[/caption]
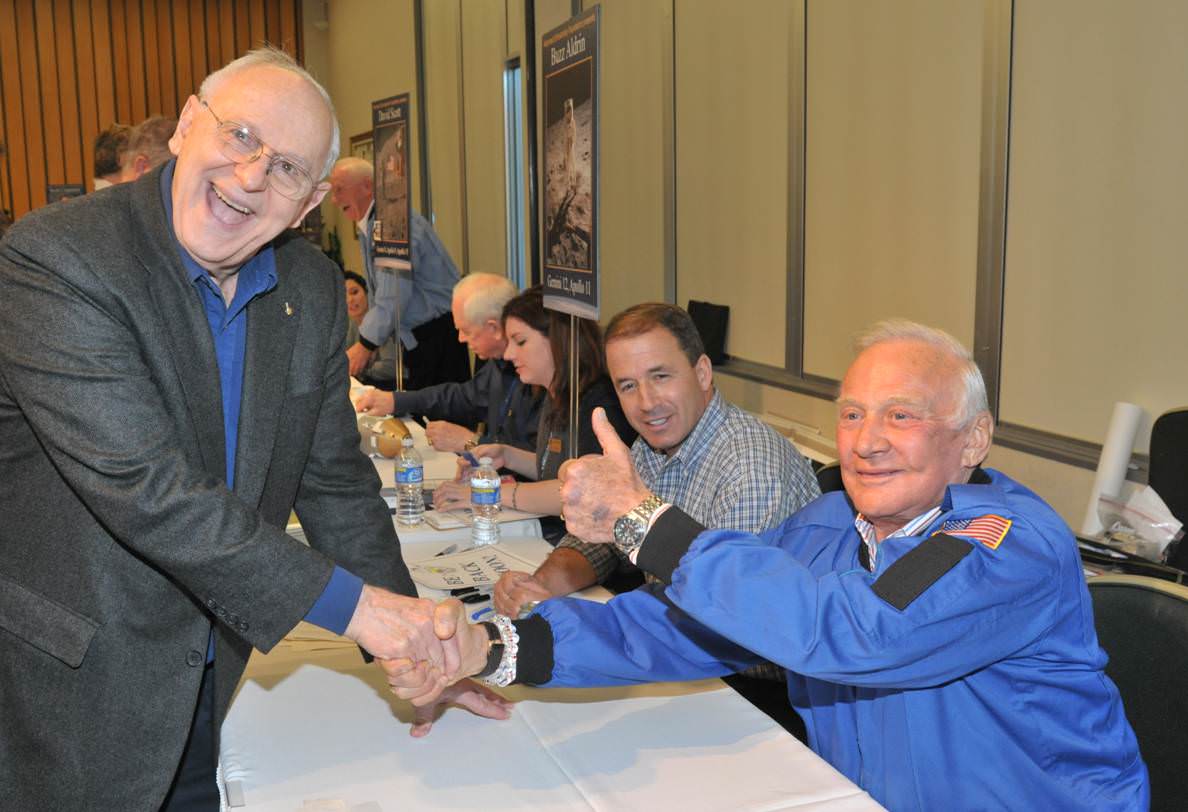
CAPE CANAVERAL, Fla – It all started – with seven. The original seven Mercury astronauts that is. They wanted to give back to the nation that had allowed them to reach the heights that they had achieved, while at the same time inspiring the nation’s young to follow in their footsteps. What arose was the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation (ASF).
There are more than 80 astronauts that are working with the ASF to ensure that the United States maintains its role as leader in terms of science and technology. The ASF accomplishes this by providing scholarships to students studying engineering, science and math.

In 1984, the then six surviving Mercury astronauts established the 501 (c) 3 organization along with the widow of the seventh (Betty Grissom, widow of astronaut Virgil “Gus” Grissom. Astronauts Malcolm Scott Carpenter, L. Gordon Cooper Jr., John H. Glenn Jr., Walter M. Schirra, Alan B. Shepard Jr., and Donald K. (Deke) Slayton were also joined by the Mercury Program’s flight surgeon William Douglas M.D. as well as a local business man, Henry Landwirth.
What started with scholarships of only $1,000 has grown to $10,000 each. Twenty-six of these scholarships are handed out every year for a grand total of $260,000. All total? The ASF has handed out $3 million in scholarships to worthy students. The ASF’s current Chairman of its Board of Directors is Apollo 16 Command Module Pilot Charlie Duke; his vice-chair is shuttle veteran Dan Brandenstein.

