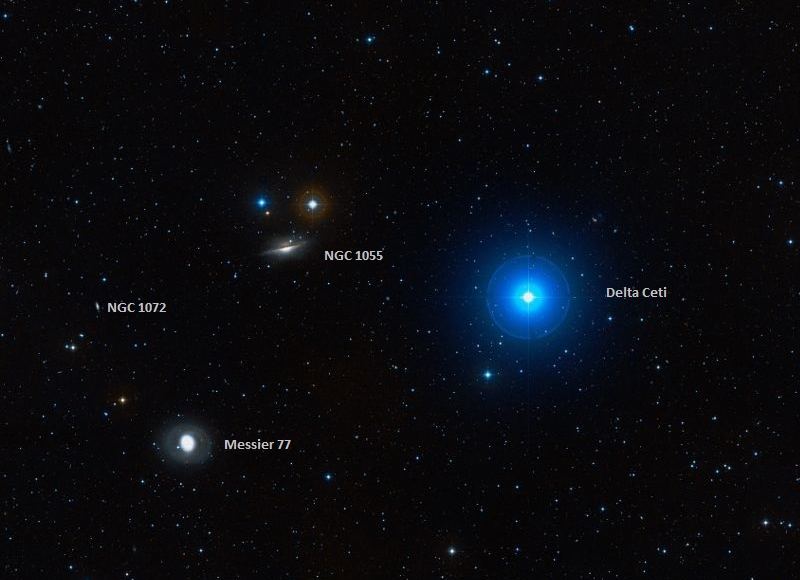
Messier 77 – the Cetus A Barred Spiral Galaxy
Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at Cetus A, the barred spiral galaxy known as Messier 77!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
One of these objects is known as Messier 77 (aka. Cetus A), a barred spiral galaxy located 47 million light-years from Earth in the constellation Cetus. Measuring some 170,000 light-years in diameter, it is one of the largest galaxies included in the Messier Catalog. Its size and bright core also make it relatively easy to spot with binoculars or small telescopes.
Continue reading “Messier 77 – the Cetus A Barred Spiral Galaxy”
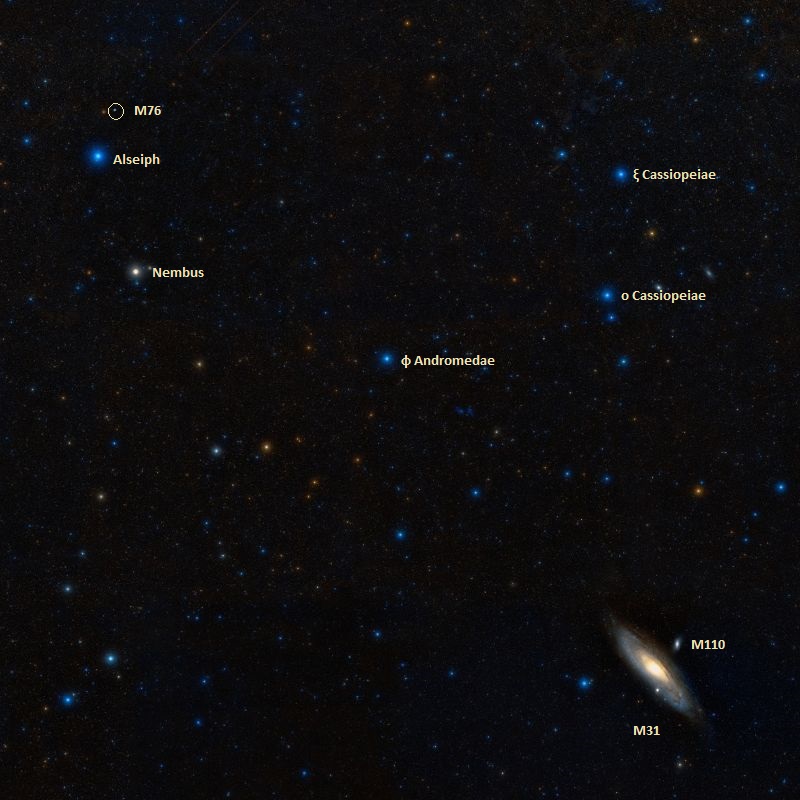
Messier 76 – the NGC 650/651 Planetary Nebula
Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the “little dumbbell” itself, the planetary nebula known as Messier 76!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
One of these objects is the Messier 76 (aka. the Little Dumbbell Nebula, the Barbell Nebula, or the Cork Nebula) a planetary nebula located about 2,500 light years away in the Perseus Constellation. While it is easy to find because of its proximity to the Cassiopeia Constellation (located just south of it), the faintness of this nebula makes it one of the more difficult Messier Objects to observe. Continue reading “Messier 76 – the NGC 650/651 Planetary Nebula”
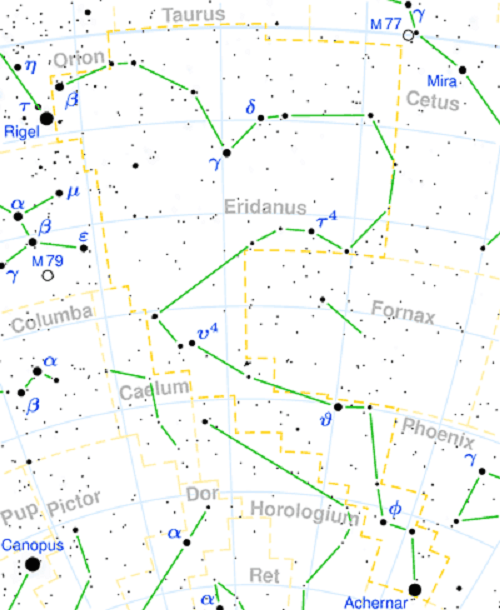
The Eridanus Constellation
Welcome to another edition of Constellation Friday! Today, in honor of the late and great Tammy Plotner, we take a look at the winding river – the Eridanus constellation. Enjoy!
