It’s an engaging thought experiment.
What if Earth had multiple moons? Our world has one large natural satellite, just over a quarter the diameter, 1/50th the volume, and less than 1/80th the mass of our fair world. In fact, the Earth-Moon system has sometimes been referred to as a “binary planet,” and our Moon stands as the largest natural satellite of any planet — that is, if you subscribe to bouncing Pluto and Charon out of “the club” — in contrast to its primary of any moon in our solar system.
But what if we had two or more moons? And are there any tiny “moonlet” candidates lurking out there, awaiting discovery and perhaps exploration?
While historical searches for tiny secondary moons of the Earth — and even “moons of our Moon” — have turned up naught, the Earth does indeed capture asteroids as temporary moons and eject them back into solar orbit from time to time.
Now, a recent paper out of the University of Hawaii written in partnership with the SETI Institute and the Department of Physics at the University of Helsinki has looked at the possible prospects for the population of captured Near-Earth asteroids, and the feasibility of detecting these with existing and future systems about to come online.
The hunt for spurious moons of the Earth has a fascinating and largely untold history. Arthur Upgren’s outstanding book Many Skies devotes an entire chapter to the possible ramifications of an Earth with multiple moons… sure, more moons would be a bane for astrophotographers, but hey, eclipses and transits of the Sun would be more common, a definite plus.
In 1846, astronomer Frederic Petit announced the discovery of a tiny Earth-orbiting moon from Toulouse observatory. “Petit’s Moon” was said to orbit the Earth once every 2 hours and 44 minutes and reach an apogee of 3,570 kilometres and a perigee of just 11.4 (!) kilometres, placing it well inside the Earth’s atmosphere on closest approach.

A slightly more believable claim came from astronomer Georg Waltemath in 1898 for a moon 700 kilometres in size — he claimed it was, of course, a very dark body and not very easily visible — orbiting the Earth at about 2.5 times the distance of the Moon. Waltemath even made an announcement of his discovery, and claimed to have found a third moon of the Earth for good measure.
And a much more dubious claim came from the astrologer Walter Gornold in 1918 of a secondary moon, dubbed Lilith. Apparently, then (as now) astrologers never actually bothered to look at the skies…
Turns out, our large Moon makes a pretty good goaltender, ejecting —and sometimes taking a beating from — any tiny second moon hopeful. Of course, you can’t blame those astronomers of yore entirely. Though none of these spurious moons survived the test of observational verification, these discoveries often stemmed from early efforts to accurately predict the precise motion of the Moon. Astronomers therefore felt they were on the right track, looking for an unseen perturbing body.
Fast forward to the 21st century. Quasi-moons of the Earth, such as 3753 Cruithne, have horseshoe-shaped orbits and seem to approach and recede from our planet as both orbit the Sun. Similar quasi-moons of Venus have also been discovered.
And even returning space junk can masquerade as a moon of Earth, as was the case of J002E3 and 2010 QW1, which turned out to be boosters from Apollo 12 and the Chinese Chang’e-2 missions, respectively.
What modern researchers are looking for are termed Temporarily Captured Orbiters, or TCOs. The study notes that perhaps an average of a few dozen asteroids up to 1 to 2 metres in size are in a “steady state” population that may be orbiting the Earth at any given time on an enter, orbit, and eject sort of conveyor belt. Estimates suggest that a large 5 to 10 metre asteroid is captured every decade so, and a 100 metre or larger TCO is temporarily captured by the Earth every 100,000 years. The study also estimates that about 1% occasionally hit the Earth. And though it wasn’t a TCO, the ability to detect an Earthbound asteroid before impact was demonstrated in 2008 with the discovery of 2008 TC3, less than 24 hours prior to striking in the Sudanese desert.
“There are currently no projects that are solely looking for minimoons at this time,” lead researcher Bryce Bolin of the University of Hawaii told Universe Today. “There are several surveys, such as PanSTARRS, the Catalina Sky Survey and the Palomar Transit Factory that are currently in operation that have the capability of discovering minimoons.”