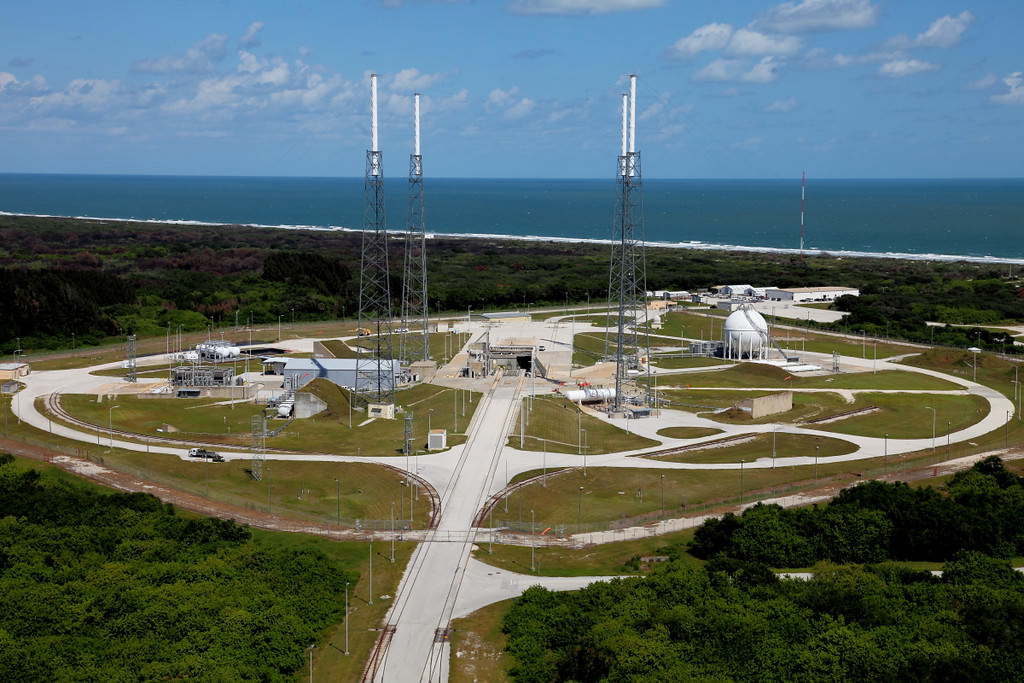
The ASF raises funds by a number of means. Astronaut guest appearance, fund-raisers, donations from different entities both public and private and autograph shows. The next of these is scheduled to take place at the Kennedy Space Center Visitor Complex located in Florida from Nov. 4-6. The annual show contains a wide range of events and tours to allow guests the opportunity to learn about the location’s history while picking up a signed item from an astronaut.

Universe Today recently sat down with two-time shuttle veteran Robert C. Springer about his thoughts regarding ASF. Here is what he had to say:
Universe Today: Hi Bob thanks for chatting with us today.
Springer: “My pleasure, thanks for having me!”
Universe Today: How long have you been affiliated with the ASF and how do you view its activities?
Springer: “I have been associated with the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation for the past ten years. The foundation has had phenomenal success, increasing the number of scholarships to the current level of 26 scholarships, each in the amount of $10,000 awarded annually to young men and women who are pursuing degrees in engineering and scientific fields that are related to space exploration.”
Universe Today: What do you find most rewarding or interesting regarding the ASF’s efforts?
Springer: “One of the most interesting aspects of the fund raising effort, is the diversity of individuals who have contributed to the foundation. It has been both a national and international group of individuals who truly believe that we need to continue to invest in our future by providing funding assistance to talented and motivated students to enable them to continue their studies in selected fields.”
Universe Today: So your experience with these folks is rewarding?
Springer: “They are great, but it’s really wonderful to meet the recipients of these scholarships – each year we have the opportunity to hear from some of the individuals who have been awarded the scholarships, and it is remarkable to hear their stories and to understand the kinds of contributions they are making today and have the potential to make in the future.”
Universe Today: I bet that must be really gratifying. It seems we have to wrap, but I wanted to thank you for telling us a bit about your experiences.
Springer: “It was great talking with you!”
For more information regarding the Astronaut Scholarship Foundation’s annual autograph show visit: astronautscholarship.org or call: 321-455-7016.