In the 2nd century CE, Greek-Egyptian astronomer Claudius Ptolemaeus (aka. Ptolemy) compiled a list of the then-known 48 constellations. This treatise, known as the Almagest, would be used by medieval European and Islamic scholars for over a thousand years to come, effectively becoming astrological and astronomical canon until the early Modern Age.
One of these is the southern constellation of Eridanus, the sixth largest modern constellation in the night sky. The constellation takes its name from the Greek name for the river Po in Italy and is represented by a celestial river. This constellation is bordered by the constellations of Caelum, Cetus, Fornax, Horologium, Hydrus, Lepus, Phoenix, Taurus, and Tucana.
Messier 75 – the NGC 6864 Globular Cluster
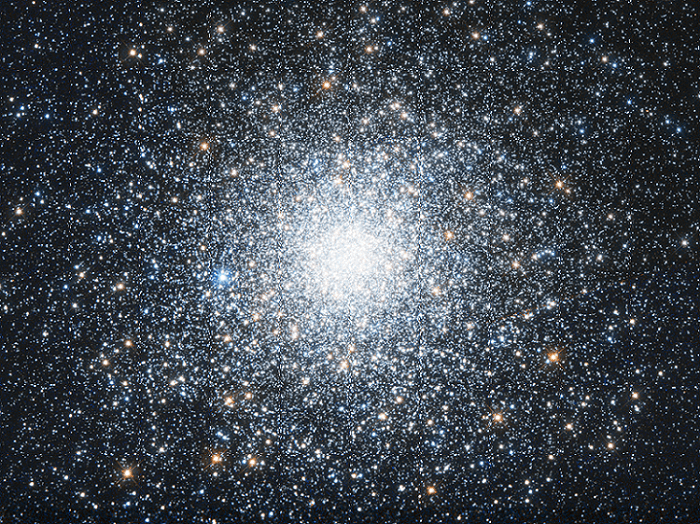
Welcome back to Messier Monday! Today, we continue in our tribute to our dear friend, Tammy Plotner, by looking at the globular cluster known as Messier 75!
During the 18th century, famed French astronomer Charles Messier noticed the presence of several “nebulous objects” while surveying the night sky. Originally mistaking these objects for comets, he began to catalog them so that others would not make the same mistake. Today, the resulting list (known as the Messier Catalog) includes over 100 objects and is one of the most influential catalogs of Deep Space Objects.
One of these objects is Messier 75 (aka. NGC 6864), a globular cluster roughly 67,500 light years from Earth near the southern constellation Sagittarius. This object is also about 14,700 light years away from the Galactic Center, and on the located on the other side relative to Earth. Because of its distance and location, this object is virtually impossible to see binoculars and difficult to resolve with small telescopes. Continue reading “Messier 75 – the NGC 6864 Globular Cluster”
The Equuleus Constellation
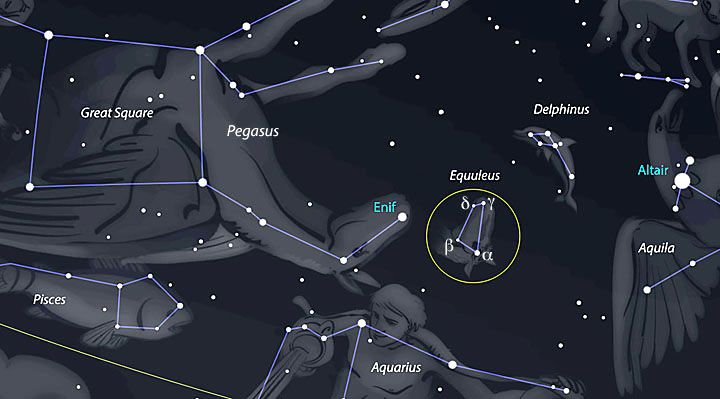
Welcome to another edition of Constellation Friday! Today, in honor of the late and great Tammy Plotner, we take a look at the “little horse” – the Equuleus constellation. Enjoy!
In the 2nd century CE, Greek-Egyptian astronomer Claudius Ptolemaeus (aka. Ptolemy) compiled a list of the then-known 48 constellations. This treatise, known as the Almagest, would be used by medieval European and Islamic scholars for over a thousand years to come, effectively becoming astrological and astronomical canon until the early Modern Age.
One of these constellation is Equuleus (aka. “little Horse”), a constellation that lies in the northern sky. This small, faint constellation is the second smallest in the night sky, after Crux (the Southern Cross). Today, it is one of the 88 modern constellations recognized by the International Astronomical Union (IAU) and is bordered by the constellations of Aquarius, Delphinus and Pegasus. Continue reading “The Equuleus Constellation”