We’re getting better at this hazardous asteroid detection business, that’s for sure. The researchers modeled paths and orbits for TCOs in the study, and also noted that collections may “clump” at the anti-sunward L2 opposition point, and the L1 sunward point, with smaller distributions located at the east and west quadrature points located 90 degrees on either side of the Earth. The L2 point in particular might make a good place to start the search.
Ironically, systems such as LINEAR and PanSTARRS may have already captured a TCO in their data and disregarded them in their quest for traditional Near Earth Objects.
“Surveys such as PanSTARRS/LINEAR utilize a filtration process to remove artifacts and false positives in the data as it gets processed through the data pipeline,” Researcher Bryce Bolin told Universe Today. “A common method is to apply a rate of motion cut… this is effective in eliminating many artifacts (which) tend to have a rate of motion as measured by the pipeline which is very high.”
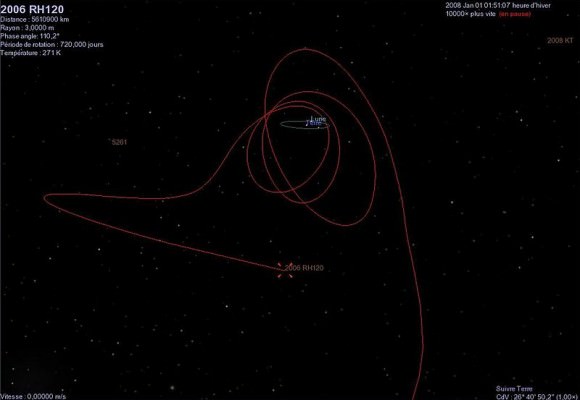
Such systems aren’t always looking for fast movers near Earth orbit that can produce a trail or streak which may reassemble space junk or become lost in the gaps over multiple detection devices. And speaking of which, researchers note that Arecibo and the U.S. Air Force’s Space Surveillance System may be recruited in this effort as well. To date, one definite TCO, named 2006 RH120 has been documented orbiting and departing from the vicinity of the Earth, and such worldlets might make enticing targets for future manned missions due to their relatively low Delta-V for arrival and departure.

PanSTARRS-2 saw first light last year in 2013, and is slated to go online for full science operations by the end of 2014. Eventually, the PanSTARRS system will employ four telescopes, and may find a bevy of TCOs. The researchers estimate in the study that a telescope such as Subaru stands a 90% chance of nabbing a TCO after only five nights of dedicated sweeps of the sky.
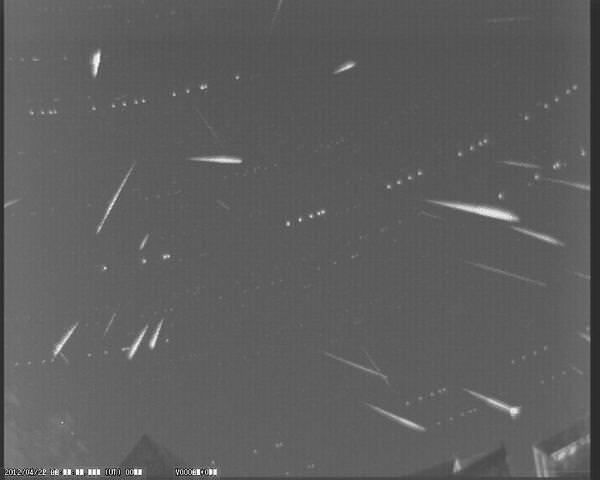
Finally, the study also notes that evidence miniature moonlets orbiting Earth may lurk in the all sky data gathered by automated cameras and amateur observers during meteor showers. Of course, we’re talking tiny, dust-to-pebble sized evidence, but there’s no lower limit as to what constitutes a moon…
And so, although moons such a “Lilith” and “Petit’s Moon” belong to the annuals of astronomical history, temporary “minimoons” of Earth are modern realities. And as events such as Chelyabinsk remind us, it’s always worthwhile to hunt for hazardous NEOs (and TCOs) that may be headed our way. Hey, to paraphrase science fiction author Larry Niven: unlike the dinosaurs, we have a space program!
Read more about the fascinating history of moons that never were and more in the classic book The Haunted Observatory.